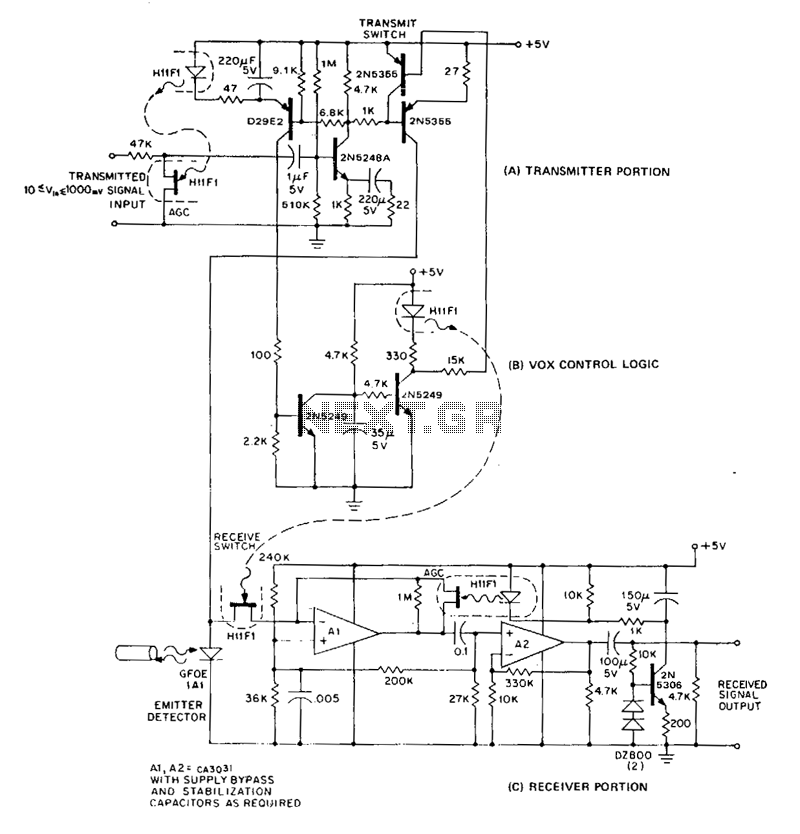
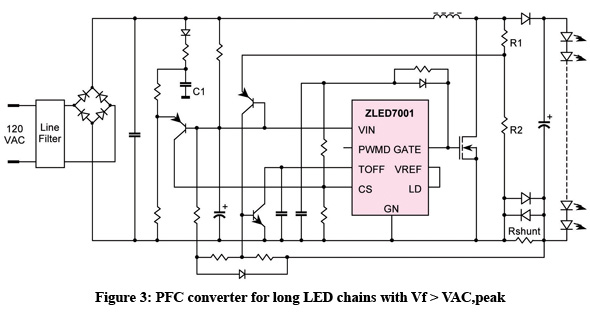
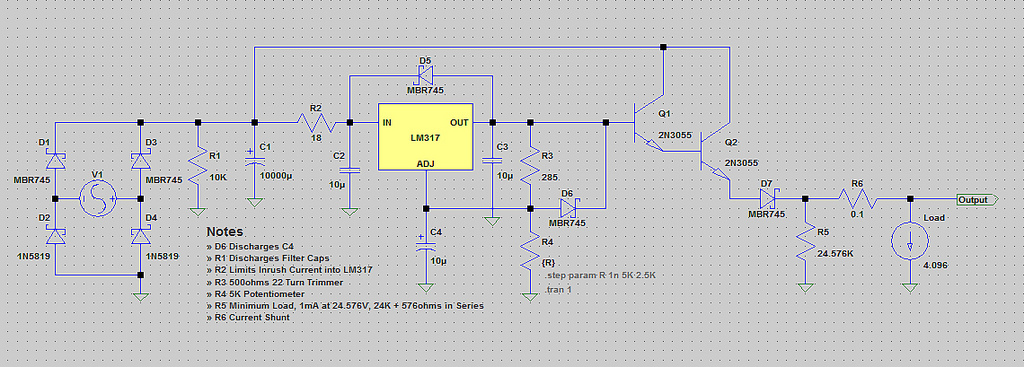
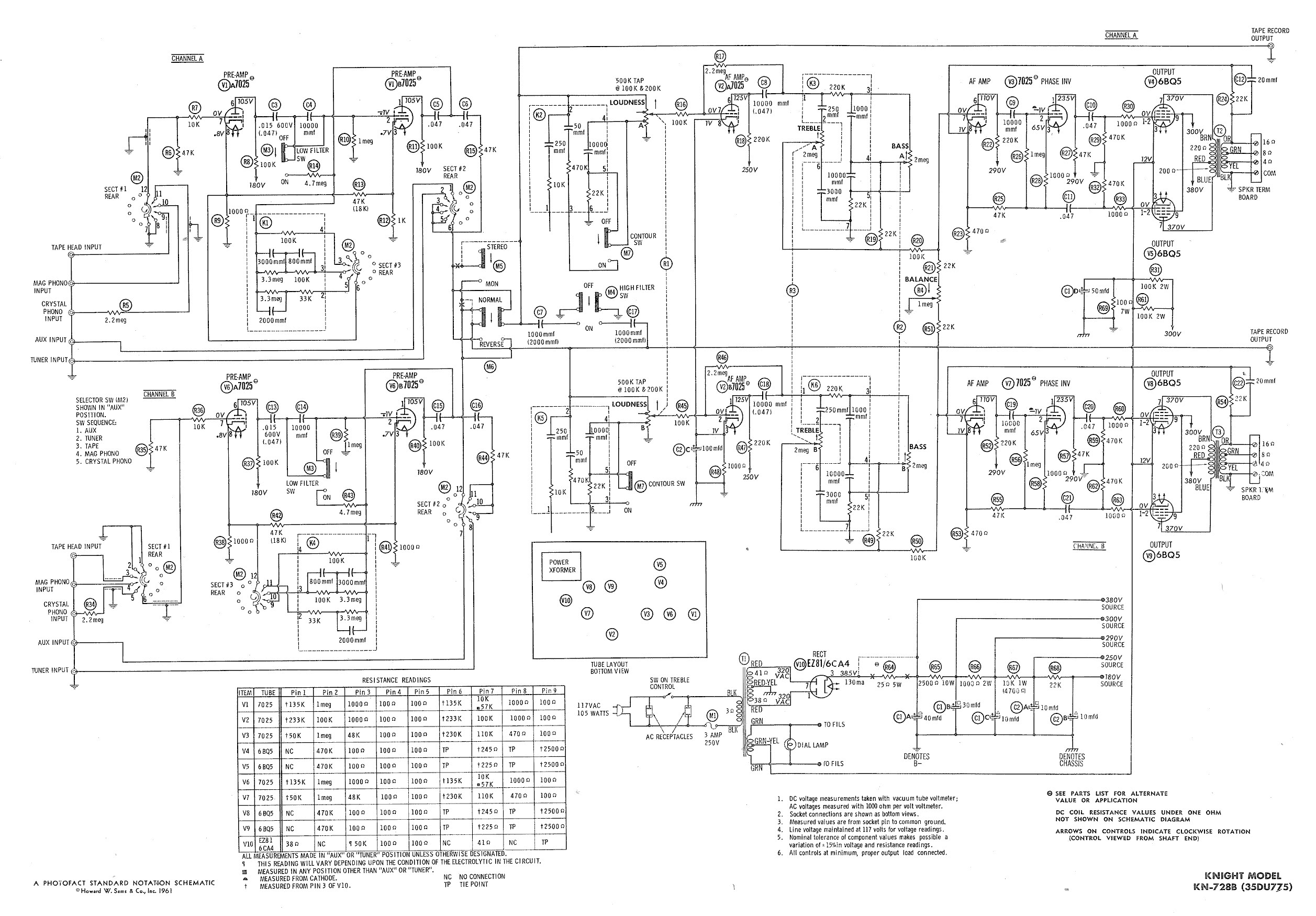
High And Low Voltage Cut Off With Time Delays
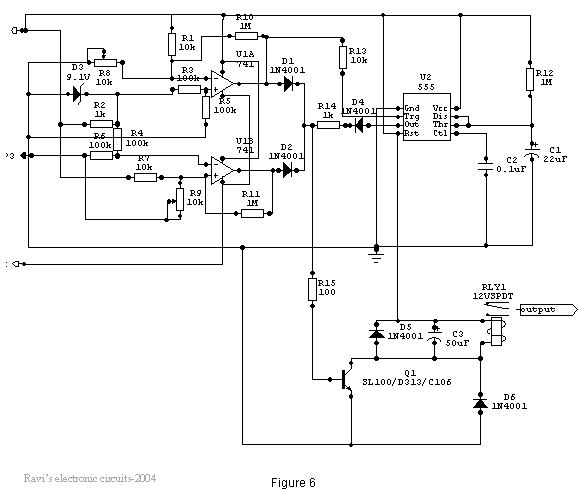
The under/over voltage protection circuit with time delay presented here is a low-cost and reliable circuit for protecting equipment from damage.
This under/over voltage protection circuit is designed to safeguard electronic equipment from voltage fluctuations that can lead to potential damage. The circuit operates by monitoring the input voltage levels and activating a protective mechanism when the voltage exceeds or falls below predetermined thresholds.
Key components of the circuit typically include a voltage sensing device, such as a Zener diode or a voltage comparator, which continuously measures the input voltage. When the sensed voltage deviates from the set limits, the circuit initiates a delay mechanism, often implemented using a timer IC, such as the 555 timer, to prevent nuisance tripping due to transient voltage spikes or dips.
The design incorporates a relay or a solid-state switch that disconnects the load from the power source when the voltage is outside the acceptable range. The time delay feature is crucial as it allows temporary voltage fluctuations to stabilize before the protective action is taken, thus ensuring that the equipment remains operational during brief disturbances.
Additionally, the circuit can be enhanced with indicators, such as LEDs, to provide visual feedback on the operational status and fault conditions. This feature aids in troubleshooting and maintenance by clearly indicating whether the circuit is active or has tripped due to voltage irregularities.
Overall, this under/over voltage protection circuit is an essential component in various applications, including industrial machinery, consumer electronics, and telecommunications equipment, ensuring longevity and reliability by preventing damage from voltage anomalies.The under/over voltage protection circuit with time delay presented here is a low cost and reliable circuit for protecting such equipments from damages.. 🔗 External reference
This under/over voltage protection circuit is designed to safeguard electronic equipment from voltage fluctuations that can lead to potential damage. The circuit operates by monitoring the input voltage levels and activating a protective mechanism when the voltage exceeds or falls below predetermined thresholds.
Key components of the circuit typically include a voltage sensing device, such as a Zener diode or a voltage comparator, which continuously measures the input voltage. When the sensed voltage deviates from the set limits, the circuit initiates a delay mechanism, often implemented using a timer IC, such as the 555 timer, to prevent nuisance tripping due to transient voltage spikes or dips.
The design incorporates a relay or a solid-state switch that disconnects the load from the power source when the voltage is outside the acceptable range. The time delay feature is crucial as it allows temporary voltage fluctuations to stabilize before the protective action is taken, thus ensuring that the equipment remains operational during brief disturbances.
Additionally, the circuit can be enhanced with indicators, such as LEDs, to provide visual feedback on the operational status and fault conditions. This feature aids in troubleshooting and maintenance by clearly indicating whether the circuit is active or has tripped due to voltage irregularities.
Overall, this under/over voltage protection circuit is an essential component in various applications, including industrial machinery, consumer electronics, and telecommunications equipment, ensuring longevity and reliability by preventing damage from voltage anomalies.The under/over voltage protection circuit with time delay presented here is a low cost and reliable circuit for protecting such equipments from damages.. 🔗 External reference