high performance gelled lead acid charger
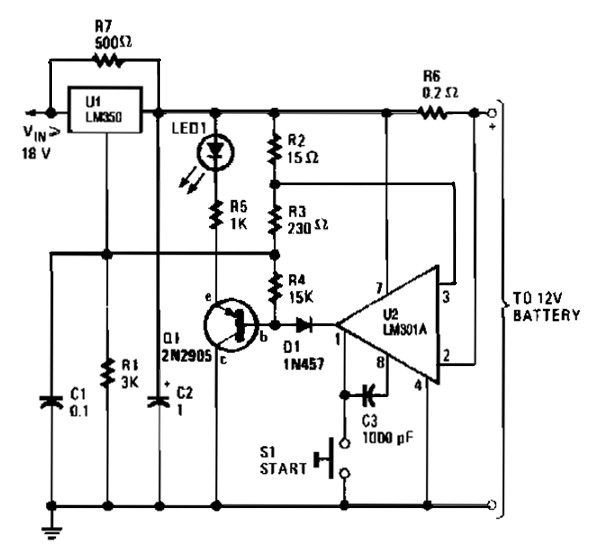
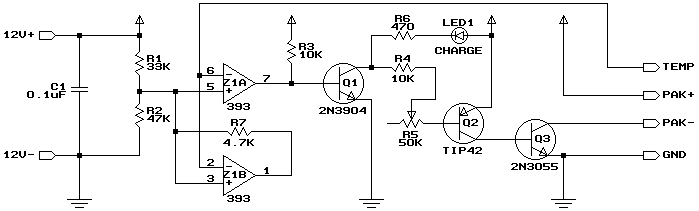
The gelled lead-acid battery charger circuit diagram enables rapid charging of gelled lead-acid batteries and automatically shuts off upon reaching full charge. Initially, the charging current is maintained at 2 A; however, as the battery voltage increases, the current gradually decreases. The schematic diagram is derived from the circuit labeled as "High Performance Gelled Lead Acid Charger Power Supply." Additional information regarding the related circuit diagram can be found on that page.
The gelled lead-acid battery charger circuit is designed to efficiently charge gelled lead-acid batteries while ensuring safety and prolonging battery life. The circuit typically includes several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and a microcontroller or comparator for charge control.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier converts the AC voltage to DC, which is necessary for charging the battery. Common rectifier configurations include full-wave or bridge rectifiers, which provide a smoother DC output.
The charging current is initially set to 2 A, which is suitable for most gelled lead-acid batteries. As the battery charges, its voltage rises, and the circuit is designed to reduce the current accordingly to prevent overcharging. This can be achieved using a current sensing resistor and a feedback loop that adjusts the output based on the battery's voltage level.
A microcontroller or an operational amplifier can be employed to monitor the battery voltage. Once the battery reaches its full charge voltage, the circuit automatically turns off the charging current. This feature is crucial for maintaining battery health and preventing damage due to overcharging.
In addition to the basic components, the circuit may also include protection features such as fuses, thermal cutoffs, and voltage clamping devices to safeguard against overcurrent and overheating conditions. The overall design prioritizes efficiency and reliability, making it suitable for various applications where gelled lead-acid batteries are used, such as in renewable energy systems, backup power supplies, and electric vehicles.
For further insights and detailed explanations regarding this circuit and its applications, refer to the original source on the high-performance gelled lead-acid charger power supply.Gelled lead acid battery charger circuit diagram allow quickly charges gelled lead-acid batteries, and automatically turns off at full charge. First, the charge current is held at 2 A, but as battery voltage rises, the current will decreases. The schematic diagram come from circuit: High Performance Gelled lead acid charger power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference
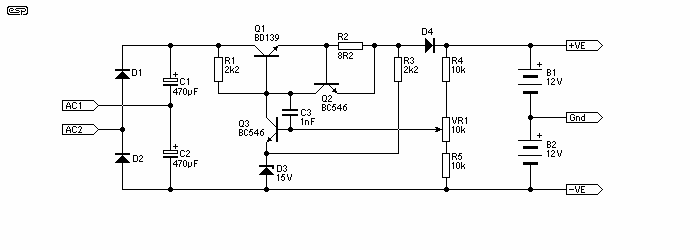
The gelled lead-acid battery charger circuit is designed to efficiently charge gelled lead-acid batteries while ensuring safety and prolonging battery life. The circuit typically includes several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and a microcontroller or comparator for charge control.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier converts the AC voltage to DC, which is necessary for charging the battery. Common rectifier configurations include full-wave or bridge rectifiers, which provide a smoother DC output.
The charging current is initially set to 2 A, which is suitable for most gelled lead-acid batteries. As the battery charges, its voltage rises, and the circuit is designed to reduce the current accordingly to prevent overcharging. This can be achieved using a current sensing resistor and a feedback loop that adjusts the output based on the battery's voltage level.
A microcontroller or an operational amplifier can be employed to monitor the battery voltage. Once the battery reaches its full charge voltage, the circuit automatically turns off the charging current. This feature is crucial for maintaining battery health and preventing damage due to overcharging.
In addition to the basic components, the circuit may also include protection features such as fuses, thermal cutoffs, and voltage clamping devices to safeguard against overcurrent and overheating conditions. The overall design prioritizes efficiency and reliability, making it suitable for various applications where gelled lead-acid batteries are used, such as in renewable energy systems, backup power supplies, and electric vehicles.
For further insights and detailed explanations regarding this circuit and its applications, refer to the original source on the high-performance gelled lead-acid charger power supply.Gelled lead acid battery charger circuit diagram allow quickly charges gelled lead-acid batteries, and automatically turns off at full charge. First, the charge current is held at 2 A, but as battery voltage rises, the current will decreases. The schematic diagram come from circuit: High Performance Gelled lead acid charger power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference