High-performance power supply LM334
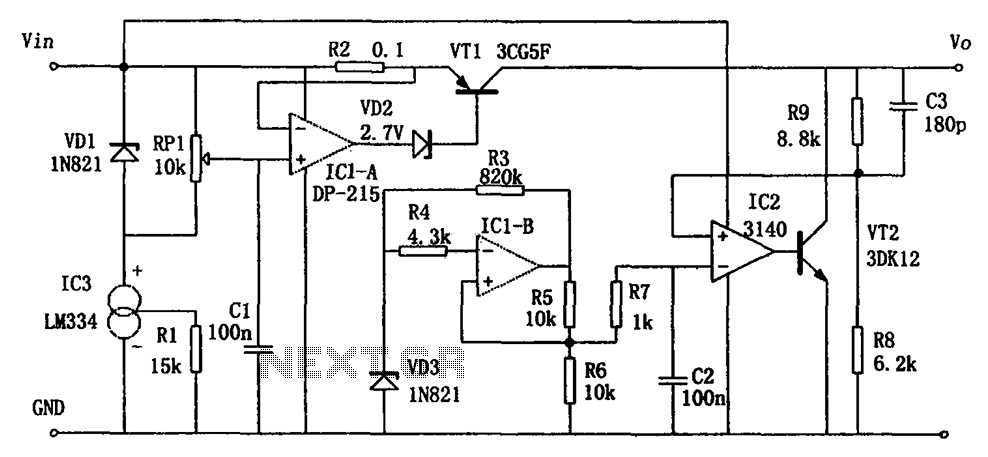
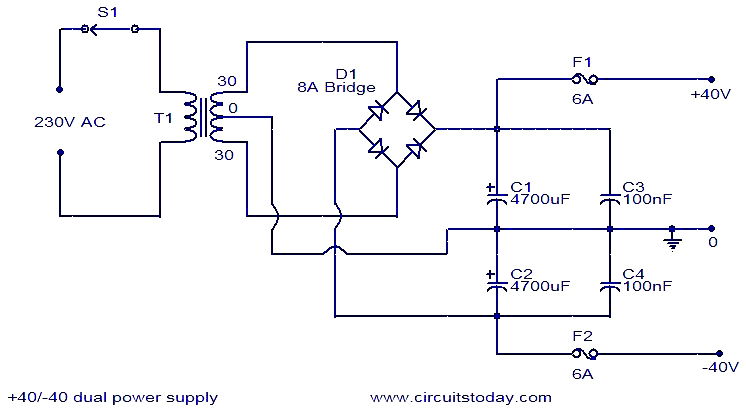
The circuit functions as a switching power supply designed to operate alongside a linear regulated power supply. Key characteristics include high efficiency and low dropout voltage. It effectively filters out high-frequency ripple voltage and manages instantaneous voltage variations, making it ideal for small load applications. The circuit incorporates a current limiting feature. Key components include VD3, IC1-b, and others that generate the reference voltage. R8 and R9 form a voltage sampling circuit to monitor the power supply's output voltage. IC2, VT2, and additional components create the error amplifier and shunt voltage regulator circuit. This setup compares the reference voltage with the amplified sampled voltage from IC2 to drive the regulator VT2, thereby stabilizing the output voltage. The current limiting circuit is composed of VD1, IC3, VD2, IC1-a, VT1, and other components. VD1, IC3, and RP1 establish an adjustable current limiting reference voltage generated by IC1-a. This reference voltage is compared against the sampled voltage from R2 (output current sampling resistor) to produce an error voltage that controls the operating conditions of regulator VT1, ensuring both stabilization and limitation of the output current.
The switching power supply circuit described is characterized by its ability to efficiently convert input voltage to a stable output voltage while minimizing power loss. The integration of the linear regulated power supply allows for enhanced performance in applications requiring precise voltage regulation. The circuit's high efficiency is particularly advantageous in battery-powered devices, where energy conservation is critical.
The voltage sampling circuit, comprising resistors R8 and R9, plays a crucial role in monitoring the output voltage. By providing feedback to the error amplifier, this arrangement ensures that any fluctuations in output voltage are promptly addressed. The error amplifier, formed by IC2 and VT2, amplifies the difference between the reference voltage and the sampled output voltage, adjusting the control signal to maintain a consistent output.
Moreover, the current limiting feature is essential for protecting the circuit from overload conditions. The adjustable reference voltage generated by IC1-a allows for flexibility in setting the maximum allowable output current. This is particularly useful in applications where varying load conditions may lead to excessive current draw. The output current is sampled through resistor R2, and the resulting voltage is compared to the reference voltage to produce an error voltage. This error voltage is utilized to modulate the operation of regulator VT1, ensuring that the output current remains within safe limits.
Overall, the described circuit is well-suited for applications requiring reliable power delivery with stringent voltage and current specifications. Its design effectively balances performance with safety, making it a valuable component in modern electronic systems. As shown in Figure as a switching power supply to work with linear regulated power supply. Its characteristics are: high efficiency, low dropout; having the ability to filter o ut high frequency ripple voltage and instantaneous voltage of the mutation; best suited to the needs of small loads; having a current limiting function. Figure by VD3, IC1-b and other components to generate the reference voltage. R8, R9 constitute a voltage sampling circuit for sampling the output voltage of the power supply. IC2 and VT2 and other elements constituting the error amplifier and shunt voltage regulator circuit. By comparing the reference voltage and IC2 amplify the sampled voltage, the driving regulator VT2, thereby stabilizing the output voltage.
By the VD1, IC3, VD2, IC1-a, VT1 and other elements constituting a current limiting circuit. VD1, IC3 and RP1 formed adjustable current limiting reference voltage generated by IC1-a reference to this voltage R2 (output current sampling resistor) comparing the sampled voltage amplification to form the error voltage. With the error voltage control the regulator VT1 working conditions, so as to stabilize and limit the output current.
The switching power supply circuit described is characterized by its ability to efficiently convert input voltage to a stable output voltage while minimizing power loss. The integration of the linear regulated power supply allows for enhanced performance in applications requiring precise voltage regulation. The circuit's high efficiency is particularly advantageous in battery-powered devices, where energy conservation is critical.
The voltage sampling circuit, comprising resistors R8 and R9, plays a crucial role in monitoring the output voltage. By providing feedback to the error amplifier, this arrangement ensures that any fluctuations in output voltage are promptly addressed. The error amplifier, formed by IC2 and VT2, amplifies the difference between the reference voltage and the sampled output voltage, adjusting the control signal to maintain a consistent output.
Moreover, the current limiting feature is essential for protecting the circuit from overload conditions. The adjustable reference voltage generated by IC1-a allows for flexibility in setting the maximum allowable output current. This is particularly useful in applications where varying load conditions may lead to excessive current draw. The output current is sampled through resistor R2, and the resulting voltage is compared to the reference voltage to produce an error voltage. This error voltage is utilized to modulate the operation of regulator VT1, ensuring that the output current remains within safe limits.
Overall, the described circuit is well-suited for applications requiring reliable power delivery with stringent voltage and current specifications. Its design effectively balances performance with safety, making it a valuable component in modern electronic systems. As shown in Figure as a switching power supply to work with linear regulated power supply. Its characteristics are: high efficiency, low dropout; having the ability to filter o ut high frequency ripple voltage and instantaneous voltage of the mutation; best suited to the needs of small loads; having a current limiting function. Figure by VD3, IC1-b and other components to generate the reference voltage. R8, R9 constitute a voltage sampling circuit for sampling the output voltage of the power supply. IC2 and VT2 and other elements constituting the error amplifier and shunt voltage regulator circuit. By comparing the reference voltage and IC2 amplify the sampled voltage, the driving regulator VT2, thereby stabilizing the output voltage.
By the VD1, IC3, VD2, IC1-a, VT1 and other elements constituting a current limiting circuit. VD1, IC3 and RP1 formed adjustable current limiting reference voltage generated by IC1-a reference to this voltage R2 (output current sampling resistor) comparing the sampled voltage amplification to form the error voltage. With the error voltage control the regulator VT1 working conditions, so as to stabilize and limit the output current.