High-Side Current-Sense Measurement: Circuits and Principles
This article compares high-side and low-side amplifiers used for measuring battery charging currents. It recommends selection criteria for current-sense resistors and describes a high-voltage circuit breaker designed for overcurrent protection.
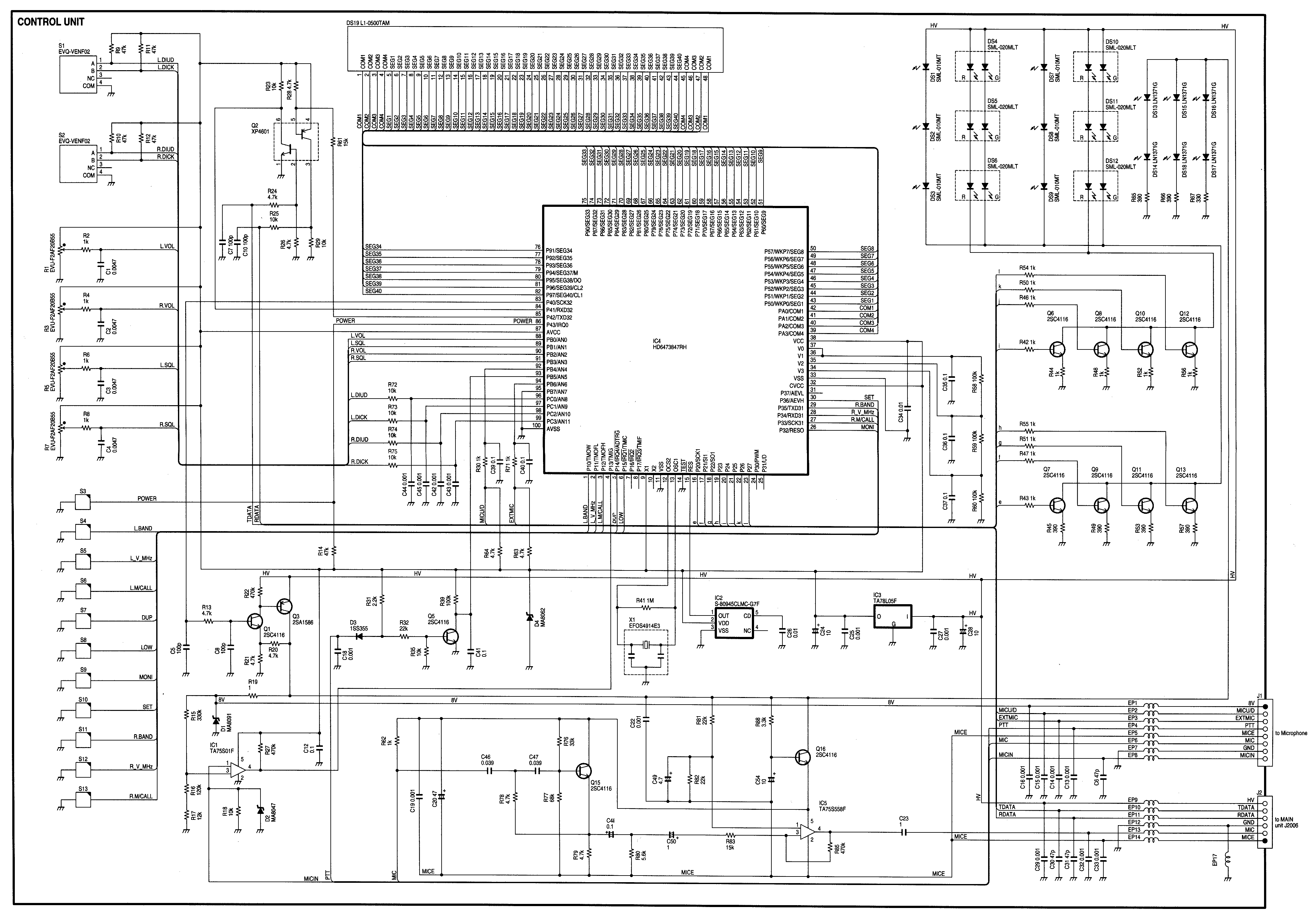
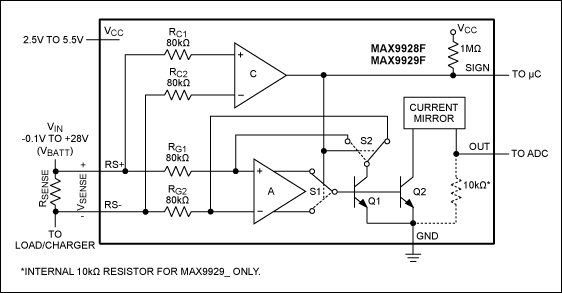
High-side and low-side amplifiers are essential components in battery management systems, particularly for monitoring charging currents. High-side amplifiers measure current flowing into the load, providing an accurate representation of the battery's charging state. They are typically connected between the power source and the load, allowing for the detection of both positive and negative current flows. In contrast, low-side amplifiers are connected between the load and ground, measuring the voltage drop across a current-sense resistor placed in series with the load. While low-side configurations are simpler and less expensive, they may introduce ground reference issues and are less suitable for applications where the load can be grounded.
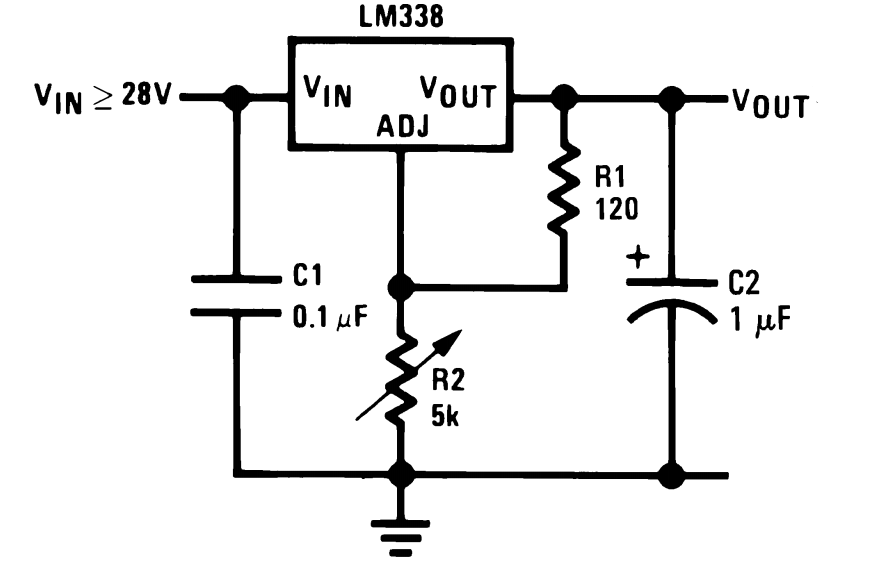
When selecting current-sense resistors, several criteria must be considered to ensure optimal performance. These include resistance value, power rating, temperature coefficient, and tolerance. The resistance value should be low enough to minimize power loss while still providing a measurable voltage drop for accurate current sensing. The power rating must be adequate to handle the maximum expected current without overheating. Additionally, the temperature coefficient should be low to maintain accuracy across varying operating temperatures.
The high-voltage circuit breaker is a critical safety feature in battery management systems, providing overcurrent protection to prevent damage from excessive currents. This device disconnects the circuit in the event of a fault, such as a short circuit or overload, thus safeguarding both the battery and the connected load. The circuit breaker operates by sensing the current flowing through the system and tripping when it exceeds a predetermined threshold. This action interrupts the current flow, preventing potential damage and ensuring system reliability.
In summary, the comparison of high-side and low-side amplifiers, the careful selection of current-sense resistors, and the implementation of high-voltage circuit breakers are fundamental aspects of designing efficient and safe battery charging systems. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring accurate current measurement and protection against overcurrent conditions, contributing to the overall reliability and longevity of battery-operated devices.Article compares high- and low-side amplifiers to measure battery charging currents, recommends selection criteria for current-sense resistors, and describes a high-voltage circuit breaker for overcurrent protection.. 🔗 External reference
High-side and low-side amplifiers are essential components in battery management systems, particularly for monitoring charging currents. High-side amplifiers measure current flowing into the load, providing an accurate representation of the battery's charging state. They are typically connected between the power source and the load, allowing for the detection of both positive and negative current flows. In contrast, low-side amplifiers are connected between the load and ground, measuring the voltage drop across a current-sense resistor placed in series with the load. While low-side configurations are simpler and less expensive, they may introduce ground reference issues and are less suitable for applications where the load can be grounded.
When selecting current-sense resistors, several criteria must be considered to ensure optimal performance. These include resistance value, power rating, temperature coefficient, and tolerance. The resistance value should be low enough to minimize power loss while still providing a measurable voltage drop for accurate current sensing. The power rating must be adequate to handle the maximum expected current without overheating. Additionally, the temperature coefficient should be low to maintain accuracy across varying operating temperatures.
The high-voltage circuit breaker is a critical safety feature in battery management systems, providing overcurrent protection to prevent damage from excessive currents. This device disconnects the circuit in the event of a fault, such as a short circuit or overload, thus safeguarding both the battery and the connected load. The circuit breaker operates by sensing the current flowing through the system and tripping when it exceeds a predetermined threshold. This action interrupts the current flow, preventing potential damage and ensuring system reliability.
In summary, the comparison of high-side and low-side amplifiers, the careful selection of current-sense resistors, and the implementation of high-voltage circuit breakers are fundamental aspects of designing efficient and safe battery charging systems. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring accurate current measurement and protection against overcurrent conditions, contributing to the overall reliability and longevity of battery-operated devices.Article compares high- and low-side amplifiers to measure battery charging currents, recommends selection criteria for current-sense resistors, and describes a high-voltage circuit breaker for overcurrent protection.. 🔗 External reference