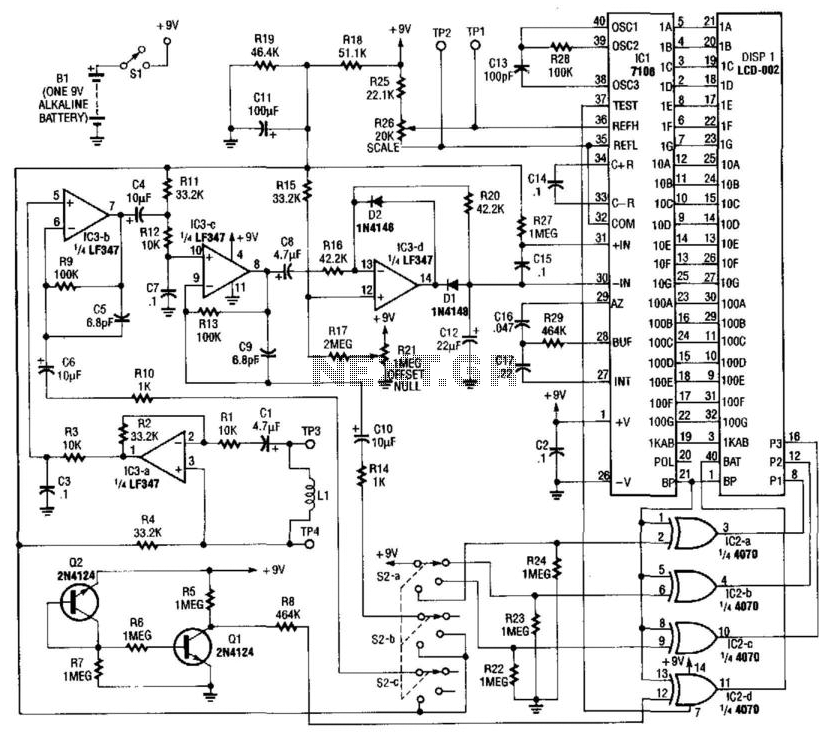
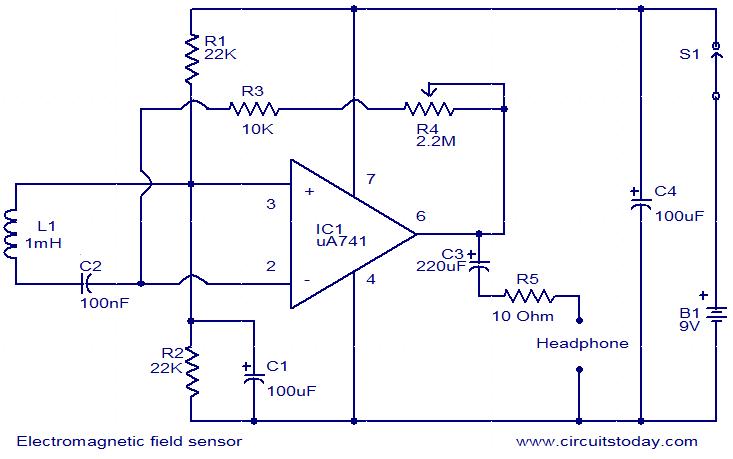
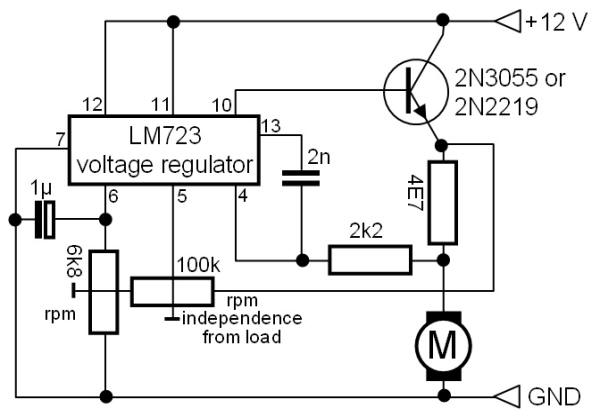
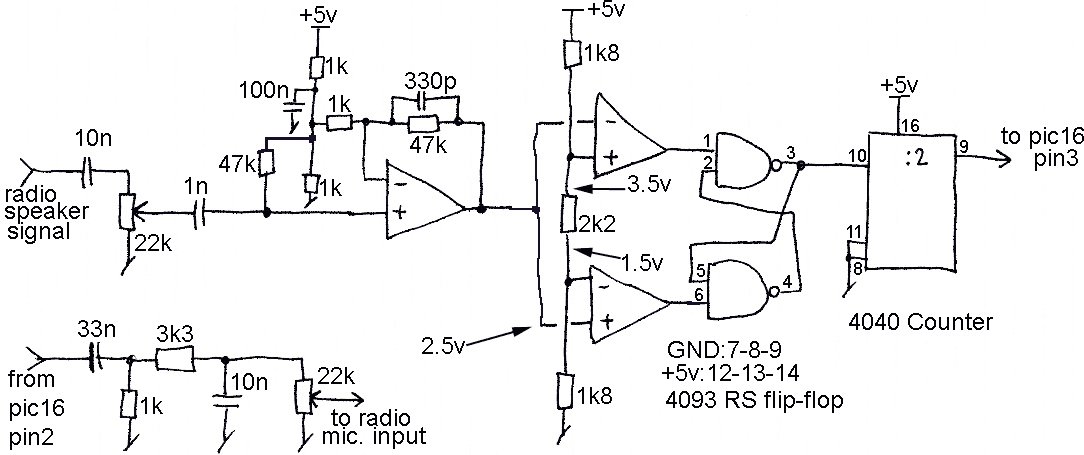
Home Built Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer

Home-built NMR spectrometer, illustrating the construction and circuitry. Demonstrates 90-degree and 180-degree pulse sequences, as well as the generation of FIDs and spin echoes at 18 MHz.
The home-built NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) spectrometer is an intricate device designed for analyzing the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei. The construction comprises a combination of hardware and software components that work together to generate and detect radiofrequency (RF) pulses.
The primary components of the spectrometer include a strong magnet, RF transmitter, RF receiver, and a computer interface for data acquisition and processing. The magnet creates a uniform magnetic field that aligns the nuclear spins of the sample. The RF transmitter generates the 90-degree and 180-degree pulse sequences essential for exciting the nuclei. A 90-degree pulse flips the spins into the transverse plane, while a 180-degree pulse is used for refocusing the spins, creating spin echoes.
The spectrometer operates at a frequency of 18 MHz, which corresponds to the resonant frequency of the nuclei being studied, typically protons in organic compounds. The generated Free Induction Decay (FID) signals are captured by the RF receiver, which converts the RF signals into digital data for further analysis. The computer interface processes these signals to reconstruct the NMR spectrum, revealing information about the molecular structure and dynamics of the sample.
The design may also incorporate various safety features and calibration mechanisms to ensure accuracy and reliability during operation. Overall, this NMR spectrometer serves as a valuable tool for research and educational purposes in the field of chemistry and material science.Home built NMR spectrometer, showing the construction and circuitry. Demonstates 90 degree and 180 degree pulse sequence, and generation of FIDs and spin echos at 18 MHz.. 🔗 External reference
The home-built NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) spectrometer is an intricate device designed for analyzing the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei. The construction comprises a combination of hardware and software components that work together to generate and detect radiofrequency (RF) pulses.
The primary components of the spectrometer include a strong magnet, RF transmitter, RF receiver, and a computer interface for data acquisition and processing. The magnet creates a uniform magnetic field that aligns the nuclear spins of the sample. The RF transmitter generates the 90-degree and 180-degree pulse sequences essential for exciting the nuclei. A 90-degree pulse flips the spins into the transverse plane, while a 180-degree pulse is used for refocusing the spins, creating spin echoes.
The spectrometer operates at a frequency of 18 MHz, which corresponds to the resonant frequency of the nuclei being studied, typically protons in organic compounds. The generated Free Induction Decay (FID) signals are captured by the RF receiver, which converts the RF signals into digital data for further analysis. The computer interface processes these signals to reconstruct the NMR spectrum, revealing information about the molecular structure and dynamics of the sample.
The design may also incorporate various safety features and calibration mechanisms to ensure accuracy and reliability during operation. Overall, this NMR spectrometer serves as a valuable tool for research and educational purposes in the field of chemistry and material science.Home built NMR spectrometer, showing the construction and circuitry. Demonstates 90 degree and 180 degree pulse sequence, and generation of FIDs and spin echos at 18 MHz.. 🔗 External reference