how servo motors work
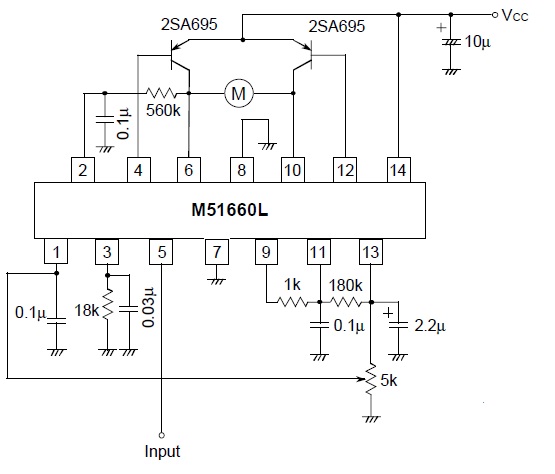
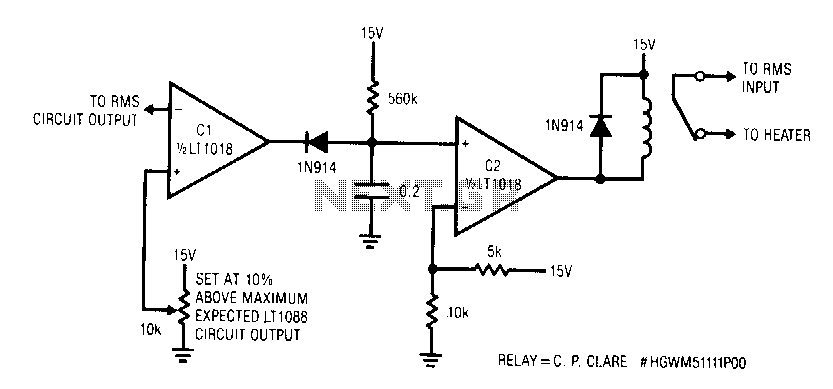
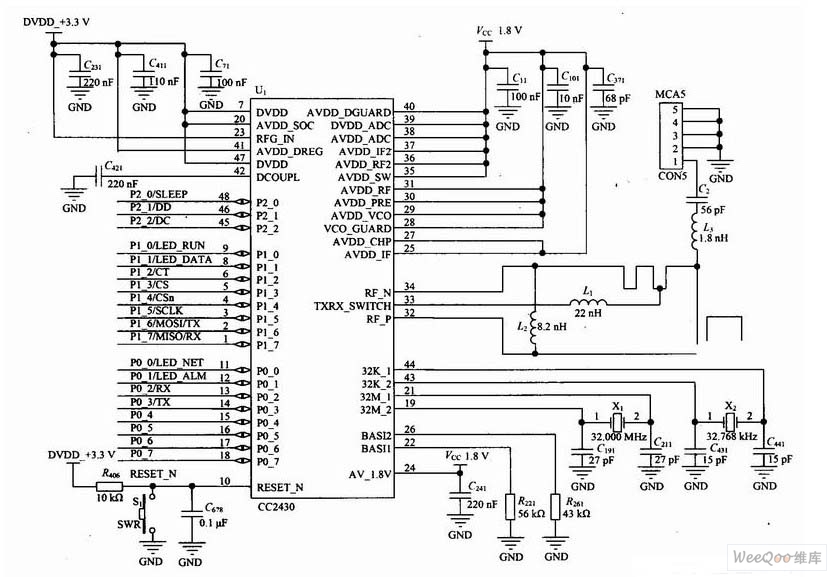
A servo is a compact motor capable of precise positioning at various angles. It incorporates internal circuitry designed to maintain its position automatically.
A servo motor typically consists of a DC motor, a gear system, a potentiometer, and a control circuit. The DC motor provides the necessary torque to move the output shaft, while the gear system reduces the speed and increases the torque, allowing for more accurate positioning. The potentiometer is used to provide feedback on the current position of the shaft, enabling the control circuit to adjust the motor's movement and maintain the desired angle.
Servos are commonly used in applications requiring precise control, such as robotics, radio-controlled vehicles, and automated machinery. They can be classified into different types, including positional rotation servos, continuous rotation servos, and linear servos, each serving specific applications based on their movement capabilities.
The control of a servo motor is typically achieved through pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals, where the width of the pulse determines the angle to which the servo will move. This allows for a straightforward interface with microcontrollers and other control systems, making servos highly versatile components in various electronic designs.
In summary, servo motors are essential components in systems that require accurate motion control, with their design and functionality enabling a wide range of applications in modern electronics.What is a servo? A servo is a small motor that you can position at any angle very accurately. It contains internal circuits that will automatically maintain.. 🔗 External reference
A servo motor typically consists of a DC motor, a gear system, a potentiometer, and a control circuit. The DC motor provides the necessary torque to move the output shaft, while the gear system reduces the speed and increases the torque, allowing for more accurate positioning. The potentiometer is used to provide feedback on the current position of the shaft, enabling the control circuit to adjust the motor's movement and maintain the desired angle.
Servos are commonly used in applications requiring precise control, such as robotics, radio-controlled vehicles, and automated machinery. They can be classified into different types, including positional rotation servos, continuous rotation servos, and linear servos, each serving specific applications based on their movement capabilities.
The control of a servo motor is typically achieved through pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals, where the width of the pulse determines the angle to which the servo will move. This allows for a straightforward interface with microcontrollers and other control systems, making servos highly versatile components in various electronic designs.
In summary, servo motors are essential components in systems that require accurate motion control, with their design and functionality enabling a wide range of applications in modern electronics.What is a servo? A servo is a small motor that you can position at any angle very accurately. It contains internal circuits that will automatically maintain.. 🔗 External reference