How to work with External Interrupts in AVR micro controller (Atmega8)
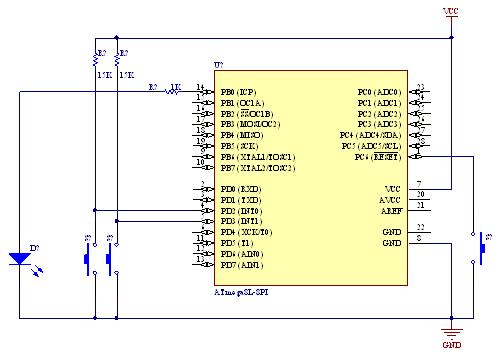
A demonstration of external interrupts in the AVR (Atmega8) microcontroller, including a circuit diagram and C code for the interrupt service routine (ISR).
The Atmega8 microcontroller is a versatile device widely used in embedded systems, particularly for applications requiring external interrupt handling. External interrupts allow the microcontroller to respond immediately to external events, enhancing its ability to interact with the environment.
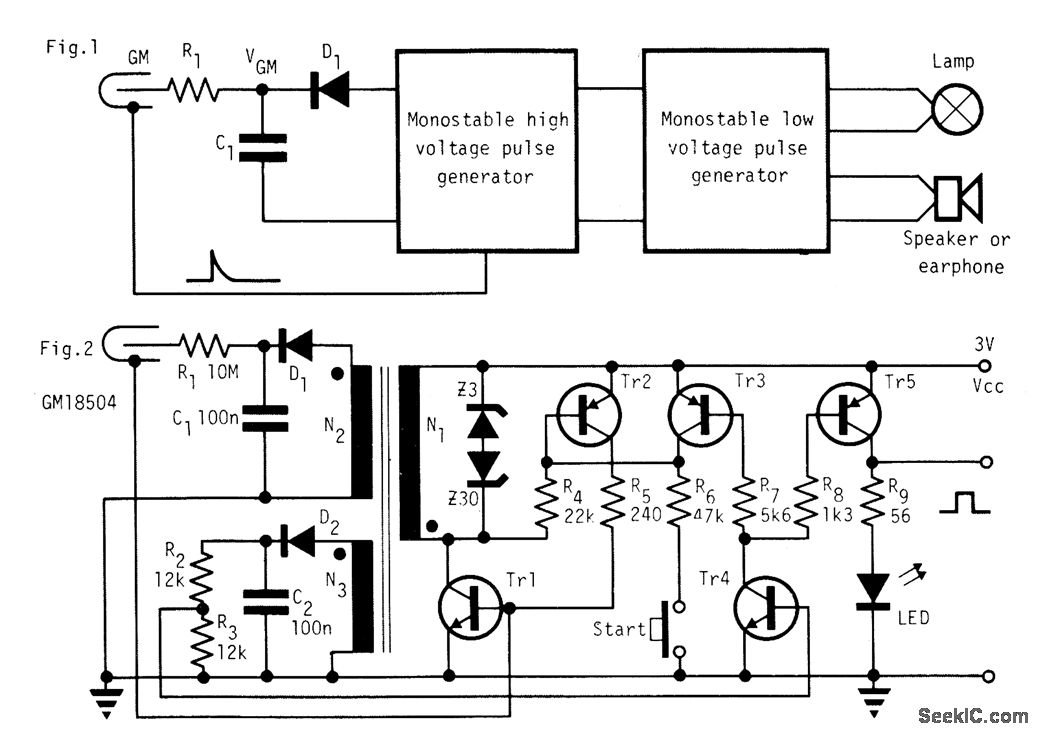
In this demonstration, the circuit is designed to showcase how an external interrupt can be triggered by a push-button switch. The circuit typically includes the Atmega8 microcontroller, a resistor, a capacitor, and the push-button switch connected to one of the external interrupt pins, such as INT0.
When the button is pressed, the voltage at the interrupt pin changes, signaling the microcontroller to execute the ISR. The ISR is a special function written in C that defines the actions to be taken when the interrupt occurs. For example, the ISR could toggle an LED, increment a counter, or send a signal to another part of the system.
The circuit diagram would illustrate the connections between the Atmega8 and the components, ensuring that the pull-up resistor is properly connected to maintain a stable high state until the button is pressed. The microcontroller's configuration registers must be set to enable the external interrupt and define its triggering condition (rising edge, falling edge, or both).
The C code would typically include the necessary header files, initialization of the microcontroller, configuration of the interrupt registers, and the ISR definition. The code should also contain a main loop that allows the microcontroller to remain in a low-power state or perform other tasks while waiting for the interrupt to occur.
This demonstration effectively illustrates the functionality of external interrupts in the Atmega8 microcontroller, providing a practical application for those learning about embedded systems and real-time processing.A demo of external interrupts in AVR (Atmega8) micro controller with circuit diagram and C code/program as ISR (interrupt service routine).. 🔗 External reference
The Atmega8 microcontroller is a versatile device widely used in embedded systems, particularly for applications requiring external interrupt handling. External interrupts allow the microcontroller to respond immediately to external events, enhancing its ability to interact with the environment.
In this demonstration, the circuit is designed to showcase how an external interrupt can be triggered by a push-button switch. The circuit typically includes the Atmega8 microcontroller, a resistor, a capacitor, and the push-button switch connected to one of the external interrupt pins, such as INT0.
When the button is pressed, the voltage at the interrupt pin changes, signaling the microcontroller to execute the ISR. The ISR is a special function written in C that defines the actions to be taken when the interrupt occurs. For example, the ISR could toggle an LED, increment a counter, or send a signal to another part of the system.
The circuit diagram would illustrate the connections between the Atmega8 and the components, ensuring that the pull-up resistor is properly connected to maintain a stable high state until the button is pressed. The microcontroller's configuration registers must be set to enable the external interrupt and define its triggering condition (rising edge, falling edge, or both).
The C code would typically include the necessary header files, initialization of the microcontroller, configuration of the interrupt registers, and the ISR definition. The code should also contain a main loop that allows the microcontroller to remain in a low-power state or perform other tasks while waiting for the interrupt to occur.
This demonstration effectively illustrates the functionality of external interrupts in the Atmega8 microcontroller, providing a practical application for those learning about embedded systems and real-time processing.A demo of external interrupts in AVR (Atmega8) micro controller with circuit diagram and C code/program as ISR (interrupt service routine).. 🔗 External reference