The input circuit common mode noise suppression microphone amplifier with balance
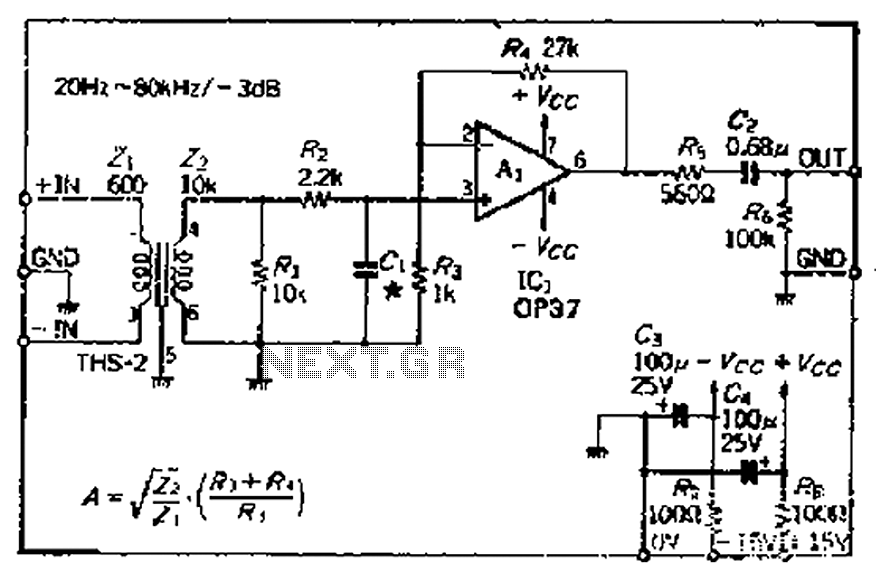
The common mode signal rejection ratio is influenced by the input transformer, which should either be a commercially available or a well-balanced homemade transformer. It is important to note that as frequency increases, the balance may decrease. The transmission frequency range and boost ratio must be considered, with the step-up ratio defined as the primary to secondary turns ratio. This ratio can also be represented as the square root of the impedance ratio. The circuit utilizes a commercially available THS-2 transformer with an impedance ratio of 6000:100k, yielding a boost ratio of approximately 12 dB voltage gain from the input conversion noise, which is relatively favorable. The resistance R, across the transformer, does not require a value of 10kΩ; however, the frequency characteristics of the transformer are affected by the resistance value. Therefore, frequency characteristics must be measured to determine the output, where high noise suppression is achieved through a low-pass filter. The effectiveness of this filter depends on the components used. The OP amplifier selected is a low-noise type, specifically the OP37, which is configured in a closed-loop for improved frequency characteristics. If a high offset voltage OP amplifier is utilized, a series capacitor of several microfarads should be included.
The circuit design focuses on optimizing the common mode signal rejection ratio through the careful selection and configuration of transformers and operational amplifiers. The use of a THS-2 transformer with a specified impedance ratio enhances the performance, particularly in applications requiring high fidelity and low noise levels. The step-up ratio derived from the transformer’s turns ratio plays a crucial role in determining the voltage gain, which is essential for ensuring that the signal remains strong enough for further processing.
Resistance values in the circuit are critical, as they directly influence the frequency response and overall performance of the transformer. The low-pass filter implemented serves to minimize high-frequency noise, allowing for clearer signal transmission. The choice of the OP37 operational amplifier is significant due to its low noise characteristics, which are vital in sensitive applications where signal integrity is paramount. The configuration of the amplifier in a closed-loop manner ensures stability and enhances the frequency response, making it suitable for high-performance audio or data acquisition systems.
In cases where a high offset voltage is present, the inclusion of a series capacitor is recommended to mitigate potential issues caused by DC offsets, ensuring that the signal remains within the operational limits of the amplifier. This careful consideration of component selection and circuit configuration is essential for achieving optimal performance in electronic systems that require high levels of signal integrity and noise reduction. Because the common mode signal rejection ratio depends on the input transformer, it should be used or homemade good balance transformer (It should be noted l frequency increase s, the balance will fall), is determined to consider the transmission frequency range boost ratio. Step-up ratio is primary to secondary turns ratio. Terminal can also be used to represent the square root of the impedance ratio. The circuit uses a utility available on the market THS-2 transformer impedance ratio of 6000: iookQ, so the boost ratio:/1 xo Lily F4, this kind available 12dB voltage gain from the input conversion noise this point look relatively favorable. Resistance R, and in the sub-Yi across the transformer, it seems no need to use iokfl, but the frequency characteristics of the transformer with a resistance value becomes, so the frequency characteristics measured to determine a post- chu t, cl high noise suppression is a low-pass filter for high inhibition effect depends dry cl, Zhang Rz available plus the equivalent output resistance is obtained.
OP zoom uses a closed-loop frequency characteristics of a good low-noise type OP37, straight surprised coupling. If you use a high OP amplifier offset voltage, should the series with a roar of dozens of micro-ho capacitance mouth
The circuit design focuses on optimizing the common mode signal rejection ratio through the careful selection and configuration of transformers and operational amplifiers. The use of a THS-2 transformer with a specified impedance ratio enhances the performance, particularly in applications requiring high fidelity and low noise levels. The step-up ratio derived from the transformer’s turns ratio plays a crucial role in determining the voltage gain, which is essential for ensuring that the signal remains strong enough for further processing.
Resistance values in the circuit are critical, as they directly influence the frequency response and overall performance of the transformer. The low-pass filter implemented serves to minimize high-frequency noise, allowing for clearer signal transmission. The choice of the OP37 operational amplifier is significant due to its low noise characteristics, which are vital in sensitive applications where signal integrity is paramount. The configuration of the amplifier in a closed-loop manner ensures stability and enhances the frequency response, making it suitable for high-performance audio or data acquisition systems.
In cases where a high offset voltage is present, the inclusion of a series capacitor is recommended to mitigate potential issues caused by DC offsets, ensuring that the signal remains within the operational limits of the amplifier. This careful consideration of component selection and circuit configuration is essential for achieving optimal performance in electronic systems that require high levels of signal integrity and noise reduction. Because the common mode signal rejection ratio depends on the input transformer, it should be used or homemade good balance transformer (It should be noted l frequency increase s, the balance will fall), is determined to consider the transmission frequency range boost ratio. Step-up ratio is primary to secondary turns ratio. Terminal can also be used to represent the square root of the impedance ratio. The circuit uses a utility available on the market THS-2 transformer impedance ratio of 6000: iookQ, so the boost ratio:/1 xo Lily F4, this kind available 12dB voltage gain from the input conversion noise this point look relatively favorable. Resistance R, and in the sub-Yi across the transformer, it seems no need to use iokfl, but the frequency characteristics of the transformer with a resistance value becomes, so the frequency characteristics measured to determine a post- chu t, cl high noise suppression is a low-pass filter for high inhibition effect depends dry cl, Zhang Rz available plus the equivalent output resistance is obtained.
OP zoom uses a closed-loop frequency characteristics of a good low-noise type OP37, straight surprised coupling. If you use a high OP amplifier offset voltage, should the series with a roar of dozens of micro-ho capacitance mouth