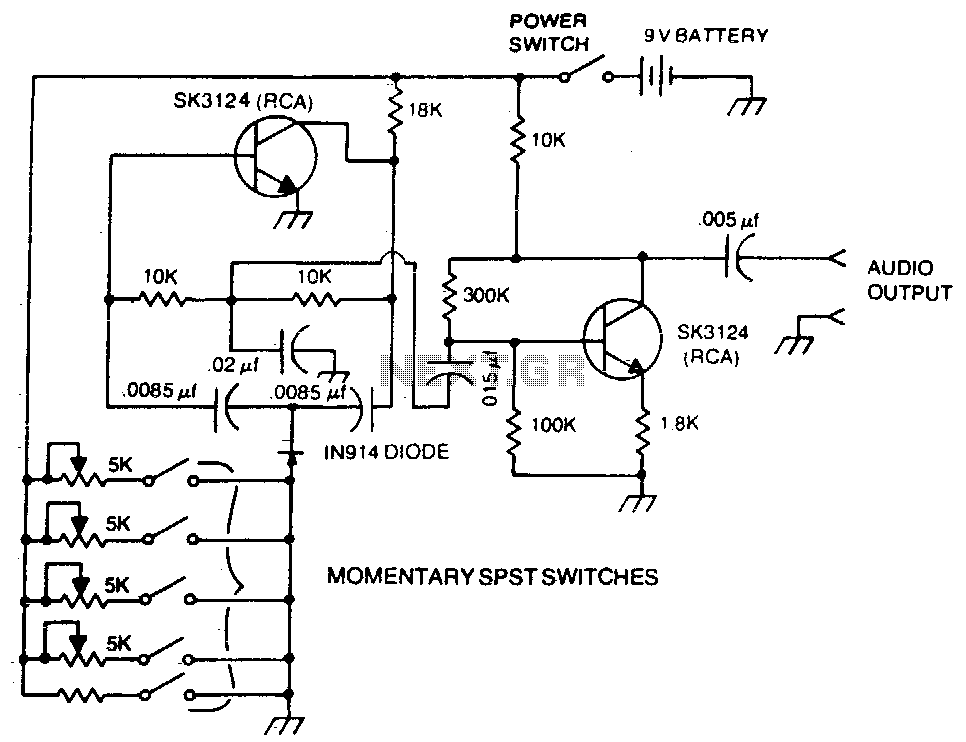
IC Excess-3 to Decimal Encoder Chip
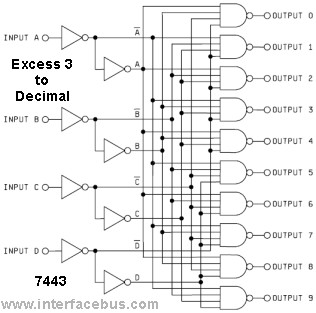
The function diagram for both the 5443 and 5444 integrated circuits (ICs) is identical, assuming a 16-pin dual in-line package. The difference lies in their internal connections, as depicted in the functional schematic, and the method of input decoding. While the pin-out and block diagram are the same, the internal connections reveal the distinction. It is uncertain whether an IC that performs an Excess-3 decode function is still in active production. Furthermore, the original 7400 series components represent the oldest segment of the 74xx family.
The 5443 and 5444 ICs are part of the 74xx series, which is a family of digital logic integrated circuits. The 5443 is designed to perform Excess-3 decoding, a binary-coded decimal (BCD) representation that allows for easy arithmetic operations. The Excess-3 code is a non-weighted code used to express decimal numbers, where each decimal digit is represented by its equivalent binary value plus three. The 5444, while serving a similar purpose, may have different internal logic configurations that affect its decoding capabilities.
Both ICs utilize a standard 16-pin dual in-line package (DIP) configuration, which facilitates easy integration into various electronic designs. The pin configuration typically includes power supply pins, ground pins, and input/output pins that correspond to the function of the IC. The identical pin-out allows for straightforward replacement of one IC with another in a circuit, provided that the specific application does not require the unique internal functionality of each.
The functional schematic illustrates how the inputs are processed and decoded into the corresponding outputs. The decoding logic is crucial for ensuring that the digital signals are interpreted correctly, especially in applications where precise numerical representation is necessary. The internal connections of the 5443 and 5444 differentiate their operational characteristics, influencing factors such as propagation delay, power consumption, and overall performance.
The 7400 series, which includes the 5443 and 5444, is foundational in digital electronics, with components that are widely used in various applications, from simple logic gates to complex arithmetic operations. As technology advances, newer families of ICs have emerged, but the legacy of the 7400 series continues to influence modern circuit design and implementation.Note that the function diagram for either the 5443 and 5444 are identical, assuming a 16-pin dual In-line package. The difference resided in the internal connections as shown in the functional schematic and how the inputs are decoded.
That is, the pin-out and block diagram is identical, but the internal connections show the difference. Editor note; It is doubtful that an IC that performs a Excess 3 decode function is still in active production. In addition; the orginal 7400 series of parts is the oldest of the 74xx family. 🔗 External reference
The 5443 and 5444 ICs are part of the 74xx series, which is a family of digital logic integrated circuits. The 5443 is designed to perform Excess-3 decoding, a binary-coded decimal (BCD) representation that allows for easy arithmetic operations. The Excess-3 code is a non-weighted code used to express decimal numbers, where each decimal digit is represented by its equivalent binary value plus three. The 5444, while serving a similar purpose, may have different internal logic configurations that affect its decoding capabilities.
Both ICs utilize a standard 16-pin dual in-line package (DIP) configuration, which facilitates easy integration into various electronic designs. The pin configuration typically includes power supply pins, ground pins, and input/output pins that correspond to the function of the IC. The identical pin-out allows for straightforward replacement of one IC with another in a circuit, provided that the specific application does not require the unique internal functionality of each.
The functional schematic illustrates how the inputs are processed and decoded into the corresponding outputs. The decoding logic is crucial for ensuring that the digital signals are interpreted correctly, especially in applications where precise numerical representation is necessary. The internal connections of the 5443 and 5444 differentiate their operational characteristics, influencing factors such as propagation delay, power consumption, and overall performance.
The 7400 series, which includes the 5443 and 5444, is foundational in digital electronics, with components that are widely used in various applications, from simple logic gates to complex arithmetic operations. As technology advances, newer families of ICs have emerged, but the legacy of the 7400 series continues to influence modern circuit design and implementation.Note that the function diagram for either the 5443 and 5444 are identical, assuming a 16-pin dual In-line package. The difference resided in the internal connections as shown in the functional schematic and how the inputs are decoded.
That is, the pin-out and block diagram is identical, but the internal connections show the difference. Editor note; It is doubtful that an IC that performs a Excess 3 decode function is still in active production. In addition; the orginal 7400 series of parts is the oldest of the 74xx family. 🔗 External reference