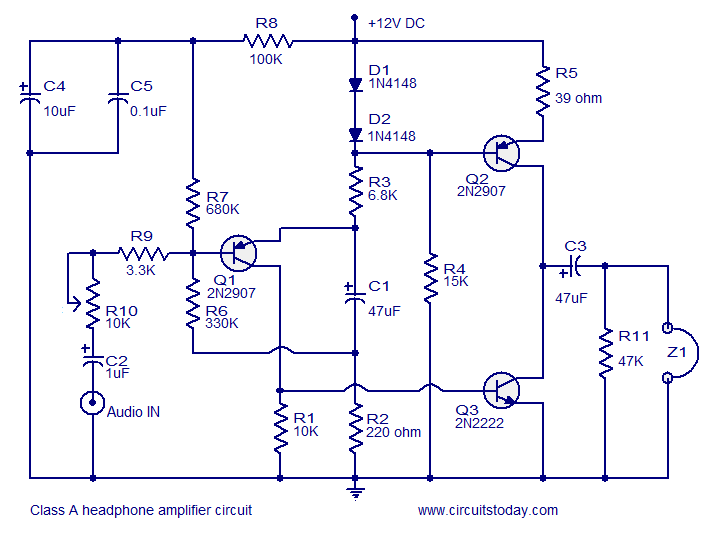
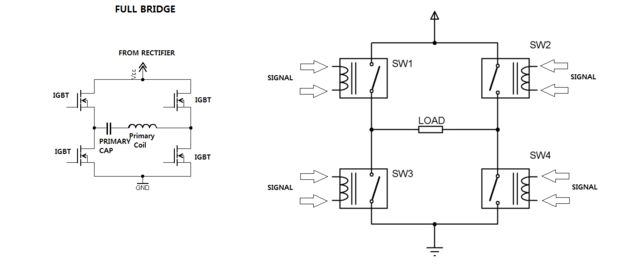
IC L298 based bidirectional H bridge DC motor control circuit

A bidirectional H-bridge DC motor control circuit is illustrated. The circuit utilizes the L298 integrated circuit from ST Microelectronics. The L298 is a dual full-bridge driver that supports a wide operating voltage range and can manage load currents up to 3A. This IC is characterized by low saturation voltage and includes over-temperature protection. In the circuit, diodes D1 to D4 serve as protection diodes. Capacitor C2 functions as the filter for the logic power supply, while another capacitor is used to filter the supply voltage. The motor's state is determined by the logic levels of pins 10, 11, and 12, as outlined in the accompanying table below the circuit diagram.
The bidirectional H-bridge configuration allows for the control of a DC motor's direction and speed by varying the voltage applied to the motor terminals. The L298 IC consists of two H-bridge circuits, enabling control of two motors or a single motor with bidirectional control. The IC operates effectively within a voltage range of 5V to 46V and can output a maximum current of 3A per channel, making it suitable for various applications requiring robust motor control.
The protection diodes (D1 to D4) are critical in safeguarding the circuit against back EMF generated by the motor during operation, especially when the motor is rapidly switched off. These diodes provide a path for the induced current, preventing damage to the L298 IC. Capacitor C2, designated for the logic power supply, ensures stable operation by filtering out noise and voltage fluctuations, while the second capacitor filters the supply voltage, maintaining a consistent power level for the motor operation.
The control logic for the motor is implemented through pins 10, 11, and 12 of the L298. The state of these pins dictates the operational mode of the motor, including forward, reverse, and stop states. A truth table typically accompanies the circuit diagram, detailing the specific pin configurations required to achieve the desired motor action. This setup allows for versatile control in applications ranging from robotics to automation systems, where precise motor function is essential.A bidirectional H bridge DC motor control circuit is shown here. The circuit is based on the IC L298 from ST Microelectronics. L298 is a dual full bridge driver that has a wide operating voltage range and can handle load currents up to 3A. The IC also features low saturation voltage and over temperature protection. In the circuit diode D1 to D4 ar e protection diodes. Capacitor C2 is the logic power supply filter and capacitor C2 is the supply voltage filter. The state of the motor will depend on the logic level of the pins 10, 11, 12 and it is described in the table shown below the circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference
The bidirectional H-bridge configuration allows for the control of a DC motor's direction and speed by varying the voltage applied to the motor terminals. The L298 IC consists of two H-bridge circuits, enabling control of two motors or a single motor with bidirectional control. The IC operates effectively within a voltage range of 5V to 46V and can output a maximum current of 3A per channel, making it suitable for various applications requiring robust motor control.
The protection diodes (D1 to D4) are critical in safeguarding the circuit against back EMF generated by the motor during operation, especially when the motor is rapidly switched off. These diodes provide a path for the induced current, preventing damage to the L298 IC. Capacitor C2, designated for the logic power supply, ensures stable operation by filtering out noise and voltage fluctuations, while the second capacitor filters the supply voltage, maintaining a consistent power level for the motor operation.
The control logic for the motor is implemented through pins 10, 11, and 12 of the L298. The state of these pins dictates the operational mode of the motor, including forward, reverse, and stop states. A truth table typically accompanies the circuit diagram, detailing the specific pin configurations required to achieve the desired motor action. This setup allows for versatile control in applications ranging from robotics to automation systems, where precise motor function is essential.A bidirectional H bridge DC motor control circuit is shown here. The circuit is based on the IC L298 from ST Microelectronics. L298 is a dual full bridge driver that has a wide operating voltage range and can handle load currents up to 3A. The IC also features low saturation voltage and over temperature protection. In the circuit diode D1 to D4 ar e protection diodes. Capacitor C2 is the logic power supply filter and capacitor C2 is the supply voltage filter. The state of the motor will depend on the logic level of the pins 10, 11, 12 and it is described in the table shown below the circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference