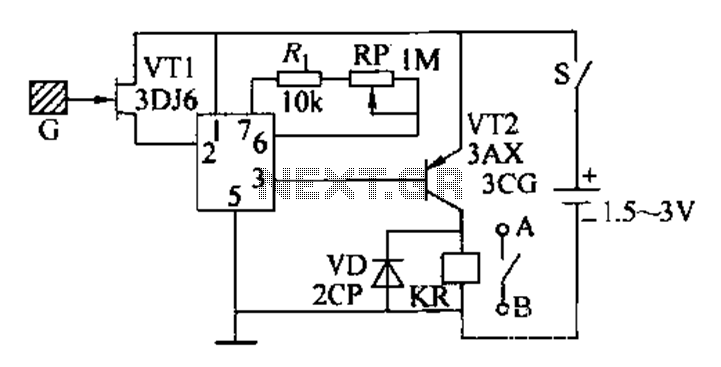
Induction automatic switch circuit
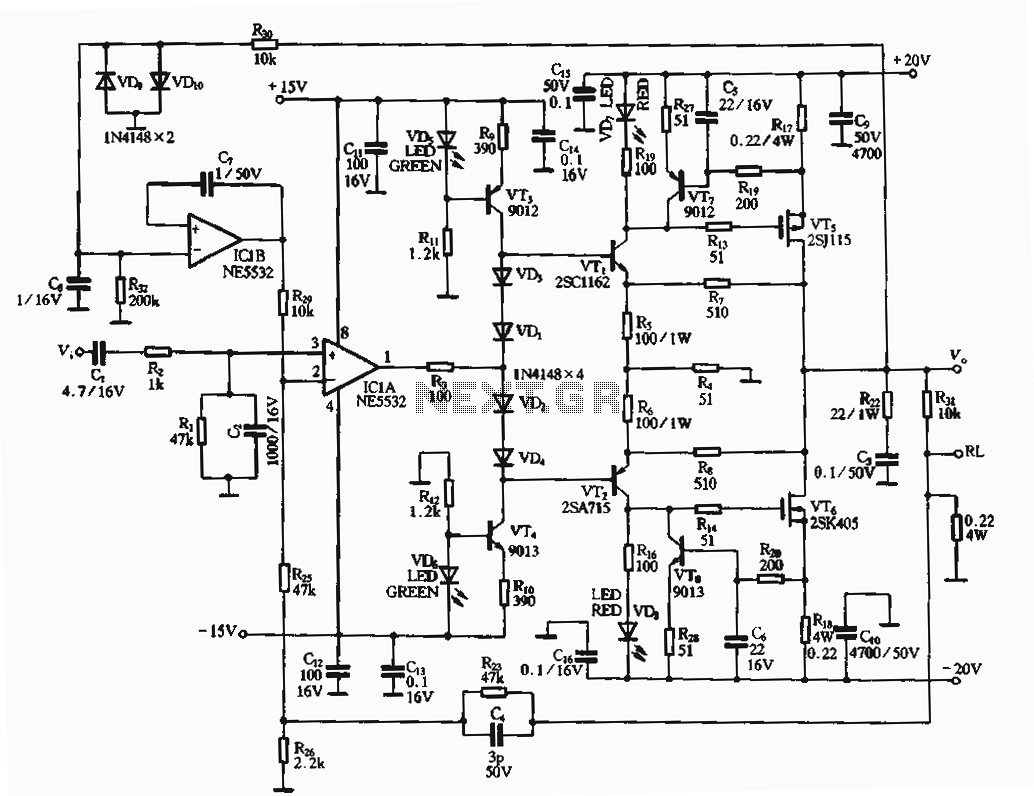
This circuit is a constant current protection type that limits the output current to a specific value in cases of over-current and short-circuit conditions. When the output current exceeds this limit, the output voltage decreases. The CW200 power management system is designed to prevent excessive damage during prolonged overcurrent situations. The circuit utilizes a Zener diode in conjunction with a transistor (VT1) to regulate current. When the output current surpasses the designated threshold, the current flows through a sensing resistor (R), activating the protective transistor VT1, which places the circuit into a constant-current protection mode. If the output voltage falls below a certain threshold (10V), the Zener diode (UD) along with resistors (RP2 and RP3) injects current into the base of VT1, further reducing the output voltage (Uo) and maintaining the CW200 in a protective state. The resistor (R) primarily acts as a protective device, while the pressure drop serves a secondary role. The circuit includes RP2 for fine-tuning the current limit and RP3 for adjusting the reduction process. Additionally, when using the integrated CW200 regulator, it is crucial to incorporate a sufficiently large heat sink to manage heat dissipation, calculated based on the power dissipation (Pw) and output current. Input and output capacitors must also be selected to minimize oscillations.
The constant current protection circuit is essential in safeguarding electronic systems from damage due to excessive current conditions. The design effectively utilizes a combination of components to ensure that the output current remains within safe limits during fault conditions. The Zener diode plays a critical role in voltage regulation by providing a stable reference voltage, which is crucial for the operation of the transistor VT1. When the output current exceeds the threshold, the sensing resistor R detects this increase and triggers the conduction of VT1, thereby limiting the output current and protecting downstream components.
The configuration of the resistors RP2 and RP3 allows for precise adjustments to the circuit's performance. RP2 is particularly important for setting the maximum allowable output current, while RP3 adjusts the rate at which the output voltage decreases during overcurrent conditions. This flexibility ensures that the circuit can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of various applications.
Thermal management is another critical aspect of the circuit design. The CW200 regulator must be equipped with an adequately sized heat sink to dissipate the heat generated during operation, especially under high load conditions. The heat sink must be selected based on the expected power dissipation, which involves calculating the difference between the input voltage and the output voltage multiplied by the output current. This calculation ensures that the temperature of the regulator remains within safe operating limits, thereby enhancing the reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Finally, the inclusion of input and output capacitors is vital to stabilize the circuit and prevent oscillations that could lead to erratic behavior. Careful selection of these capacitors, considering their equivalent series resistance (ESR) and capacitance values, contributes significantly to the overall stability and performance of the constant current protection circuit.Constant current protection circuit type, since the over-current and short-circuit, the output current is limited only to a certain value, the output voltage drops, the overcur rent room a little longer, power management and power CW200 is still possible due to excessive damage. Shown for the reduced flow high current regulator 12-44. It lies in the use of Zener diode vs impact on VT1: When the amount exceeds the value of the output current flows through the sensing resistor R., The protective crystal tube VT1 conduction, the circuit into a constant-current protection status.
When the output voltage drops to the implicit value of the pressure regulator diode vs UD time (10V) or less, vs by VD2, RP3, RP2 to the base of VT1 injection current causes the output voltage Uo into a further decline, vs will be maintained in CW200 protection status main factor, R. Pressure drop becomes a secondary factor, which played a protection device and power tube effect. Circuit RP2 to micro adjust the current limit, RP3 used to adjust the degree of reduction processes. A brief review of the integrated regulator CW200 three basic usage. When using this regulator, should pay attention to add enough wattage large heat sink, a heat sink in accordance with Pw Jo (U, - soul) estimate, where L is the output current, U; the input voltage, U is value of the output voltage t goblets -UO to 5-8v appropriate.
When using the regulator input and output capacitor must eliminate vibration with no sense of capacitors.
The constant current protection circuit is essential in safeguarding electronic systems from damage due to excessive current conditions. The design effectively utilizes a combination of components to ensure that the output current remains within safe limits during fault conditions. The Zener diode plays a critical role in voltage regulation by providing a stable reference voltage, which is crucial for the operation of the transistor VT1. When the output current exceeds the threshold, the sensing resistor R detects this increase and triggers the conduction of VT1, thereby limiting the output current and protecting downstream components.
The configuration of the resistors RP2 and RP3 allows for precise adjustments to the circuit's performance. RP2 is particularly important for setting the maximum allowable output current, while RP3 adjusts the rate at which the output voltage decreases during overcurrent conditions. This flexibility ensures that the circuit can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of various applications.
Thermal management is another critical aspect of the circuit design. The CW200 regulator must be equipped with an adequately sized heat sink to dissipate the heat generated during operation, especially under high load conditions. The heat sink must be selected based on the expected power dissipation, which involves calculating the difference between the input voltage and the output voltage multiplied by the output current. This calculation ensures that the temperature of the regulator remains within safe operating limits, thereby enhancing the reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Finally, the inclusion of input and output capacitors is vital to stabilize the circuit and prevent oscillations that could lead to erratic behavior. Careful selection of these capacitors, considering their equivalent series resistance (ESR) and capacitance values, contributes significantly to the overall stability and performance of the constant current protection circuit.Constant current protection circuit type, since the over-current and short-circuit, the output current is limited only to a certain value, the output voltage drops, the overcur rent room a little longer, power management and power CW200 is still possible due to excessive damage. Shown for the reduced flow high current regulator 12-44. It lies in the use of Zener diode vs impact on VT1: When the amount exceeds the value of the output current flows through the sensing resistor R., The protective crystal tube VT1 conduction, the circuit into a constant-current protection status.
When the output voltage drops to the implicit value of the pressure regulator diode vs UD time (10V) or less, vs by VD2, RP3, RP2 to the base of VT1 injection current causes the output voltage Uo into a further decline, vs will be maintained in CW200 protection status main factor, R. Pressure drop becomes a secondary factor, which played a protection device and power tube effect. Circuit RP2 to micro adjust the current limit, RP3 used to adjust the degree of reduction processes. A brief review of the integrated regulator CW200 three basic usage. When using this regulator, should pay attention to add enough wattage large heat sink, a heat sink in accordance with Pw Jo (U, - soul) estimate, where L is the output current, U; the input voltage, U is value of the output voltage t goblets -UO to 5-8v appropriate.
When using the regulator input and output capacitor must eliminate vibration with no sense of capacitors.