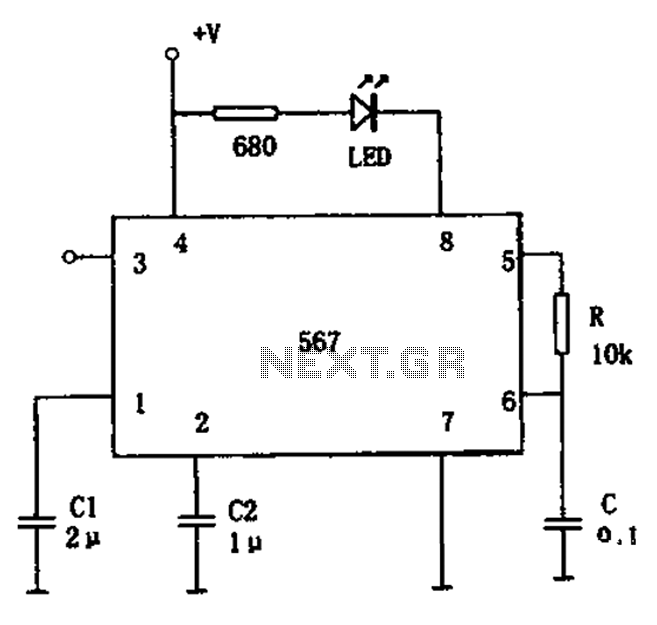
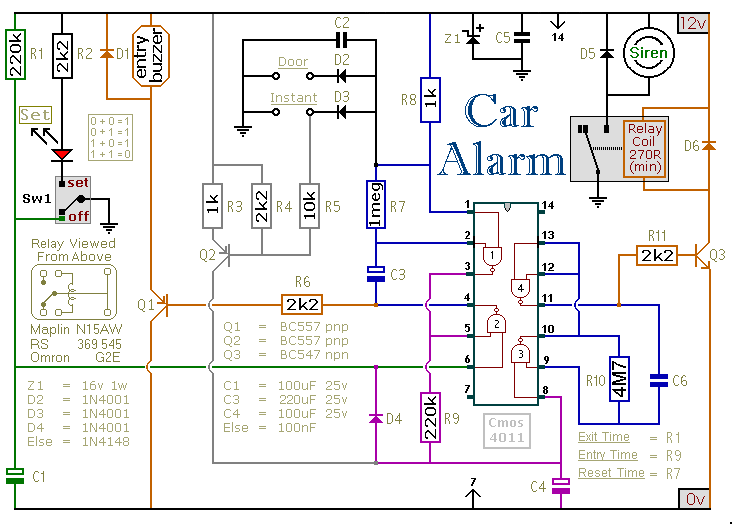
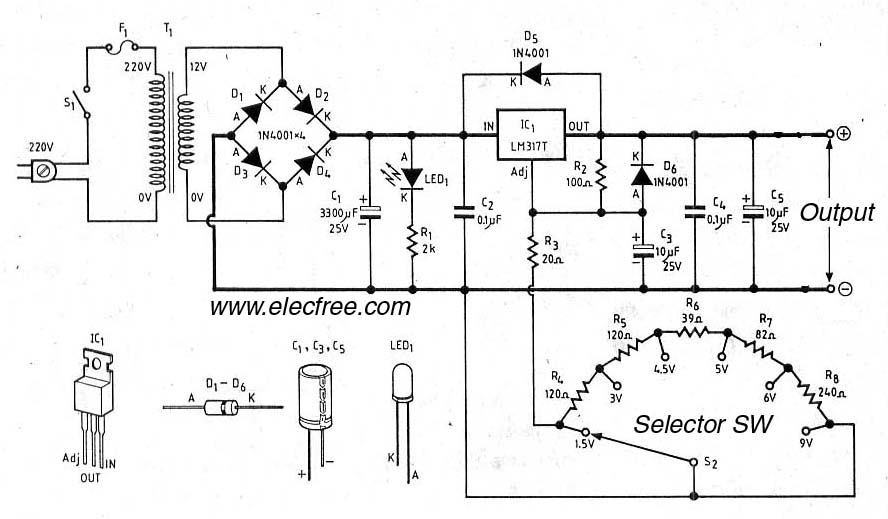
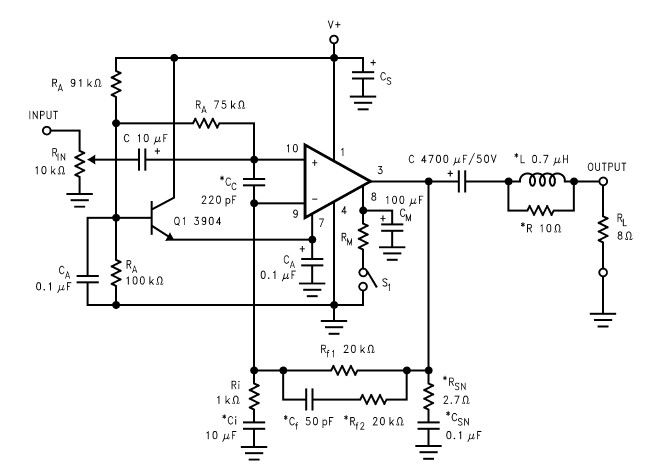
Inductorless Switching Regulator Circuit

In conventional applications, switching-regulator integrated circuits (ICs) regulate the output voltage (VQVT) by controlling the current through an external inductor. However, the IC in configuration A utilizes a diode-capacitor network in place of the inductor, providing comparable performance for small load applications. This network has the capability to double, triple, or quadruple the input voltage. Feedback from the resistor divider (RI/R2) enables IC1 to set the regulated output level. As illustrated, the circuit can derive 12 V from an input range of 5 to 12 V and provide up to 2 mA of output current. Additionally, incorporating a noninverting MOS driver (B) increases the available output current to 20 mA. By substituting the diode-capacitor network for an inductor, this switching-regulator IC can deliver 2 mA with comparable line and load regulation, albeit with slightly reduced efficiency.
The described circuit employs a switching-regulator IC designed for applications requiring efficient voltage regulation without the use of traditional inductors. The diode-capacitor network serves as an alternative energy storage mechanism, allowing for voltage multiplication while maintaining a compact form factor. This configuration is particularly advantageous in low-power applications where space and efficiency are critical.
The feedback mechanism utilizing the resistor divider (RI/R2) is essential for maintaining the desired output voltage. By adjusting the values of RI and R2, the output voltage can be finely tuned to meet specific requirements. The design's capability to derive 12 V from input voltages ranging from 5 to 12 V demonstrates its versatility and adaptability to various power supply scenarios.
The addition of a noninverting MOS driver enhances the circuit's output capabilities, allowing it to supply up to 20 mA of current, which is beneficial for driving loads that require higher current levels. This modification may involve careful selection of the MOSFET to ensure it operates efficiently within the given parameters.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies innovative approaches in voltage regulation, particularly for applications where traditional inductive components may introduce size, weight, or efficiency challenges. The combination of a diode-capacitor network and a MOS driver provides a robust solution for achieving reliable voltage regulation in compact electronic systems. In conventional applications, switching-regulator ICs regulate VQVT by controlling the current through an external inductor. The IC in A, however, driving a diode-capacitor network in place of the inductor, offers comparable performance for small loads.
The network can double, triple, or quadruple the input voltage. Feedback from the RI/R2 voltage divider enables IC1 to set the regulated-output, level. (As shown, the circuit derives 12 V from a 5- to 12-V input and provides as much as 2 mA of output current). Adding a noninverting MOS driver (B) boosts the available output current to 20 mA. Substituting the diode-capacitor network shown for an inductor allows this switching-regulator IC to deliver 2 mA at comparable line and load regulation, with somewhat reduced efficiency.
The described circuit employs a switching-regulator IC designed for applications requiring efficient voltage regulation without the use of traditional inductors. The diode-capacitor network serves as an alternative energy storage mechanism, allowing for voltage multiplication while maintaining a compact form factor. This configuration is particularly advantageous in low-power applications where space and efficiency are critical.
The feedback mechanism utilizing the resistor divider (RI/R2) is essential for maintaining the desired output voltage. By adjusting the values of RI and R2, the output voltage can be finely tuned to meet specific requirements. The design's capability to derive 12 V from input voltages ranging from 5 to 12 V demonstrates its versatility and adaptability to various power supply scenarios.
The addition of a noninverting MOS driver enhances the circuit's output capabilities, allowing it to supply up to 20 mA of current, which is beneficial for driving loads that require higher current levels. This modification may involve careful selection of the MOSFET to ensure it operates efficiently within the given parameters.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies innovative approaches in voltage regulation, particularly for applications where traditional inductive components may introduce size, weight, or efficiency challenges. The combination of a diode-capacitor network and a MOS driver provides a robust solution for achieving reliable voltage regulation in compact electronic systems. In conventional applications, switching-regulator ICs regulate VQVT by controlling the current through an external inductor. The IC in A, however, driving a diode-capacitor network in place of the inductor, offers comparable performance for small loads.
The network can double, triple, or quadruple the input voltage. Feedback from the RI/R2 voltage divider enables IC1 to set the regulated-output, level. (As shown, the circuit derives 12 V from a 5- to 12-V input and provides as much as 2 mA of output current). Adding a noninverting MOS driver (B) boosts the available output current to 20 mA. Substituting the diode-capacitor network shown for an inductor allows this switching-regulator IC to deliver 2 mA at comparable line and load regulation, with somewhat reduced efficiency.