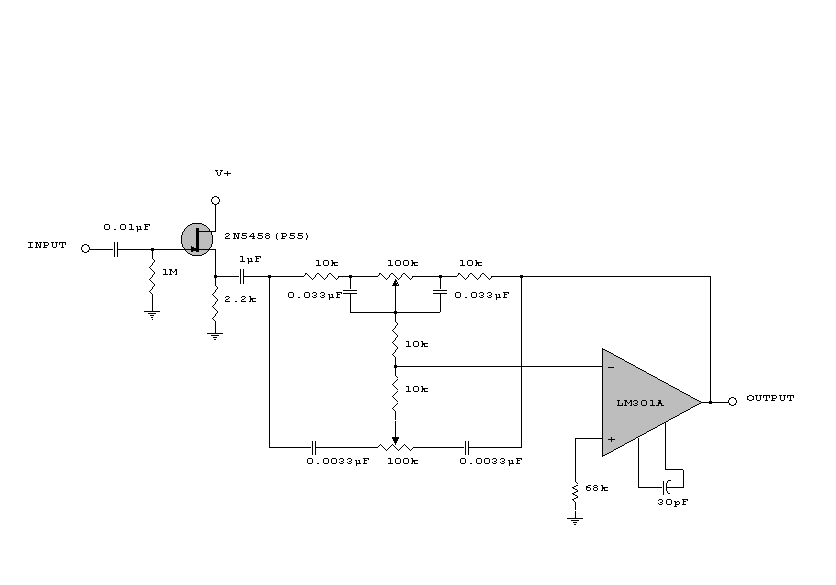
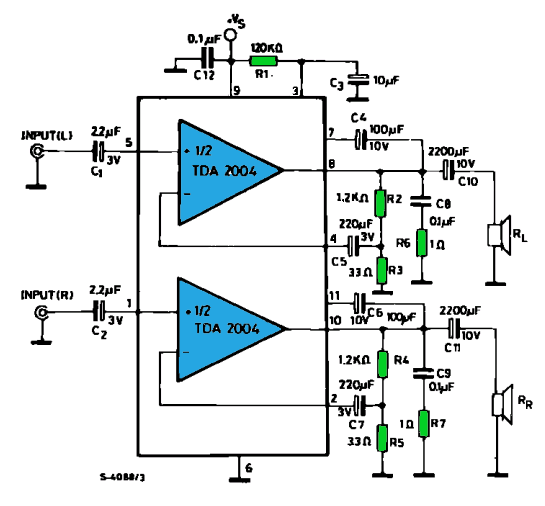
Integrated operational amplifier tone control circuit of a simplified equivalent circuit a
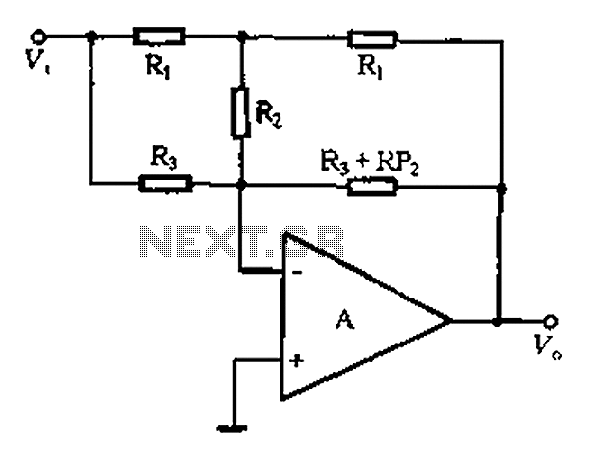
At high frequencies, the capacitor Cz can be considered a short circuit (i.e., the resistance of the RPi is negligible). This is illustrated in Figure 4-6 (a) of the apparatus, which corresponds to the equivalent circuit shown in Figure 4-6 (b). The following parameters are relevant: the maximum lifting capacity at high frequencies is given by the formula Af = F(R1 + R3 + 2R2); the maximum high-frequency attenuation value is expressed as vc = F/(R1 + R3 + 2R2). These formulas assume that RP2 is equal to (R1 + R3 + 2R2). The high-frequency boost corner frequency is defined by the equation fc = 1/(2πR3C2), where the units are denoted as follows: f is in hertz, R is in ohms (Europe), and C is in farads.
At high frequencies, the behavior of capacitors and resistors within a circuit significantly influences the overall performance. In this context, capacitor Cz is effectively acting as a short circuit, which simplifies the analysis of the circuit by removing the impedance of the RPi. This allows for a clearer understanding of how the remaining components interact under high-frequency conditions.
The maximum lifting capacity formula indicates how the circuit can handle power at elevated frequencies, taking into account the resistances R1, R3, and R2. Each of these resistors contributes to the total impedance experienced by the circuit, and their values must be optimized to achieve desired performance characteristics.
The maximum high-frequency attenuation value provided by the equation shows how the signal strength diminishes as it passes through the circuit. This attenuation is critical in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as communication systems or high-speed digital circuits.
The assumption that RP2 equals the sum of R1, R3, and twice R2 is essential for simplifying circuit calculations and ensuring accurate modeling of the system's response. This relationship illustrates how the resistive elements work together to define the overall impedance.
Finally, the high-frequency boost corner frequency formula indicates the frequency at which the circuit begins to exhibit significant gain, determined by the resistor R3 and capacitor C2. This frequency is crucial for applications requiring specific bandwidths, as it dictates the operational limits of the circuit. The use of standard units for resistance and capacitance ensures that the calculations can be universally applied and understood within the field of electronics. At high frequencies, q, Cz can be seen as a short circuit (i.e. RPi not present), as shown in Figure 4-6 (a) in the apparatus shown in FIG equivalent to 4-6 (b). Then there are : a high-frequency maximum lifting capacity: A f F (RI + R3 + 2Rz) cuddle 3; maximum high-frequency attenuation value: vc F feet 3/(Ri + R3 ten 2Rz). On two formula assumes: RP2 (Rt ® 3 + 2R2), high-frequency boost corner frequency:, s l/. 7tR3 C2. (Unit: f a ratio, R- fl (Europe), C- F (scared))
At high frequencies, the behavior of capacitors and resistors within a circuit significantly influences the overall performance. In this context, capacitor Cz is effectively acting as a short circuit, which simplifies the analysis of the circuit by removing the impedance of the RPi. This allows for a clearer understanding of how the remaining components interact under high-frequency conditions.
The maximum lifting capacity formula indicates how the circuit can handle power at elevated frequencies, taking into account the resistances R1, R3, and R2. Each of these resistors contributes to the total impedance experienced by the circuit, and their values must be optimized to achieve desired performance characteristics.
The maximum high-frequency attenuation value provided by the equation shows how the signal strength diminishes as it passes through the circuit. This attenuation is critical in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as communication systems or high-speed digital circuits.
The assumption that RP2 equals the sum of R1, R3, and twice R2 is essential for simplifying circuit calculations and ensuring accurate modeling of the system's response. This relationship illustrates how the resistive elements work together to define the overall impedance.
Finally, the high-frequency boost corner frequency formula indicates the frequency at which the circuit begins to exhibit significant gain, determined by the resistor R3 and capacitor C2. This frequency is crucial for applications requiring specific bandwidths, as it dictates the operational limits of the circuit. The use of standard units for resistance and capacitance ensures that the calculations can be universally applied and understood within the field of electronics. At high frequencies, q, Cz can be seen as a short circuit (i.e. RPi not present), as shown in Figure 4-6 (a) in the apparatus shown in FIG equivalent to 4-6 (b). Then there are : a high-frequency maximum lifting capacity: A f F (RI + R3 + 2Rz) cuddle 3; maximum high-frequency attenuation value: vc F feet 3/(Ri + R3 ten 2Rz). On two formula assumes: RP2 (Rt ® 3 + 2R2), high-frequency boost corner frequency:, s l/. 7tR3 C2. (Unit: f a ratio, R- fl (Europe), C- F (scared))