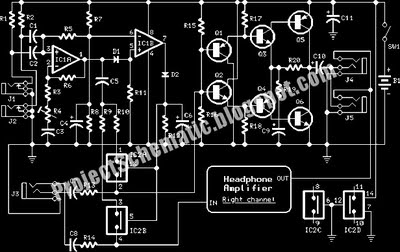
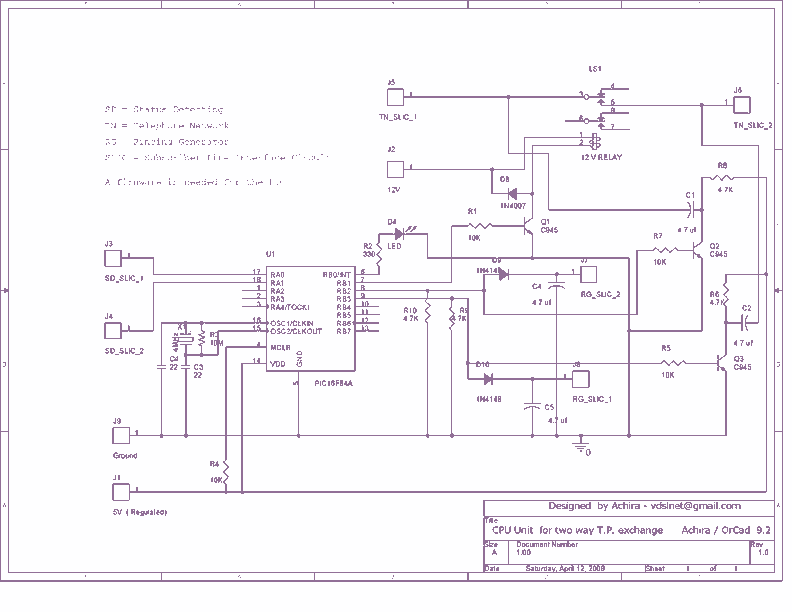
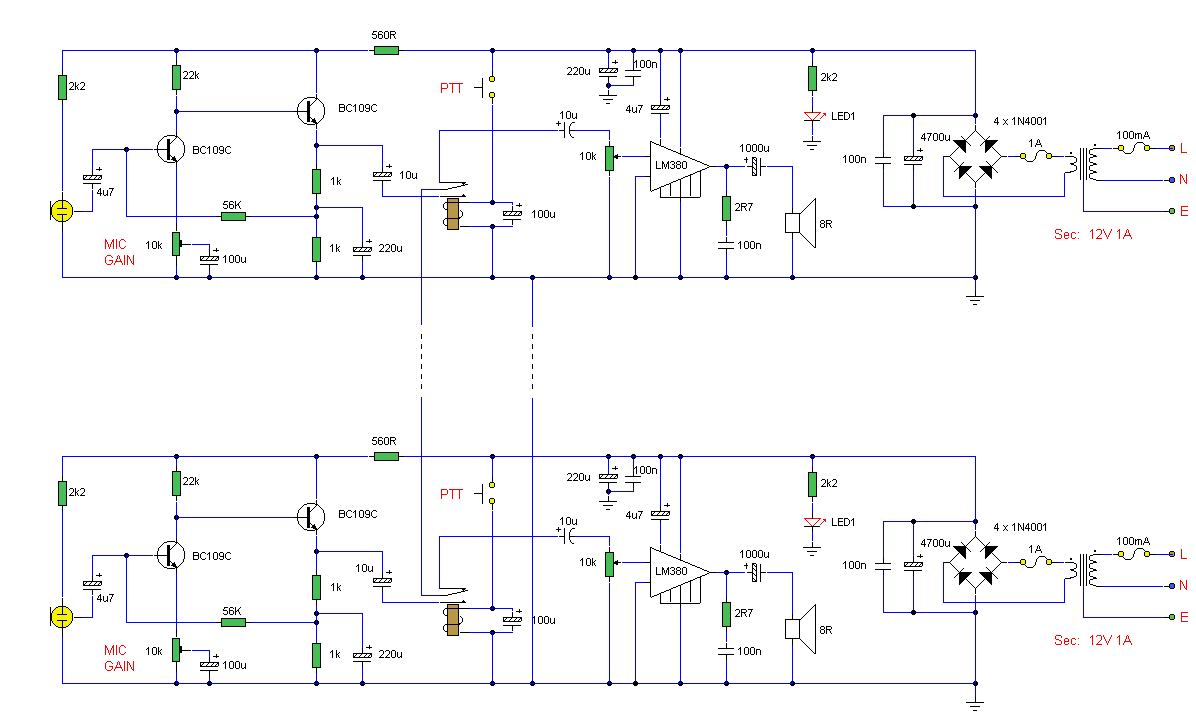
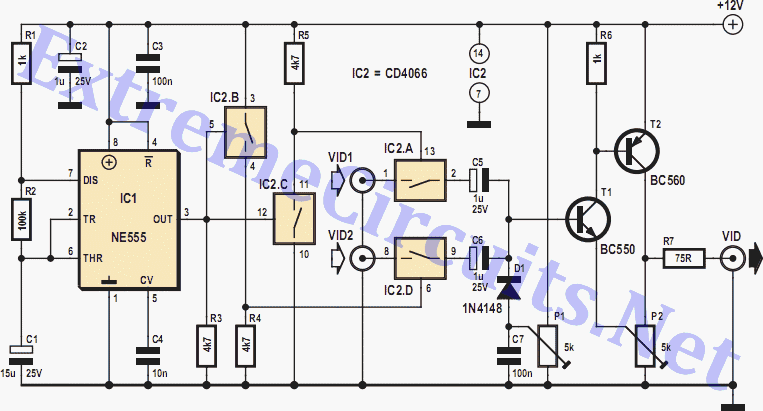
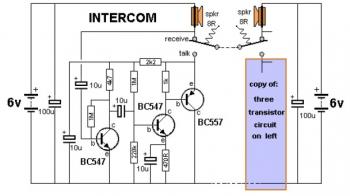
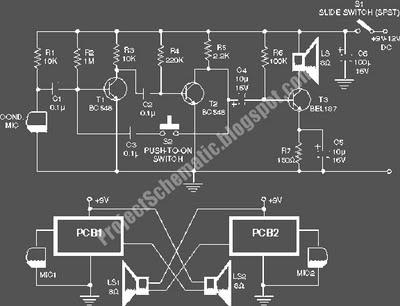
Intercom
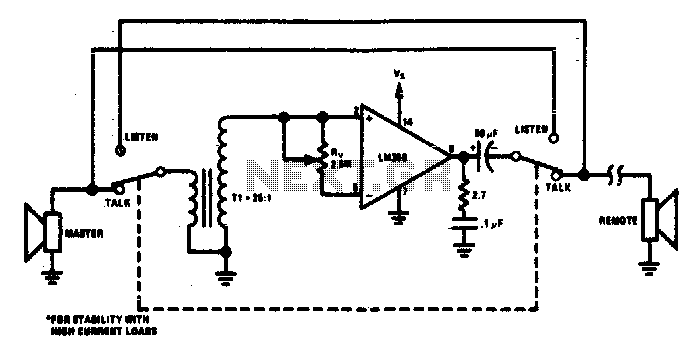
The circuit functions as a minimal component intercom system. When switch SI is set to the talk position, the speaker of the master station operates as the microphone with the assistance of step-up transformer T1. With a turns ratio of 25 and a device gain of 50, the maximum loop gain reaches 1250. Resistor Rv serves as a common mode volume control. Switching SI to the listen position reverses the roles of the master and remote speakers.
The intercom circuit described operates on a simple yet effective design, utilizing a minimal number of components to achieve communication between stations. The core of the system is the master station, which features a speaker that doubles as a microphone when in the talk position. This dual functionality is facilitated by a step-up transformer, T1, which is critical for amplifying the audio signal. The transformer has a turns ratio of 25, meaning that it increases the voltage of the audio signal by a factor of 25, enhancing the overall audio quality and ensuring clear communication.
The audio gain provided by the device is 50, which, when combined with the transformer’s turns ratio, results in a maximum loop gain of 1250. This high gain is advantageous for ensuring that even faint sounds are amplified adequately for clear transmission. The resistor Rv plays a significant role in the circuit by providing a common mode volume control, allowing users to adjust the volume of the audio signal based on their preferences or environmental noise levels.
When the switch SI is toggled to the listen position, the functionality of the system changes. In this mode, the master station's speaker becomes the output for audio received from the remote station, effectively allowing for two-way communication. This switching capability is essential for intercom systems, enabling users to alternate between speaking and listening without the need for additional hardware.
Overall, this intercom circuit exemplifies a straightforward design that balances functionality and simplicity, making it suitable for various applications where intercommunication is required.The circuit provides a minimum component intercom. With switch SI in the talk position, the speaker of the master station acts as the microphone with the aid of step-up transformer Tl. A turns ratio of 25 and a device gain of 50 allows a maximum loop gain of 1250. Rv provides a common mode volume control Switching Si to the listen position reverses the role of the master and remote speakers.
The intercom circuit described operates on a simple yet effective design, utilizing a minimal number of components to achieve communication between stations. The core of the system is the master station, which features a speaker that doubles as a microphone when in the talk position. This dual functionality is facilitated by a step-up transformer, T1, which is critical for amplifying the audio signal. The transformer has a turns ratio of 25, meaning that it increases the voltage of the audio signal by a factor of 25, enhancing the overall audio quality and ensuring clear communication.
The audio gain provided by the device is 50, which, when combined with the transformer’s turns ratio, results in a maximum loop gain of 1250. This high gain is advantageous for ensuring that even faint sounds are amplified adequately for clear transmission. The resistor Rv plays a significant role in the circuit by providing a common mode volume control, allowing users to adjust the volume of the audio signal based on their preferences or environmental noise levels.
When the switch SI is toggled to the listen position, the functionality of the system changes. In this mode, the master station's speaker becomes the output for audio received from the remote station, effectively allowing for two-way communication. This switching capability is essential for intercom systems, enabling users to alternate between speaking and listening without the need for additional hardware.
Overall, this intercom circuit exemplifies a straightforward design that balances functionality and simplicity, making it suitable for various applications where intercommunication is required.The circuit provides a minimum component intercom. With switch SI in the talk position, the speaker of the master station acts as the microphone with the aid of step-up transformer Tl. A turns ratio of 25 and a device gain of 50 allows a maximum loop gain of 1250. Rv provides a common mode volume control Switching Si to the listen position reverses the role of the master and remote speakers.