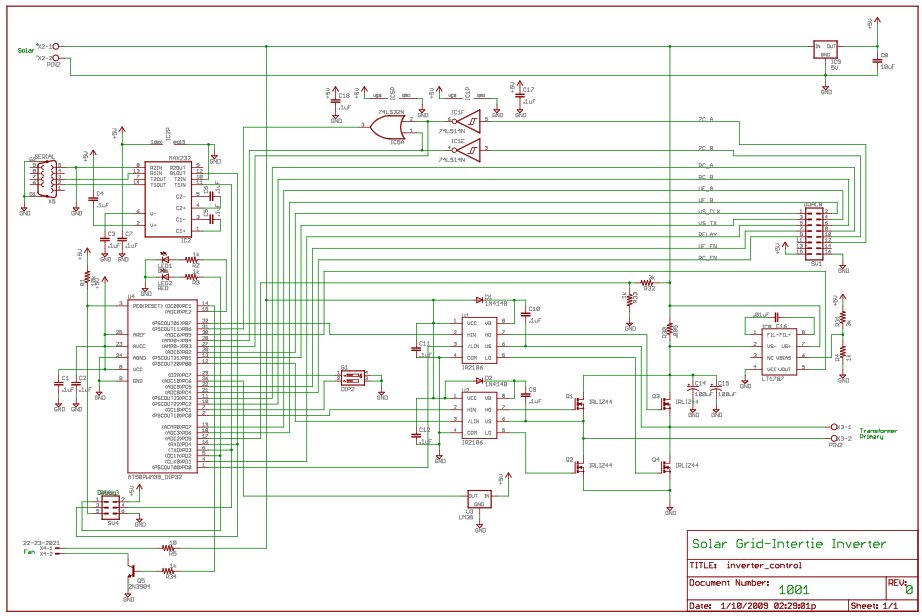
inverter design shines photovoltaic systems
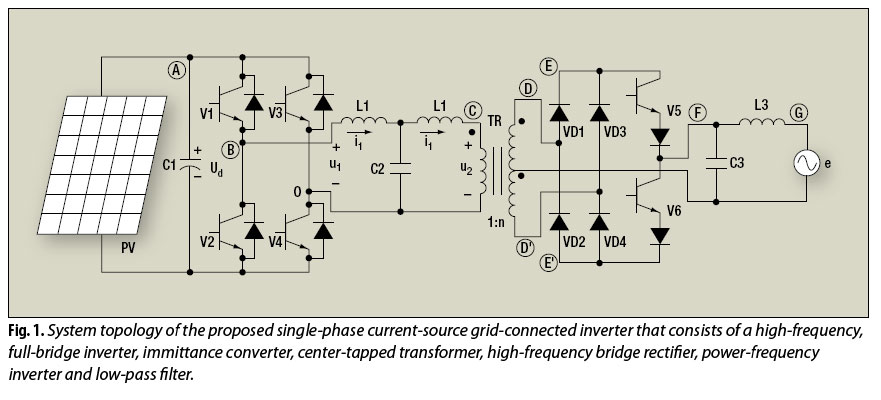
The electric utility grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) system is a significant technology for future renewable energy applications.
The electric utility grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) system plays a crucial role in the advancement of renewable energy technologies. This system integrates solar panels into the existing electrical grid, allowing for the conversion of sunlight into electricity that can be used locally or fed back into the grid.
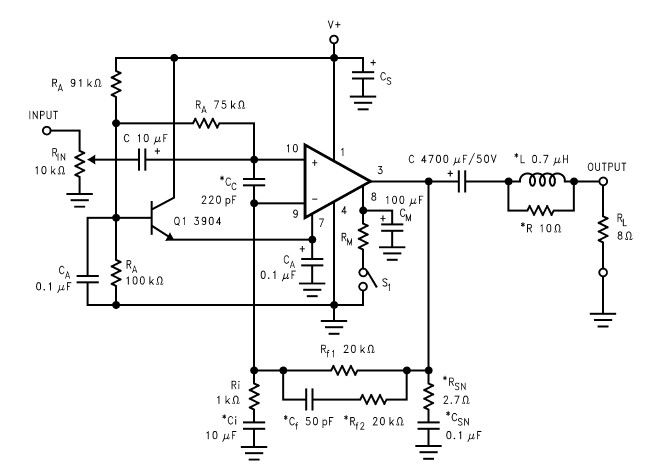
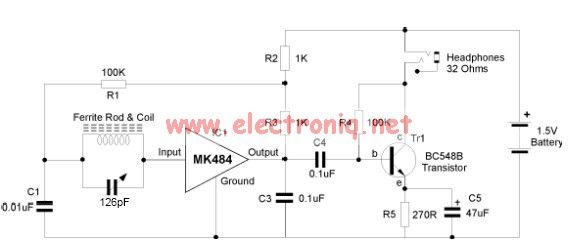
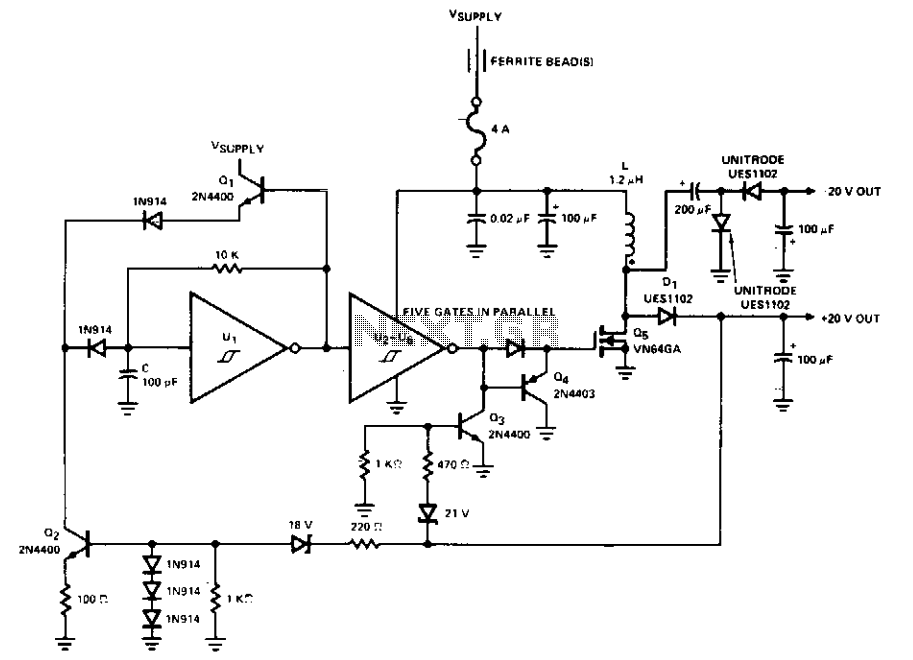
A typical grid-connected PV system consists of several key components: solar panels (modules), an inverter, a mounting system, and electrical wiring. The solar panels, made up of photovoltaic cells, capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The inverter then converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is compatible with the electrical grid and can be used by household appliances or fed into the grid for use by others.
The mounting system secures the solar panels in place, optimizing their angle and exposure to sunlight for maximum energy capture. Additionally, electrical wiring connects all components, ensuring efficient power transfer and adherence to safety standards.
Grid-tied systems often include net metering capabilities, allowing users to receive credit for the excess electricity generated by their PV system that is sent back to the grid. This feature not only enhances the economic viability of solar energy but also contributes to the overall stability and sustainability of the electrical grid.
In conclusion, grid-connected photovoltaic systems represent a vital technology in the transition to renewable energy, offering both environmental benefits and economic opportunities while enhancing the resilience of energy infrastructure.The electric utility grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) system is an important technology for future renewable energy applications.. 🔗 External reference
The electric utility grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) system plays a crucial role in the advancement of renewable energy technologies. This system integrates solar panels into the existing electrical grid, allowing for the conversion of sunlight into electricity that can be used locally or fed back into the grid.
A typical grid-connected PV system consists of several key components: solar panels (modules), an inverter, a mounting system, and electrical wiring. The solar panels, made up of photovoltaic cells, capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The inverter then converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is compatible with the electrical grid and can be used by household appliances or fed into the grid for use by others.
The mounting system secures the solar panels in place, optimizing their angle and exposure to sunlight for maximum energy capture. Additionally, electrical wiring connects all components, ensuring efficient power transfer and adherence to safety standards.
Grid-tied systems often include net metering capabilities, allowing users to receive credit for the excess electricity generated by their PV system that is sent back to the grid. This feature not only enhances the economic viability of solar energy but also contributes to the overall stability and sustainability of the electrical grid.
In conclusion, grid-connected photovoltaic systems represent a vital technology in the transition to renewable energy, offering both environmental benefits and economic opportunities while enhancing the resilience of energy infrastructure.The electric utility grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) system is an important technology for future renewable energy applications.. 🔗 External reference