Ir Detector

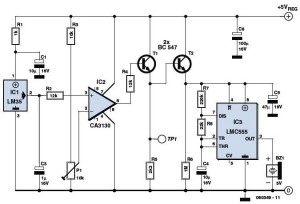
This circuit is useful for checking TV remote controls, IR-based alarm systems, and IR sources. It activates LED1 for two seconds in the presence of IR light pulses. U1A functions as a voltage follower for detector Q1. Capacitor C1 and resistor R2 create a differentiating network, while U1B amplifies the pulses, charging capacitor C2. Voltage follower U1C samples the voltage on C2 and drives comparator U1D, which controls the on/off state of LED1.
The circuit operates by detecting infrared (IR) light pulses emitted from remote controls or other IR sources. The primary component, Q1, is an IR photodetector that converts incoming IR light into an electrical signal. The output of Q1 is fed into operational amplifier U1A, configured as a voltage follower to ensure that the signal maintains its integrity without being loaded down by subsequent stages.
The differentiating network formed by capacitor C1 and resistor R2 serves to convert the continuous signal from the photodetector into sharp pulses, enhancing the detection of rapid changes in the IR light intensity. The output of this differentiating network is then amplified by operational amplifier U1B, which increases the amplitude of the signal for further processing.
Capacitor C2 is charged by the amplified pulses, and its voltage level is monitored by voltage follower U1C. This configuration allows U1C to provide a stable output that reflects the charge level of C2. The final stage of the circuit involves comparator U1D, which compares the sampled voltage against a reference level. When the voltage from C2 exceeds the reference, U1D activates LED1, indicating the presence of IR light pulses. The LED remains illuminated for a duration of two seconds, providing a clear visual indication of IR signal detection.
This circuit can be effectively used in various applications, including troubleshooting remote controls, testing IR-based alarm systems, and verifying the functionality of other IR-emitting devices. The design ensures reliable operation and clear feedback through the LED indicator, making it a practical tool for electronics testing and diagnostics. Useful for checking TV remote controls, IR-based alarm systems, and IR sources, this circuit causes LED1 to turn on for two sec onds in the presence of IR light pulses. UlA acts as a voltage follower for detector Ql. CI and R2 form a differentiating network and U1B acts as an amplifier for the pulses, which charges C2. Voltage follower U1C samples the voltage on C2 and drives comparator U1D, which switches LED1 on or off.
The circuit operates by detecting infrared (IR) light pulses emitted from remote controls or other IR sources. The primary component, Q1, is an IR photodetector that converts incoming IR light into an electrical signal. The output of Q1 is fed into operational amplifier U1A, configured as a voltage follower to ensure that the signal maintains its integrity without being loaded down by subsequent stages.
The differentiating network formed by capacitor C1 and resistor R2 serves to convert the continuous signal from the photodetector into sharp pulses, enhancing the detection of rapid changes in the IR light intensity. The output of this differentiating network is then amplified by operational amplifier U1B, which increases the amplitude of the signal for further processing.
Capacitor C2 is charged by the amplified pulses, and its voltage level is monitored by voltage follower U1C. This configuration allows U1C to provide a stable output that reflects the charge level of C2. The final stage of the circuit involves comparator U1D, which compares the sampled voltage against a reference level. When the voltage from C2 exceeds the reference, U1D activates LED1, indicating the presence of IR light pulses. The LED remains illuminated for a duration of two seconds, providing a clear visual indication of IR signal detection.
This circuit can be effectively used in various applications, including troubleshooting remote controls, testing IR-based alarm systems, and verifying the functionality of other IR-emitting devices. The design ensures reliable operation and clear feedback through the LED indicator, making it a practical tool for electronics testing and diagnostics. Useful for checking TV remote controls, IR-based alarm systems, and IR sources, this circuit causes LED1 to turn on for two sec onds in the presence of IR light pulses. UlA acts as a voltage follower for detector Ql. CI and R2 form a differentiating network and U1B acts as an amplifier for the pulses, which charges C2. Voltage follower U1C samples the voltage on C2 and drives comparator U1D, which switches LED1 on or off.