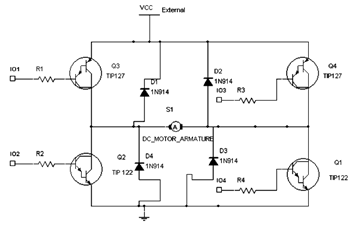
Ir Pulse To Audio Converter Circuit
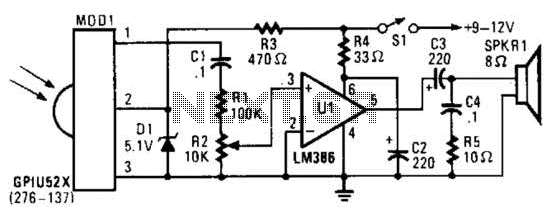
This circuit utilizes an infrared pulse-to-audio converter to assist in troubleshooting infrared remote controls, making it an effective tool for detecting infrared light sources. It employs a photo cell module (Radio Shack P/N 276-137) to detect IR radiation and drive audio IC U1.
The infrared pulse-to-audio converter circuit operates by converting the infrared signals emitted by remote controls into audible sound. The heart of the circuit is the photo cell module, which is sensitive to infrared light. When an infrared signal is detected, the module generates a corresponding electrical signal. This signal is then fed into audio IC U1, which processes it to produce an audible output.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: the photo cell module (P/N 276-137), audio IC U1, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply. The photo cell module is connected to the input of the audio IC, and it typically requires a power supply of around 5V to operate efficiently. Resistors may be used to adjust the sensitivity of the photo cell and to limit the current flowing into the audio IC, ensuring that it operates within its safe limits.
Capacitors can be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply to the audio IC, providing a cleaner output signal. The output from the audio IC can be connected to a small speaker or an audio output jack, allowing the user to hear the converted infrared signals as audible sounds.
This circuit can be particularly useful for technicians and hobbyists who need to diagnose issues with remote controls or for educational purposes to demonstrate the principles of infrared communication and audio signal processing. By providing audible feedback when an infrared signal is detected, users can easily identify the operation of remote controls and analyze their functionality. If your ear is good, you can use this IR-pulse-to-audio converter to troubleshoot infrared remote-controls. It is also a good project for detecting infrared-light sources. A photo cell module (Radio Shack P/N 276-137) detects IR radiation and drives audio IC Ul. This circuit is useful for troubleshooting IR remote controls.
The infrared pulse-to-audio converter circuit operates by converting the infrared signals emitted by remote controls into audible sound. The heart of the circuit is the photo cell module, which is sensitive to infrared light. When an infrared signal is detected, the module generates a corresponding electrical signal. This signal is then fed into audio IC U1, which processes it to produce an audible output.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: the photo cell module (P/N 276-137), audio IC U1, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply. The photo cell module is connected to the input of the audio IC, and it typically requires a power supply of around 5V to operate efficiently. Resistors may be used to adjust the sensitivity of the photo cell and to limit the current flowing into the audio IC, ensuring that it operates within its safe limits.
Capacitors can be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply to the audio IC, providing a cleaner output signal. The output from the audio IC can be connected to a small speaker or an audio output jack, allowing the user to hear the converted infrared signals as audible sounds.
This circuit can be particularly useful for technicians and hobbyists who need to diagnose issues with remote controls or for educational purposes to demonstrate the principles of infrared communication and audio signal processing. By providing audible feedback when an infrared signal is detected, users can easily identify the operation of remote controls and analyze their functionality. If your ear is good, you can use this IR-pulse-to-audio converter to troubleshoot infrared remote-controls. It is also a good project for detecting infrared-light sources. A photo cell module (Radio Shack P/N 276-137) detects IR radiation and drives audio IC Ul. This circuit is useful for troubleshooting IR remote controls.