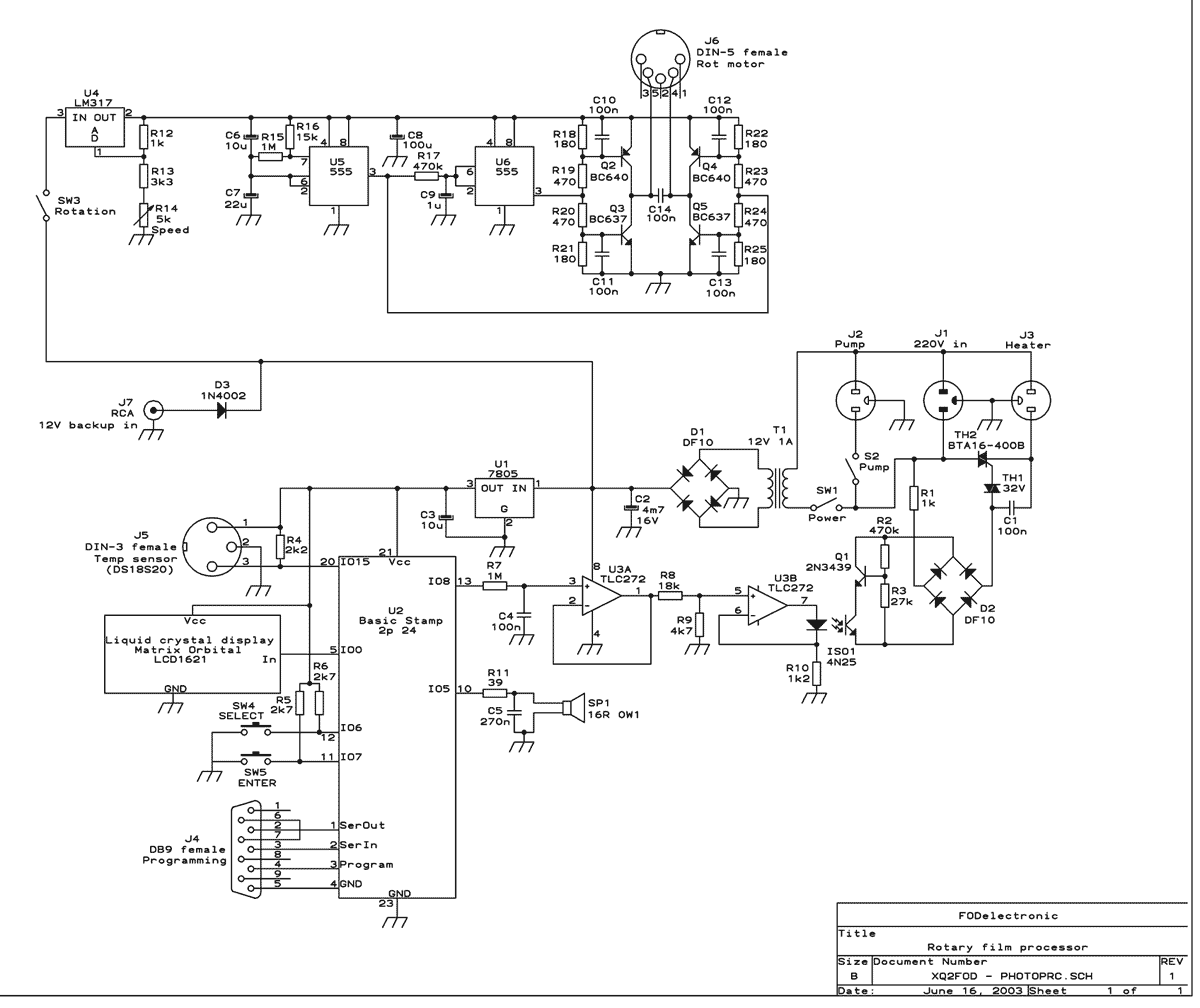
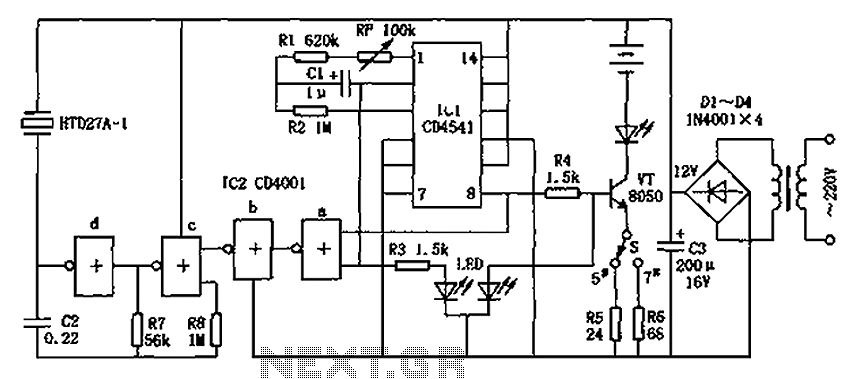
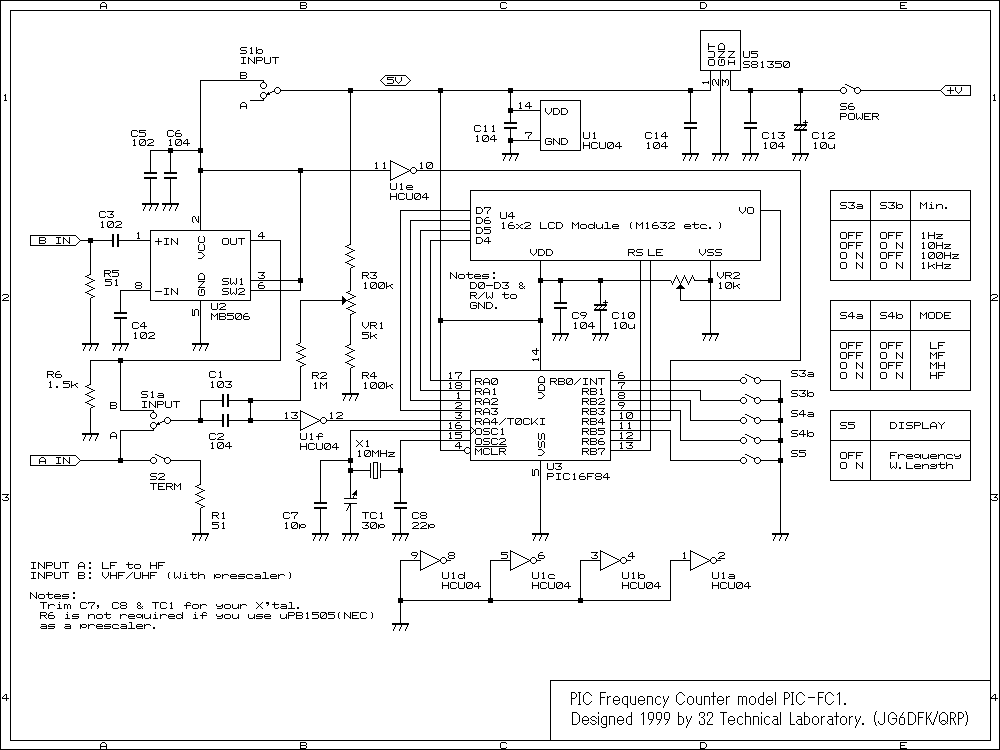
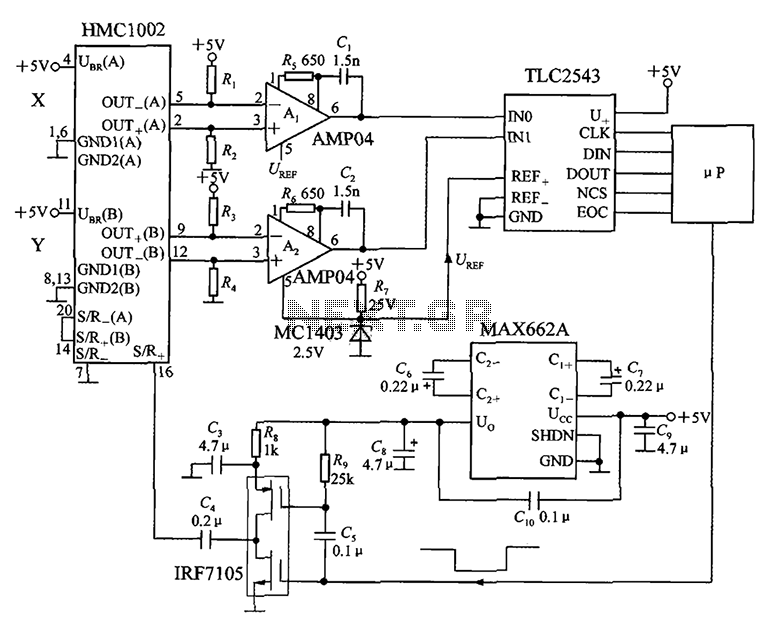
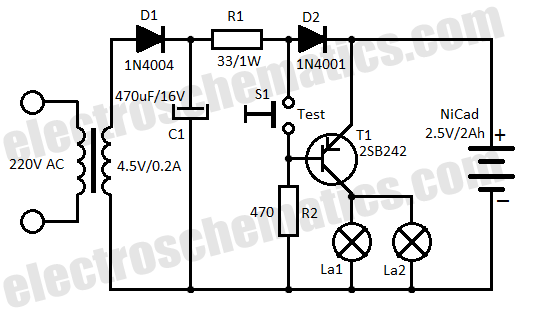
It ZD1 type forklift battery control circuit
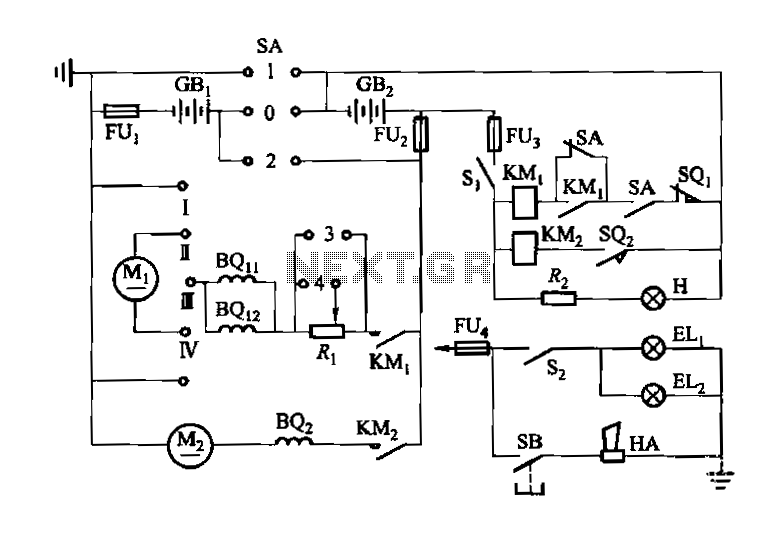
Denote cam controller SA 1 contact closure case. M1 is 1.35 kW driving motor, M2 is a 4 kW pump motor.
The circuit involves a cam controller designated as SA 1, which is responsible for managing the operation of two motors: M1, a driving motor rated at 1.35 kW, and M2, a pump motor rated at 4 kW. The contact closure case indicates that the controller utilizes a mechanical switch or relay system to initiate or terminate the operation of these motors based on the position of the cam.
The cam controller operates by detecting the position of the cam mechanism, which is typically linked to the operational cycle of the machinery. When the cam reaches a certain position, it causes the contact closure to occur, sending a signal to activate M1 or M2. The driving motor (M1) is primarily responsible for powering the mechanical components of the system, while the pump motor (M2) facilitates fluid movement, essential for the overall operation.
The control circuit may include additional components such as fuses for overload protection, contactors for motor control, and potentially a feedback loop to monitor the performance of the motors. The design must ensure that the current ratings and voltage levels are suitable for the motors in use, and that the contact closure mechanism is reliable to prevent unintended motor activation.
In summary, the schematic for this circuit will consist of the cam controller, relay contacts for M1 and M2, protection devices, and the necessary wiring to connect the motors to the power supply. Proper grounding and safety measures should also be incorporated to ensure safe operation within the designated parameters.Denote cam controller SA 1 contact closure case. M1 is 1. 35kW driving motor, Mz to 4kW pump motor.
The circuit involves a cam controller designated as SA 1, which is responsible for managing the operation of two motors: M1, a driving motor rated at 1.35 kW, and M2, a pump motor rated at 4 kW. The contact closure case indicates that the controller utilizes a mechanical switch or relay system to initiate or terminate the operation of these motors based on the position of the cam.
The cam controller operates by detecting the position of the cam mechanism, which is typically linked to the operational cycle of the machinery. When the cam reaches a certain position, it causes the contact closure to occur, sending a signal to activate M1 or M2. The driving motor (M1) is primarily responsible for powering the mechanical components of the system, while the pump motor (M2) facilitates fluid movement, essential for the overall operation.
The control circuit may include additional components such as fuses for overload protection, contactors for motor control, and potentially a feedback loop to monitor the performance of the motors. The design must ensure that the current ratings and voltage levels are suitable for the motors in use, and that the contact closure mechanism is reliable to prevent unintended motor activation.
In summary, the schematic for this circuit will consist of the cam controller, relay contacts for M1 and M2, protection devices, and the necessary wiring to connect the motors to the power supply. Proper grounding and safety measures should also be incorporated to ensure safe operation within the designated parameters.Denote cam controller SA 1 contact closure case. M1 is 1. 35kW driving motor, Mz to 4kW pump motor.