keyboard circuit
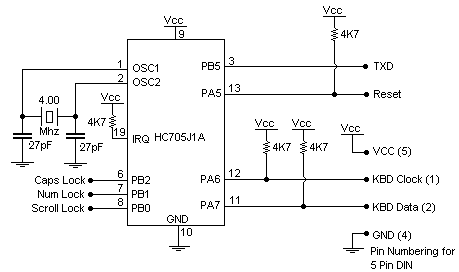
This document details the AT Keyboard Interface and AT Keyboard Protocols. It includes an example of a Keyboard to ASCII decoder utilizing a 68HC705J1A microcontroller.
The AT Keyboard Interface is a standard communication protocol used primarily in personal computers to facilitate interaction between the keyboard and the system. It operates using a serial communication method, allowing the keyboard to send keystroke information to the computer. The protocol is characterized by a simple command structure, where each key press generates a unique scan code that is transmitted to the microcontroller.
The 68HC705J1A microcontroller, a member of the Motorola 68HC05 family, is well-suited for this application due to its built-in features that support keyboard interfacing. It contains a programmable input/output port that can be configured to receive data from the keyboard. The microcontroller processes the incoming scan codes and converts them into ASCII characters, which can be utilized by software applications running on the host system.
In the implementation of a Keyboard to ASCII decoder, the microcontroller is programmed to recognize specific scan codes corresponding to each key on the keyboard. Upon receiving a scan code, the microcontroller checks its internal lookup table, which maps scan codes to their respective ASCII values. The decoded ASCII character can then be sent to the output port for further processing or display.
The schematic for this system typically includes the microcontroller connected to the keyboard via a serial line, pull-up resistors for signal integrity, and possibly a debounce circuit to ensure clean signal transitions when keys are pressed. The design may also incorporate power supply filtering to stabilize the operation of the microcontroller and the keyboard interface.
Overall, the AT Keyboard Interface and the corresponding decoding process enable effective user input management in various electronic systems, demonstrating the integration of hardware and software in embedded applications.Details the AT Keyboard Interface and AT Keyboard Protocols. Includes an example Keyboard to ASCII decoder using a 68HC705J1A MCU.. 🔗 External reference
The AT Keyboard Interface is a standard communication protocol used primarily in personal computers to facilitate interaction between the keyboard and the system. It operates using a serial communication method, allowing the keyboard to send keystroke information to the computer. The protocol is characterized by a simple command structure, where each key press generates a unique scan code that is transmitted to the microcontroller.
The 68HC705J1A microcontroller, a member of the Motorola 68HC05 family, is well-suited for this application due to its built-in features that support keyboard interfacing. It contains a programmable input/output port that can be configured to receive data from the keyboard. The microcontroller processes the incoming scan codes and converts them into ASCII characters, which can be utilized by software applications running on the host system.
In the implementation of a Keyboard to ASCII decoder, the microcontroller is programmed to recognize specific scan codes corresponding to each key on the keyboard. Upon receiving a scan code, the microcontroller checks its internal lookup table, which maps scan codes to their respective ASCII values. The decoded ASCII character can then be sent to the output port for further processing or display.
The schematic for this system typically includes the microcontroller connected to the keyboard via a serial line, pull-up resistors for signal integrity, and possibly a debounce circuit to ensure clean signal transitions when keys are pressed. The design may also incorporate power supply filtering to stabilize the operation of the microcontroller and the keyboard interface.
Overall, the AT Keyboard Interface and the corresponding decoding process enable effective user input management in various electronic systems, demonstrating the integration of hardware and software in embedded applications.Details the AT Keyboard Interface and AT Keyboard Protocols. Includes an example Keyboard to ASCII decoder using a 68HC705J1A MCU.. 🔗 External reference