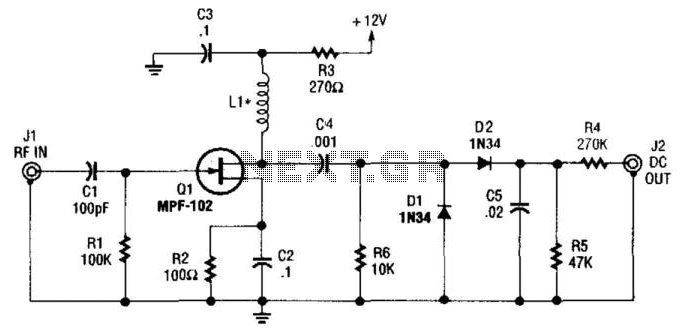
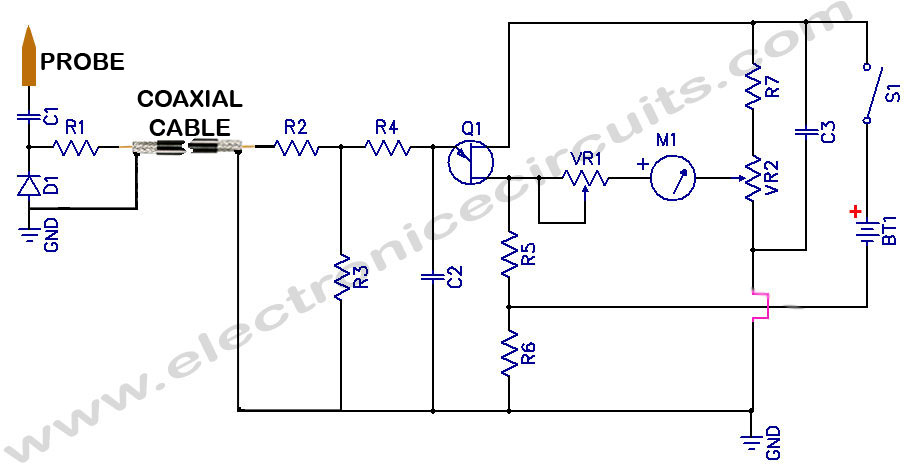
Lambda Probe Readout For Carburettor Tuning
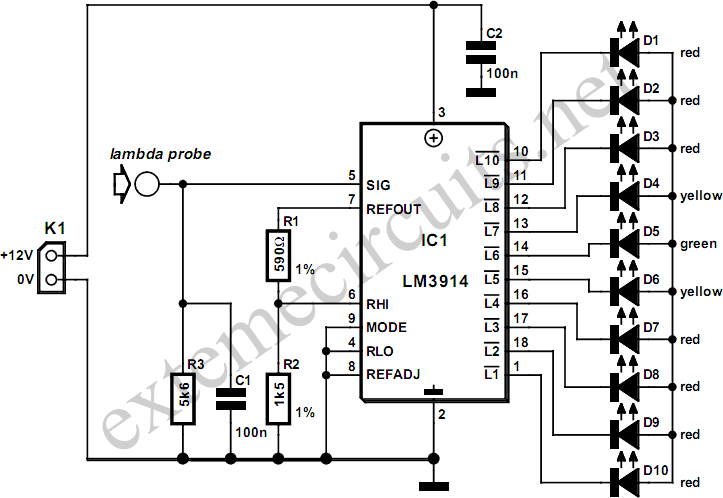
A lambda probe, also known as an oxygen sensor, is typically located on the exhaust system of most vehicles that operate on unleaded fuel. It functions effectively once it has reached its normal operating temperature.
A lambda probe is a critical component in modern automotive exhaust systems, playing an essential role in optimizing engine performance and reducing emissions. The sensor measures the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing real-time feedback to the engine control unit (ECU). This data is vital for adjusting the air-fuel mixture, ensuring that the engine runs efficiently and within the optimal stoichiometric ratio.
The lambda probe operates based on the principle of electrochemical sensing. It consists of a zirconia ceramic element that generates a voltage proportional to the difference in oxygen levels between the exhaust gases and the ambient air. This voltage signal is then transmitted to the ECU, which interprets the information to make necessary adjustments in fuel injection and ignition timing.
There are typically two types of lambda probes: narrowband and wideband. Narrowband sensors provide a simple on-off signal indicating whether the mixture is rich or lean, while wideband sensors offer a more precise measurement of the air-fuel ratio across a broader range, allowing for finer control of the combustion process.
The placement of the lambda probe is crucial for accurate measurements; it is usually installed in the exhaust manifold or downpipe, before the catalytic converter. In vehicles equipped with multiple exhaust banks, multiple lambda probes may be utilized to monitor each bank separately, ensuring balanced performance and emissions control.
Regular maintenance and monitoring of the lambda probe's performance are essential, as a malfunctioning sensor can lead to increased fuel consumption, reduced engine efficiency, and higher emissions. Common signs of a failing lambda probe include poor fuel economy, rough engine idle, and the illumination of the check engine light.A lambda probe (or oxygen sensor) can be found on the exhaust system of most cars running on unleaded fuel. Having reached its normal operating temperatur.. 🔗 External reference
A lambda probe is a critical component in modern automotive exhaust systems, playing an essential role in optimizing engine performance and reducing emissions. The sensor measures the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing real-time feedback to the engine control unit (ECU). This data is vital for adjusting the air-fuel mixture, ensuring that the engine runs efficiently and within the optimal stoichiometric ratio.
The lambda probe operates based on the principle of electrochemical sensing. It consists of a zirconia ceramic element that generates a voltage proportional to the difference in oxygen levels between the exhaust gases and the ambient air. This voltage signal is then transmitted to the ECU, which interprets the information to make necessary adjustments in fuel injection and ignition timing.
There are typically two types of lambda probes: narrowband and wideband. Narrowband sensors provide a simple on-off signal indicating whether the mixture is rich or lean, while wideband sensors offer a more precise measurement of the air-fuel ratio across a broader range, allowing for finer control of the combustion process.
The placement of the lambda probe is crucial for accurate measurements; it is usually installed in the exhaust manifold or downpipe, before the catalytic converter. In vehicles equipped with multiple exhaust banks, multiple lambda probes may be utilized to monitor each bank separately, ensuring balanced performance and emissions control.
Regular maintenance and monitoring of the lambda probe's performance are essential, as a malfunctioning sensor can lead to increased fuel consumption, reduced engine efficiency, and higher emissions. Common signs of a failing lambda probe include poor fuel economy, rough engine idle, and the illumination of the check engine light.A lambda probe (or oxygen sensor) can be found on the exhaust system of most cars running on unleaded fuel. Having reached its normal operating temperatur.. 🔗 External reference