Laser Activated Switch
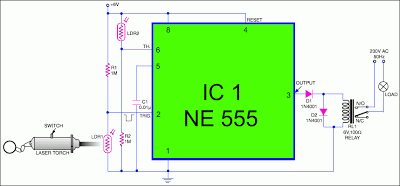
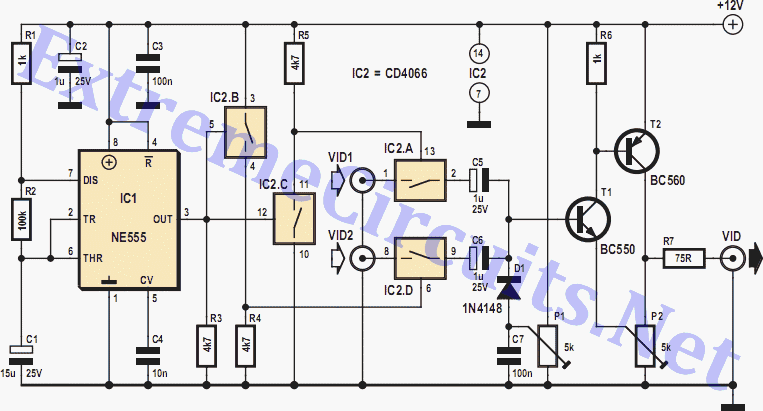
This circuit is designed around a 555 timer and utilizes very few components. Its simplicity allows even novices to construct and use it as a control device. A laser pointer, widely available in the market, can be employed to operate this circuit. It has been tested under operational conditions from a distance of 500 meters and has been found to work satisfactorily, with potential for control from even longer distances. Aiming the laser beam directly at the light-dependent resistor (LDR) presents a practical challenge. The circuit is particularly useful for turning a fan on or off at night without the need to get out of bed. Additionally, it can be used to control various other devices, such as radios or music systems. However, the circuit is limited to functioning in dark or low-light environments. By directing the laser beam onto LDR1, the connected device can be activated via a relay, while directing the beam onto LDR2 will deactivate the device. The timer is configured to operate in bistable mode. Laser pointers are available for less than Rs 30, and the total cost of the circuit is under Rs 25.
This circuit utilizes the popular 555 timer IC, which is known for its versatility and ease of use. In this particular application, the 555 timer is configured in bistable mode, allowing it to switch between two stable states based on input signals from the laser pointers. The circuit comprises two light-dependent resistors (LDRs), which serve as sensors to detect the laser beam. When the laser beam is directed onto LDR1, the resistance of LDR1 decreases, triggering the timer to activate the relay, which in turn powers the connected device. Conversely, when the laser beam is aimed at LDR2, the resistance of LDR2 decreases, causing the timer to deactivate the relay and turn off the device.
The operational range of 500 meters suggests that the circuit is suitable for various applications where remote control is desired, such as in home automation or remote device management. However, the requirement for low-light conditions is a critical design consideration, as the LDRs rely on ambient light levels to function correctly. In bright environments, the effectiveness of the LDRs may be compromised, leading to unreliable operation.
The circuit's simplicity is a significant advantage, making it accessible to hobbyists and individuals with basic electronics knowledge. The low cost of the components, with the circuit totaling under Rs 25, makes it an economical solution for remote control applications. Overall, this circuit exemplifies an effective and straightforward approach to utilizing a laser pointer for remote device control, with practical applications in everyday scenarios.This circuit is built around a 555 timer using very few components. Since the circuit is very simple, even a novice can easily build it and use it as a controlling device. A laser pointer, now easily available in the market, can be used to operate this device. This circuit has been tested in operational conditions from a distance of 500 metres and was found to work satisfactorily, though it can be controlled from still longer distances. Aiming the laser beam exactly on to the LDR is a practical problem. The circuit is very useful in switching on/off a fan at night without getting off the bed. It can also be used for controlling a variety of other devices like radio or music system. The limitation is that the circuit is operational only in dark or dull-lit environments. By focusing the laser beam on LDR1 the connected gadget can be activated through the relay, whereas by focusing laser beam on LDR2 we can switch off the gadget. The timer is configured to operate in bistable mode. The laser pointers are available for less than Rs 30 in the market. The cost of the actual circuit is less than Rs 25. 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes the popular 555 timer IC, which is known for its versatility and ease of use. In this particular application, the 555 timer is configured in bistable mode, allowing it to switch between two stable states based on input signals from the laser pointers. The circuit comprises two light-dependent resistors (LDRs), which serve as sensors to detect the laser beam. When the laser beam is directed onto LDR1, the resistance of LDR1 decreases, triggering the timer to activate the relay, which in turn powers the connected device. Conversely, when the laser beam is aimed at LDR2, the resistance of LDR2 decreases, causing the timer to deactivate the relay and turn off the device.
The operational range of 500 meters suggests that the circuit is suitable for various applications where remote control is desired, such as in home automation or remote device management. However, the requirement for low-light conditions is a critical design consideration, as the LDRs rely on ambient light levels to function correctly. In bright environments, the effectiveness of the LDRs may be compromised, leading to unreliable operation.
The circuit's simplicity is a significant advantage, making it accessible to hobbyists and individuals with basic electronics knowledge. The low cost of the components, with the circuit totaling under Rs 25, makes it an economical solution for remote control applications. Overall, this circuit exemplifies an effective and straightforward approach to utilizing a laser pointer for remote device control, with practical applications in everyday scenarios.This circuit is built around a 555 timer using very few components. Since the circuit is very simple, even a novice can easily build it and use it as a controlling device. A laser pointer, now easily available in the market, can be used to operate this device. This circuit has been tested in operational conditions from a distance of 500 metres and was found to work satisfactorily, though it can be controlled from still longer distances. Aiming the laser beam exactly on to the LDR is a practical problem. The circuit is very useful in switching on/off a fan at night without getting off the bed. It can also be used for controlling a variety of other devices like radio or music system. The limitation is that the circuit is operational only in dark or dull-lit environments. By focusing the laser beam on LDR1 the connected gadget can be activated through the relay, whereas by focusing laser beam on LDR2 we can switch off the gadget. The timer is configured to operate in bistable mode. The laser pointers are available for less than Rs 30 in the market. The cost of the actual circuit is less than Rs 25. 🔗 External reference