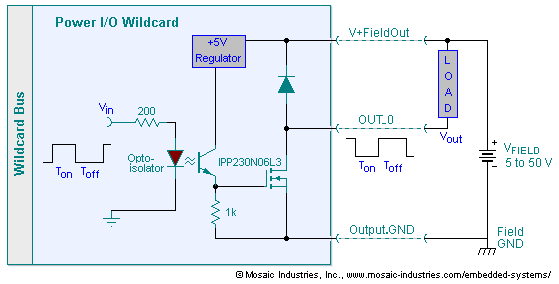
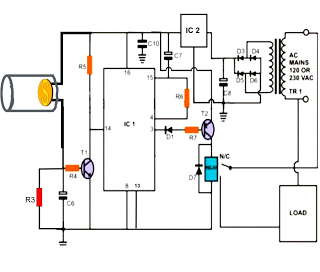
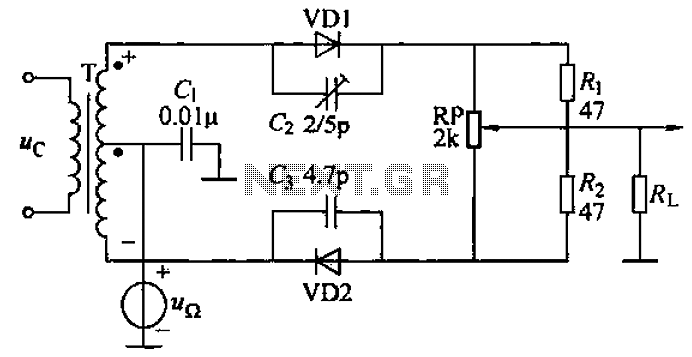
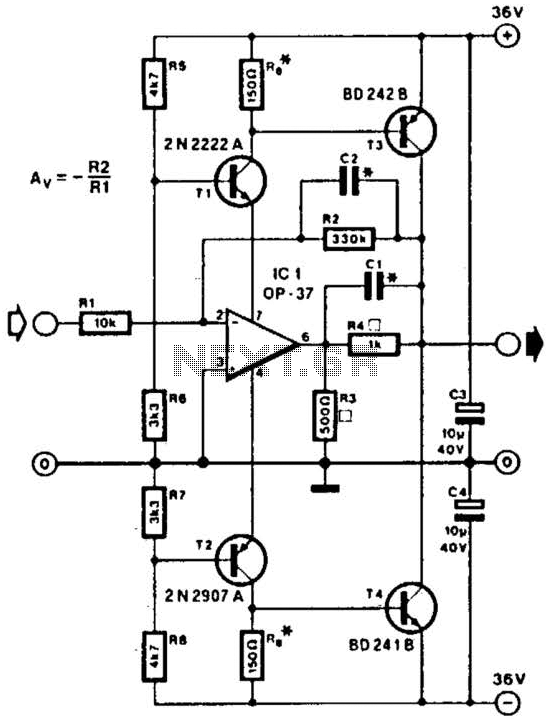
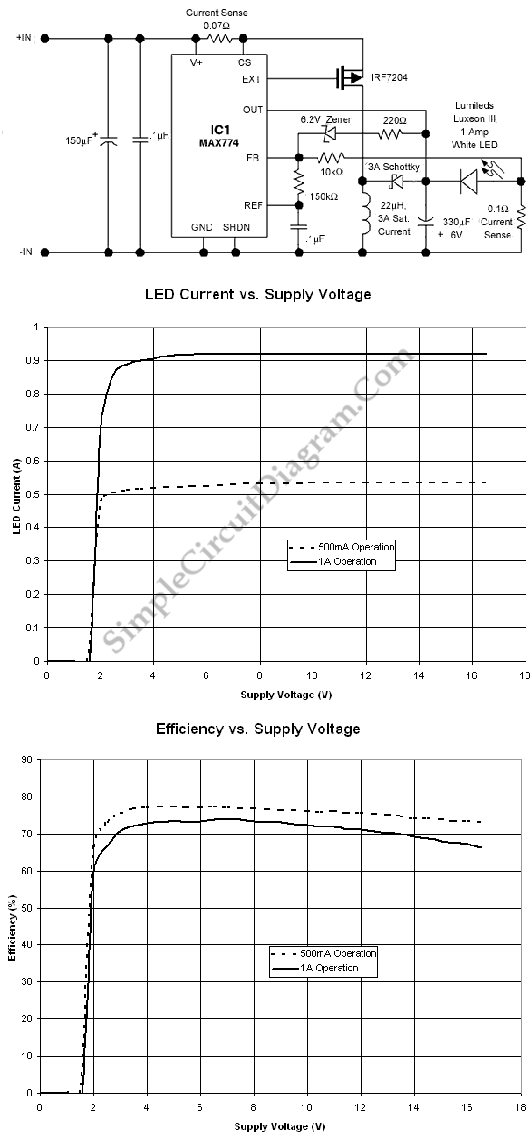
Laser Diode Driver
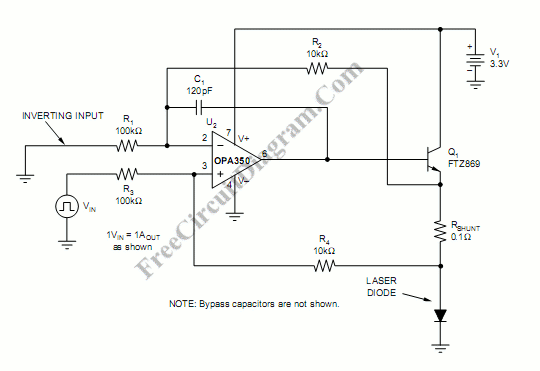
A laser diode driver can be implemented using a voltage-controlled current source. This simple linear laser diode driver provides a cleaner drive current than other methods.
A laser diode driver is an essential component in laser systems, responsible for supplying the appropriate current to the laser diode while ensuring stability and precision. The voltage-controlled current source (VCCS) configuration is particularly advantageous due to its ability to maintain a constant current output despite variations in load or supply voltage, which is critical for the performance and longevity of the laser diode.
In a typical VCCS laser diode driver circuit, the input voltage is applied to a control element, such as an operational amplifier, which regulates the output current flowing through the laser diode. The operational amplifier compares the feedback from a sense resistor, which is placed in series with the diode, to the reference voltage set by the user. This feedback loop allows for precise control over the current, minimizing fluctuations that could lead to undesirable effects such as mode hopping or thermal runaway.
The circuit may also incorporate additional features such as temperature compensation, which adjusts the output current based on the diode's operating temperature. This is crucial, as laser diodes are sensitive to temperature changes that can affect their performance and efficiency.
Furthermore, protection mechanisms such as current limiting and over-temperature shutdown can be integrated into the design to safeguard the laser diode from damage due to excessive current or heat. These enhancements contribute to the reliability and robustness of the laser driver, making it suitable for various applications, including telecommunications, medical devices, and industrial laser systems.
Overall, the use of a voltage-controlled current source in a linear laser diode driver results in improved current stability, reduced noise, and enhanced performance, making it a preferred choice for high-precision laser applications.A? laser diode driver can be implemented using voltage-controlled current source.? This simple? linear laser diode driver gives cleaner drive current than a. 🔗 External reference
A laser diode driver is an essential component in laser systems, responsible for supplying the appropriate current to the laser diode while ensuring stability and precision. The voltage-controlled current source (VCCS) configuration is particularly advantageous due to its ability to maintain a constant current output despite variations in load or supply voltage, which is critical for the performance and longevity of the laser diode.
In a typical VCCS laser diode driver circuit, the input voltage is applied to a control element, such as an operational amplifier, which regulates the output current flowing through the laser diode. The operational amplifier compares the feedback from a sense resistor, which is placed in series with the diode, to the reference voltage set by the user. This feedback loop allows for precise control over the current, minimizing fluctuations that could lead to undesirable effects such as mode hopping or thermal runaway.
The circuit may also incorporate additional features such as temperature compensation, which adjusts the output current based on the diode's operating temperature. This is crucial, as laser diodes are sensitive to temperature changes that can affect their performance and efficiency.
Furthermore, protection mechanisms such as current limiting and over-temperature shutdown can be integrated into the design to safeguard the laser diode from damage due to excessive current or heat. These enhancements contribute to the reliability and robustness of the laser driver, making it suitable for various applications, including telecommunications, medical devices, and industrial laser systems.
Overall, the use of a voltage-controlled current source in a linear laser diode driver results in improved current stability, reduced noise, and enhanced performance, making it a preferred choice for high-precision laser applications.A? laser diode driver can be implemented using voltage-controlled current source.? This simple? linear laser diode driver gives cleaner drive current than a. 🔗 External reference