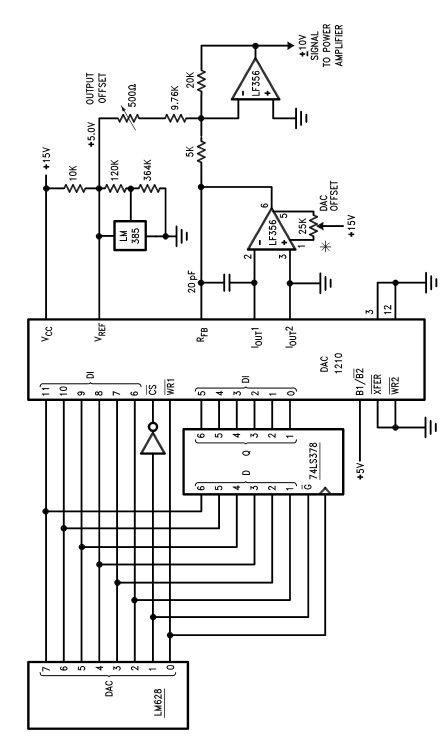
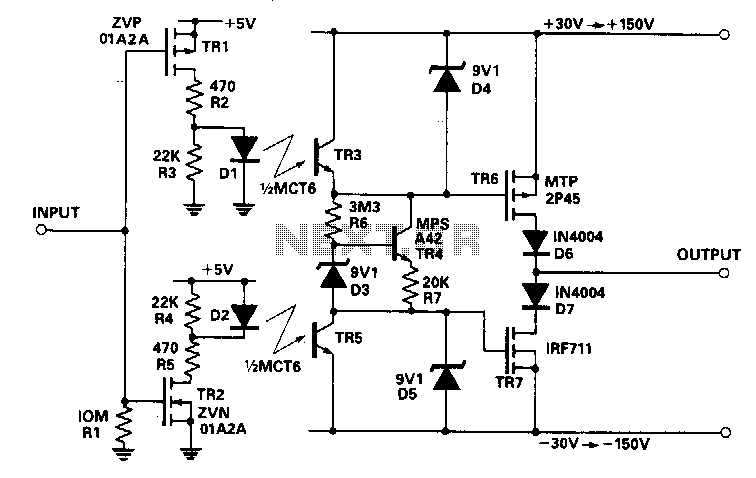
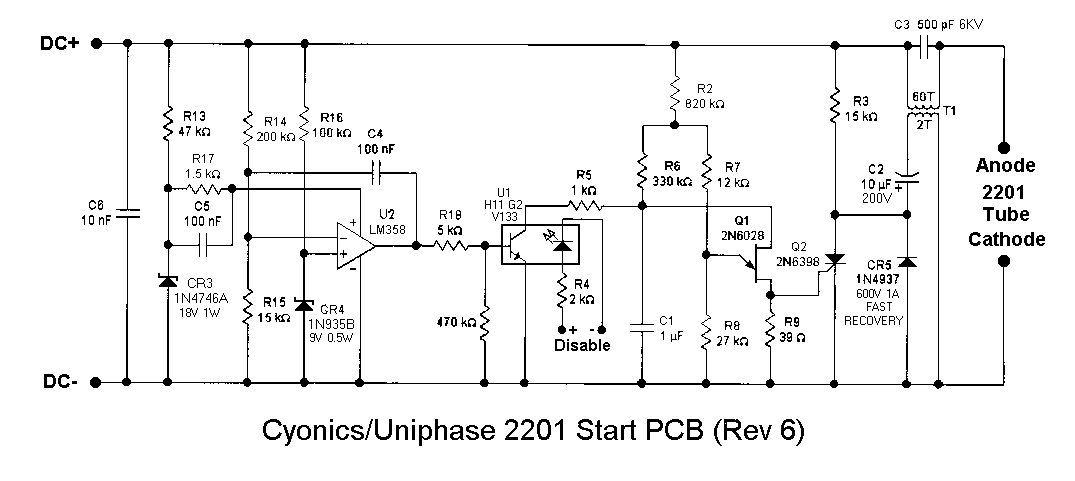
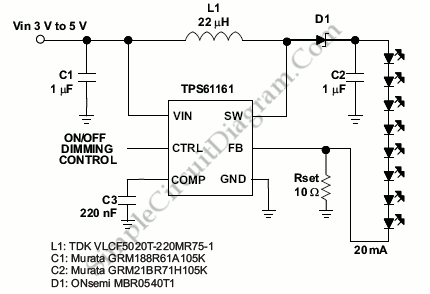
Laser Diode Driver
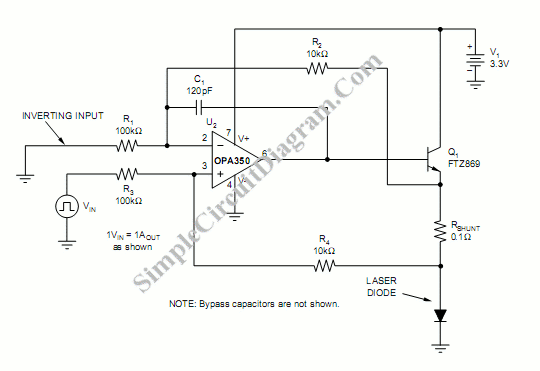
A voltage-controlled current source can be utilized to implement a laser diode driver. In comparison to switched (PWM) drivers, this simple linear laser diode driver offers distinct advantages.
A voltage-controlled current source (VCCS) is a crucial component in driving laser diodes, as it allows for precise control of the current flowing through the diode. The operation of a laser diode is highly sensitive to current variations; thus, maintaining a constant current is essential for optimal performance and longevity of the device.
In a linear laser diode driver circuit, the VCCS can be designed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) in conjunction with precision resistors. The op-amp can be configured to monitor the voltage across a sense resistor, which is placed in series with the laser diode. By adjusting the input voltage to the op-amp, the output current can be regulated, ensuring that the laser diode receives the required current for its operation.
The advantages of using a linear driver over a PWM driver include reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) and a smoother output current, which can lead to improved beam quality and reduced noise in laser applications. However, linear drivers may be less efficient than PWM drivers, particularly at higher power levels, as they dissipate excess energy as heat.
In practical applications, thermal management becomes an important consideration for linear laser diode drivers. Heatsinks or active cooling methods may be employed to ensure that the driver remains within safe operating temperatures, thereby enhancing reliability and performance.
Overall, the implementation of a voltage-controlled current source for laser diode driving is a robust solution that can provide precise current control and improved performance in various optical applications.We can use a voltage-controlled current source to implement a laser diode driver. Compared with a a Switched (PWM) drivers, this simple linear laser diode.. 🔗 External reference
A voltage-controlled current source (VCCS) is a crucial component in driving laser diodes, as it allows for precise control of the current flowing through the diode. The operation of a laser diode is highly sensitive to current variations; thus, maintaining a constant current is essential for optimal performance and longevity of the device.
In a linear laser diode driver circuit, the VCCS can be designed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) in conjunction with precision resistors. The op-amp can be configured to monitor the voltage across a sense resistor, which is placed in series with the laser diode. By adjusting the input voltage to the op-amp, the output current can be regulated, ensuring that the laser diode receives the required current for its operation.
The advantages of using a linear driver over a PWM driver include reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) and a smoother output current, which can lead to improved beam quality and reduced noise in laser applications. However, linear drivers may be less efficient than PWM drivers, particularly at higher power levels, as they dissipate excess energy as heat.
In practical applications, thermal management becomes an important consideration for linear laser diode drivers. Heatsinks or active cooling methods may be employed to ensure that the driver remains within safe operating temperatures, thereby enhancing reliability and performance.
Overall, the implementation of a voltage-controlled current source for laser diode driving is a robust solution that can provide precise current control and improved performance in various optical applications.We can use a voltage-controlled current source to implement a laser diode driver. Compared with a a Switched (PWM) drivers, this simple linear laser diode.. 🔗 External reference