Piezo Buzzer driver
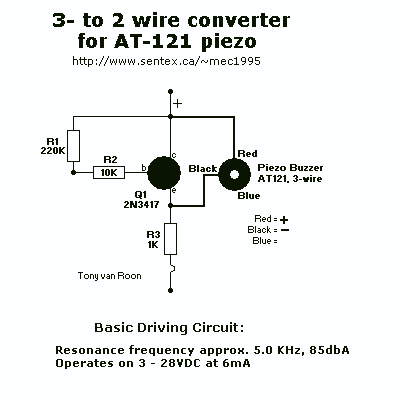
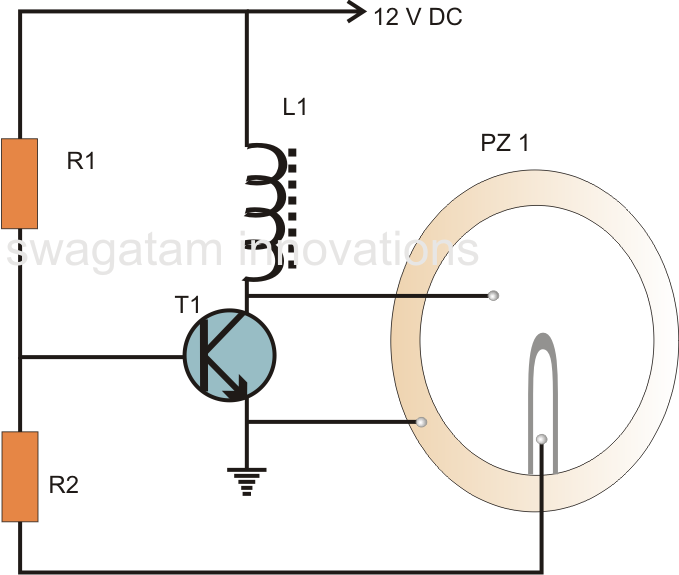
This is a basic Buzzer driver circuit with resonance frequency approximately 5 kHz, 85 dBA. It operates on 3 to 28 V DC at 6 mA.
The basic buzzer driver circuit is designed to generate an audible tone by driving a piezoelectric buzzer. The circuit operates effectively within a voltage range of 3 to 28 volts DC, making it versatile for various applications, including alarms, notifications, and signaling devices. The output sound pressure level of 85 dBA at the resonance frequency of approximately 5 kHz ensures that the buzzer is loud enough for most environments.
The core components of the circuit typically include a transistor, which acts as a switch to control the power delivered to the buzzer. When a control signal is applied to the base of the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, energizing the buzzer. The choice of transistor must accommodate the required current of 6 mA and the voltage range specified.
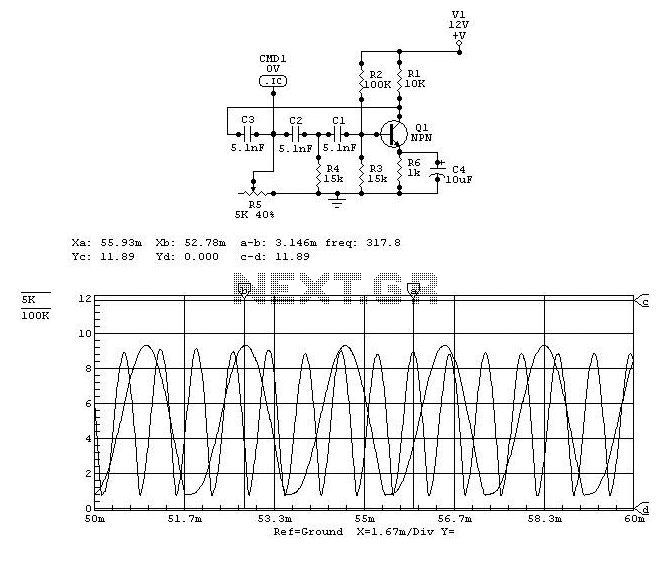
To achieve the desired resonance frequency, the circuit may incorporate passive components such as resistors and capacitors. These components can be arranged in an oscillator configuration to produce a square wave signal, which is essential for driving the piezoelectric buzzer at its optimal frequency. The selection of the capacitor value will influence the frequency of oscillation, enabling fine-tuning of the output tone.
In summary, this buzzer driver circuit is a straightforward yet effective solution for generating audible alerts, leveraging a combination of transistors and passive components to achieve the desired frequency and sound output. The design's flexibility in voltage operation makes it suitable for a wide range of electronic projects.This is a basic Buzzer driver circuit with resonance frequncy approximatly 5 Khz, 85 dBA. It operates on 3 to 28 v DC at 6mA. 🔗 External reference
The basic buzzer driver circuit is designed to generate an audible tone by driving a piezoelectric buzzer. The circuit operates effectively within a voltage range of 3 to 28 volts DC, making it versatile for various applications, including alarms, notifications, and signaling devices. The output sound pressure level of 85 dBA at the resonance frequency of approximately 5 kHz ensures that the buzzer is loud enough for most environments.
The core components of the circuit typically include a transistor, which acts as a switch to control the power delivered to the buzzer. When a control signal is applied to the base of the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, energizing the buzzer. The choice of transistor must accommodate the required current of 6 mA and the voltage range specified.
To achieve the desired resonance frequency, the circuit may incorporate passive components such as resistors and capacitors. These components can be arranged in an oscillator configuration to produce a square wave signal, which is essential for driving the piezoelectric buzzer at its optimal frequency. The selection of the capacitor value will influence the frequency of oscillation, enabling fine-tuning of the output tone.
In summary, this buzzer driver circuit is a straightforward yet effective solution for generating audible alerts, leveraging a combination of transistors and passive components to achieve the desired frequency and sound output. The design's flexibility in voltage operation makes it suitable for a wide range of electronic projects.This is a basic Buzzer driver circuit with resonance frequncy approximatly 5 Khz, 85 dBA. It operates on 3 to 28 v DC at 6mA. 🔗 External reference