Laser Track Detection
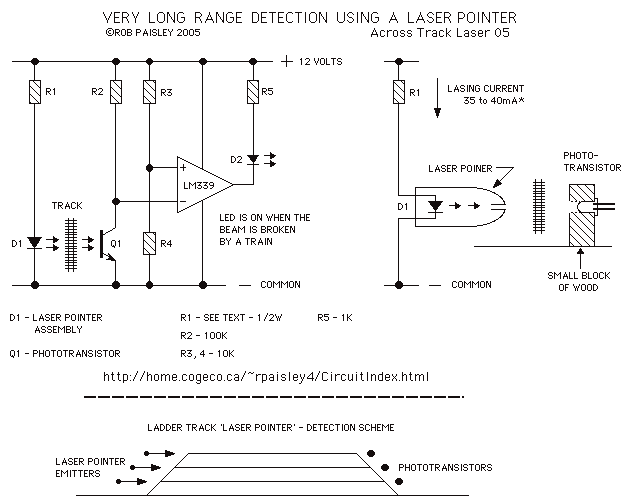
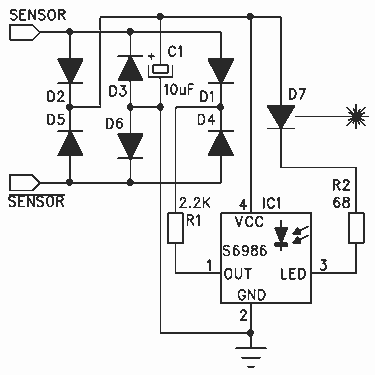
The following diagram shows the basic laser pointer circuit. It is identical to the infrared circuit except that the infrared LEDs have been replaced by the laser pointer unit. Due to the long range of these devices, this detector method can easily span great distances and could be used to detect trains in a long section of straight track such as in a ladder yard or across the throat of a very wide yard. More: Laser pointers are not designed for this type of application and careful selection of R1 is required. Testing should be carried out to determine the best resistance value for a particular pointer. It is best to start with a high resistance for R1, 50.
The basic laser pointer circuit consists of several key components that work together to produce a focused beam of light suitable for various applications, including distance detection. The primary component is the laser pointer unit itself, which emits a coherent light beam when powered. This circuit typically includes a power source, a resistor (R1), and the laser pointer.
The power source can be a battery or any suitable DC supply that meets the voltage requirements of the laser pointer. The resistor R1 is critical for limiting the current flowing through the laser pointer to prevent damage. As noted, it is advisable to start with a high resistance value, such as 50 ohms, and adjust based on testing to find the optimal resistance that allows the laser to operate efficiently without overheating.
In applications where the laser pointer is used for detection over long distances, the circuit may also incorporate a photodetector or a photodiode that can sense the laser light. This component will convert the light signal back into an electrical signal, which can then be processed to determine the presence of an object or train within the detection range. The distance and accuracy of detection can be influenced by the alignment of the laser pointer and the photodetector, as well as environmental factors such as ambient light conditions.
For practical implementation, it is essential to ensure that the circuit connections are secure and that the components are rated for the expected operational conditions. Proper testing and calibration should be performed to validate the circuit’s performance in the intended application.The following diagram shows the basic laser pointer circuit. It is identical to the infrared circuit except that the infrared LED`s have been replaced by the laser pointer unit. Due to the long range of these devices this detector method can easily span great distances and could be used to detect trains in a long section of straight track such as in a lader yard or across the throat of a very wide yard.
Laser pointers are not designed for this type of application and careful selection of R1 is required. testing should be carried out to determine the best resistance value for a particular pointer. It is best to start with a high resistance for R1, 50 🔗 External reference
The basic laser pointer circuit consists of several key components that work together to produce a focused beam of light suitable for various applications, including distance detection. The primary component is the laser pointer unit itself, which emits a coherent light beam when powered. This circuit typically includes a power source, a resistor (R1), and the laser pointer.
The power source can be a battery or any suitable DC supply that meets the voltage requirements of the laser pointer. The resistor R1 is critical for limiting the current flowing through the laser pointer to prevent damage. As noted, it is advisable to start with a high resistance value, such as 50 ohms, and adjust based on testing to find the optimal resistance that allows the laser to operate efficiently without overheating.
In applications where the laser pointer is used for detection over long distances, the circuit may also incorporate a photodetector or a photodiode that can sense the laser light. This component will convert the light signal back into an electrical signal, which can then be processed to determine the presence of an object or train within the detection range. The distance and accuracy of detection can be influenced by the alignment of the laser pointer and the photodetector, as well as environmental factors such as ambient light conditions.
For practical implementation, it is essential to ensure that the circuit connections are secure and that the components are rated for the expected operational conditions. Proper testing and calibration should be performed to validate the circuit’s performance in the intended application.The following diagram shows the basic laser pointer circuit. It is identical to the infrared circuit except that the infrared LED`s have been replaced by the laser pointer unit. Due to the long range of these devices this detector method can easily span great distances and could be used to detect trains in a long section of straight track such as in a lader yard or across the throat of a very wide yard.
Laser pointers are not designed for this type of application and careful selection of R1 is required. testing should be carried out to determine the best resistance value for a particular pointer. It is best to start with a high resistance for R1, 50 🔗 External reference