lcd thermometer circuit with lm35
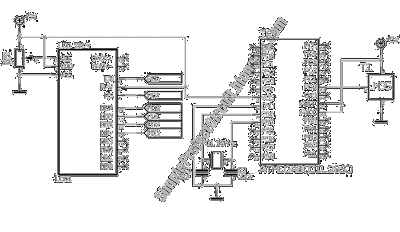
The LM35 from National Semiconductor is a precision centigrade temperature sensor that provides an analog output voltage. It operates within a temperature range of -55°C to +150°C and has an accuracy of ±0.5°C. The output voltage corresponds to 10mV per degree Celsius. This output voltage is processed by the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) of the ATmega8 microcontroller, and the temperature is displayed on an LCD module. In this example, the thermometer is designed to measure temperatures from 0°C to 40°C with a resolution of 0.5°C. For Fahrenheit readings, the LM34 sensor can be utilized. The software for this project is developed using BASCOM AVR, which includes built-in commands for reading the ADC port of an AVR microcontroller. The temperature readings are presented on the LCD module as discrete values and in a bar graph format. The ATmega8 features an A/D converter capable of producing 210 = 1024 discrete values. With a 5V supply, the resolution is calculated as 5000mV/1024 = 4.8mV. Given that the LM35 outputs 10mV/°C, the resolution of the thermometer is approximately 0.5°C. The LCD module has 20 columns, where each column represents a temperature increment of 2°C on the scale from 0°C to 40°C. [Circuit's Source: National Semiconductor, Inc].
The LM35 temperature sensor is a critical component in precision temperature measurement applications. It operates based on a linear output voltage that changes with temperature, providing a simple interface for analog measurements. The sensor’s output of 10mV per degree Celsius allows for straightforward calculations when interfaced with an ADC, such as that found in the ATmega8 microcontroller.
The ATmega8 microcontroller is equipped with an integrated 10-bit ADC, which translates the analog voltage from the LM35 into digital values. This conversion process allows for a range of 0 to 1023 corresponding to the input voltage levels. With a reference voltage of 5V, each step of the ADC corresponds to approximately 4.88mV. This resolution is sufficient for the LM35’s output, ensuring that temperature changes of 0.5°C can be accurately represented.
In the setup, the temperature readings are displayed on an LCD module, which is configured to show both numerical values and a bar graph for intuitive visualization. The LCD's 20 columns allow for a clear representation of the temperature range from 0°C to 40°C, with each column indicating a 2°C increment. This visual aid enhances user experience by providing immediate feedback on temperature changes.
For applications requiring Fahrenheit readings, the LM34 sensor can be employed as an alternative, providing a similar output characteristic but calibrated for Fahrenheit scales. The BASCOM AVR programming environment simplifies the development of the control software, allowing for efficient reading and processing of the ADC values, and managing the display output on the LCD module.
Overall, this temperature measurement circuit exemplifies a practical application of analog sensors, microcontroller interfacing, and user-friendly display technology, suitable for various temperature monitoring applications.The LM35 of National Semiconductors that is used in this project is a precision centigrade temperature sensor, which has an analog output voltage. It has a range of -55 C to +150 C and an accuracy of ±0. 5 C. The output voltage is 10mV/ C. The output voltage is converted by the AD convertor of the AT Mega8. The temperature is displayed on an LCD module. This is the figure of the circuit. In this example the thermometer has a range of 0 C to 40 C and a resolution of 0. 5 C. If you want to have a read out in Fahrenheit you can use the LM34. The software for this project is written in BASCOM AVR. The BASCOM AVR compiler has build in commands for reading out the ADC port of a AVR microcontroller. The result is displayed on a LCD module in a discrete value of the temperature and in a bar-graph. The AT Mega8 has a A/D converter which can give an output of 210 = 1024 discrete values. When a 5V supply is used you have a resolution of 5000mV/1024 = 4. 8mV. Because the LM35 has a output of 10mV/C the resolution of the thermometer is 10mV/4. 8mV ~ 0. 5 C. The LCD module has 20 columns. In the scale of 0 C to 40 C every column represents 2 C. [Circuit`s Source: National Semiconductor, Inc]. 🔗 External reference
The LM35 temperature sensor is a critical component in precision temperature measurement applications. It operates based on a linear output voltage that changes with temperature, providing a simple interface for analog measurements. The sensor’s output of 10mV per degree Celsius allows for straightforward calculations when interfaced with an ADC, such as that found in the ATmega8 microcontroller.
The ATmega8 microcontroller is equipped with an integrated 10-bit ADC, which translates the analog voltage from the LM35 into digital values. This conversion process allows for a range of 0 to 1023 corresponding to the input voltage levels. With a reference voltage of 5V, each step of the ADC corresponds to approximately 4.88mV. This resolution is sufficient for the LM35’s output, ensuring that temperature changes of 0.5°C can be accurately represented.
In the setup, the temperature readings are displayed on an LCD module, which is configured to show both numerical values and a bar graph for intuitive visualization. The LCD's 20 columns allow for a clear representation of the temperature range from 0°C to 40°C, with each column indicating a 2°C increment. This visual aid enhances user experience by providing immediate feedback on temperature changes.
For applications requiring Fahrenheit readings, the LM34 sensor can be employed as an alternative, providing a similar output characteristic but calibrated for Fahrenheit scales. The BASCOM AVR programming environment simplifies the development of the control software, allowing for efficient reading and processing of the ADC values, and managing the display output on the LCD module.
Overall, this temperature measurement circuit exemplifies a practical application of analog sensors, microcontroller interfacing, and user-friendly display technology, suitable for various temperature monitoring applications.The LM35 of National Semiconductors that is used in this project is a precision centigrade temperature sensor, which has an analog output voltage. It has a range of -55 C to +150 C and an accuracy of ±0. 5 C. The output voltage is 10mV/ C. The output voltage is converted by the AD convertor of the AT Mega8. The temperature is displayed on an LCD module. This is the figure of the circuit. In this example the thermometer has a range of 0 C to 40 C and a resolution of 0. 5 C. If you want to have a read out in Fahrenheit you can use the LM34. The software for this project is written in BASCOM AVR. The BASCOM AVR compiler has build in commands for reading out the ADC port of a AVR microcontroller. The result is displayed on a LCD module in a discrete value of the temperature and in a bar-graph. The AT Mega8 has a A/D converter which can give an output of 210 = 1024 discrete values. When a 5V supply is used you have a resolution of 5000mV/1024 = 4. 8mV. Because the LM35 has a output of 10mV/C the resolution of the thermometer is 10mV/4. 8mV ~ 0. 5 C. The LCD module has 20 columns. In the scale of 0 C to 40 C every column represents 2 C. [Circuit`s Source: National Semiconductor, Inc]. 🔗 External reference