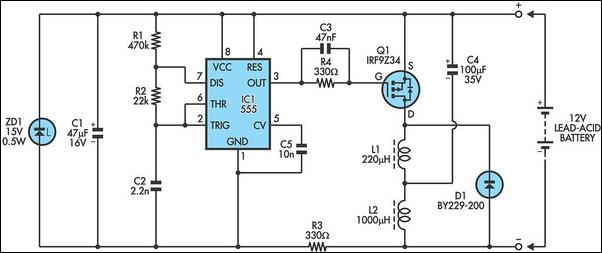
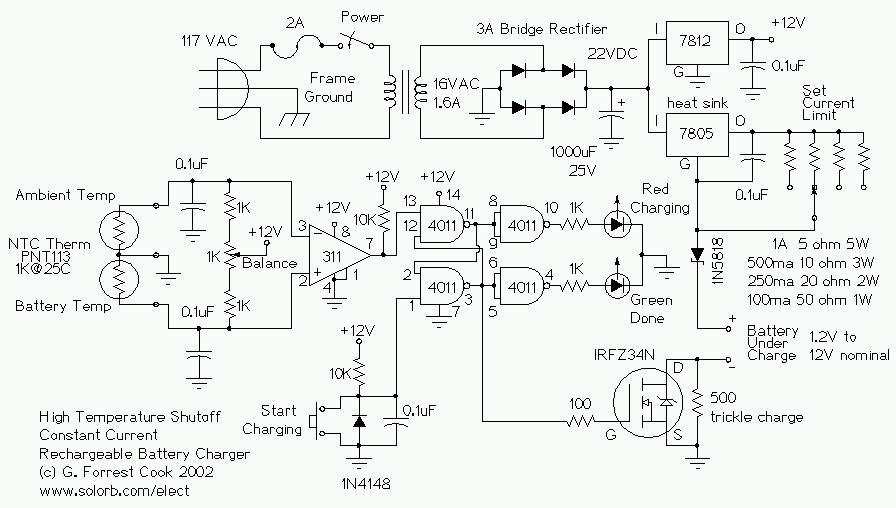
lead acid battery charger with current limit
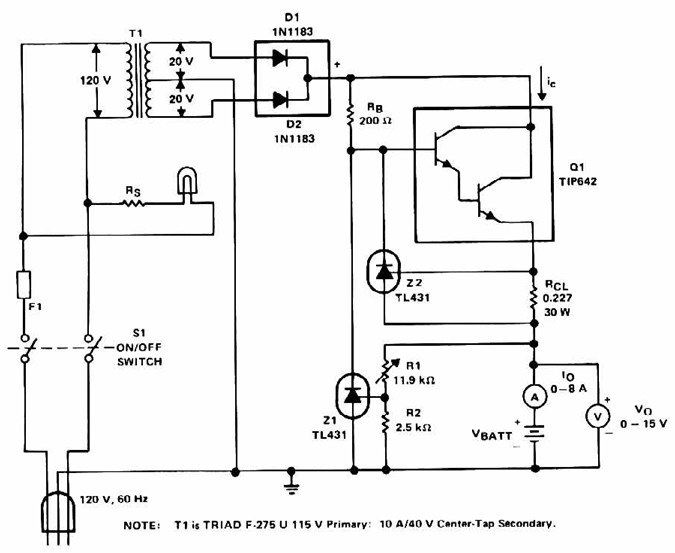
Lead Acid Battery Charger with current limit power supply. Refer to the specified page for an explanation of the related circuit diagram.
The lead-acid battery charger with a current limit power supply is designed to safely charge lead-acid batteries while preventing overcurrent conditions that could lead to damage. The circuit typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, voltage regulator, and current limiting components.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. This AC voltage is then converted to DC using a rectifier, which can be either a full-wave or half-wave rectifier configuration, depending on the design requirements.
Following the rectification process, a smoothing capacitor is employed to filter out the ripple voltage, providing a more stable DC output. The voltage regulator is crucial in maintaining a constant output voltage, which is essential for the safe charging of lead-acid batteries. Common voltage regulators include linear regulators or switching regulators, depending on efficiency and thermal management considerations.
To implement current limiting, a resistor or a dedicated current limiting circuit is integrated into the design. This component ensures that the charging current does not exceed a predetermined threshold, protecting the battery from excessive charging currents that could result in overheating or damage.
The circuit may also include additional features such as LEDs for status indication, fuses for overcurrent protection, and thermal shutdown mechanisms to enhance safety and reliability. Overall, this charger design emphasizes efficiency, safety, and adherence to the charging characteristics of lead-acid batteries.Lead Acid Battery Charger with Current Limit power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference
The lead-acid battery charger with a current limit power supply is designed to safely charge lead-acid batteries while preventing overcurrent conditions that could lead to damage. The circuit typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, voltage regulator, and current limiting components.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. This AC voltage is then converted to DC using a rectifier, which can be either a full-wave or half-wave rectifier configuration, depending on the design requirements.
Following the rectification process, a smoothing capacitor is employed to filter out the ripple voltage, providing a more stable DC output. The voltage regulator is crucial in maintaining a constant output voltage, which is essential for the safe charging of lead-acid batteries. Common voltage regulators include linear regulators or switching regulators, depending on efficiency and thermal management considerations.
To implement current limiting, a resistor or a dedicated current limiting circuit is integrated into the design. This component ensures that the charging current does not exceed a predetermined threshold, protecting the battery from excessive charging currents that could result in overheating or damage.
The circuit may also include additional features such as LEDs for status indication, fuses for overcurrent protection, and thermal shutdown mechanisms to enhance safety and reliability. Overall, this charger design emphasizes efficiency, safety, and adherence to the charging characteristics of lead-acid batteries.Lead Acid Battery Charger with Current Limit power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference