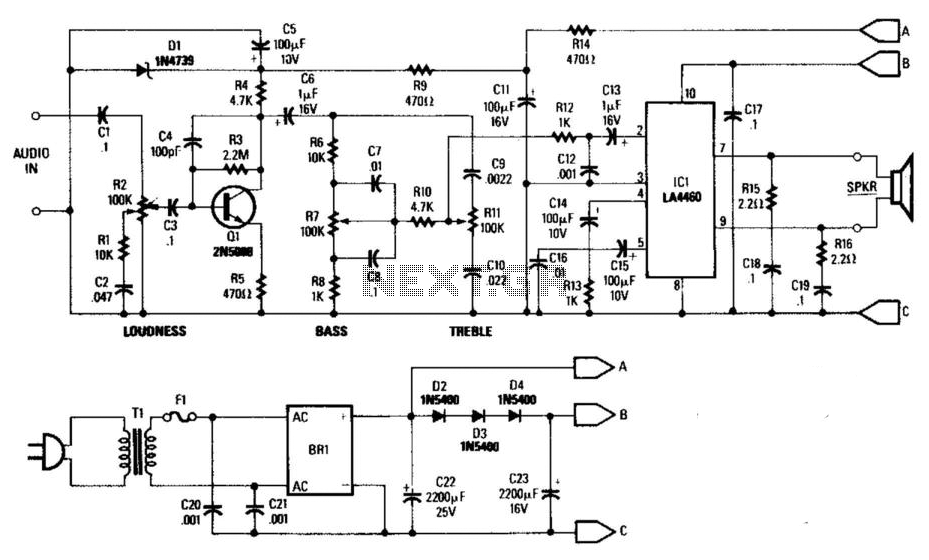
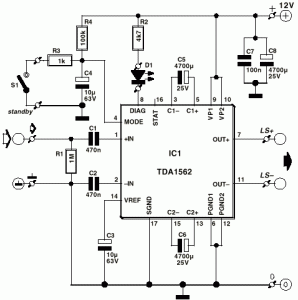
Audio Shunt Noise Limiter
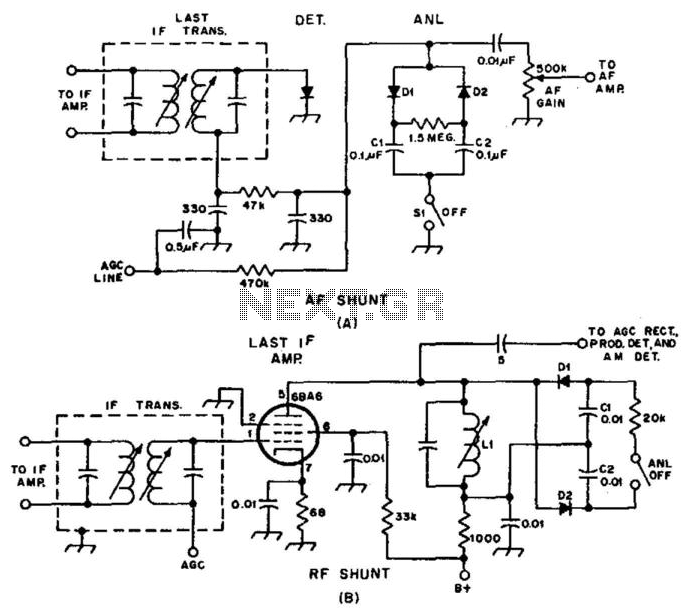
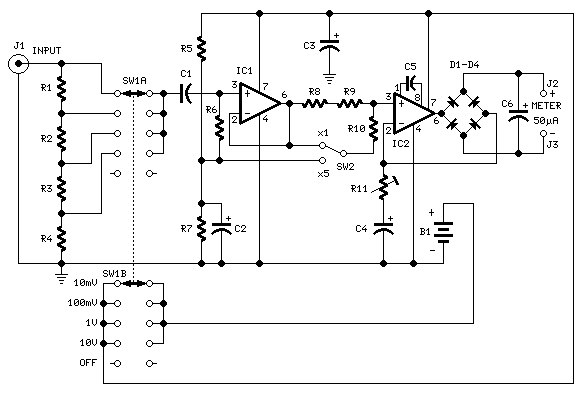
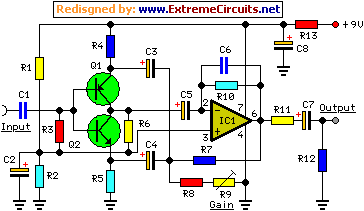
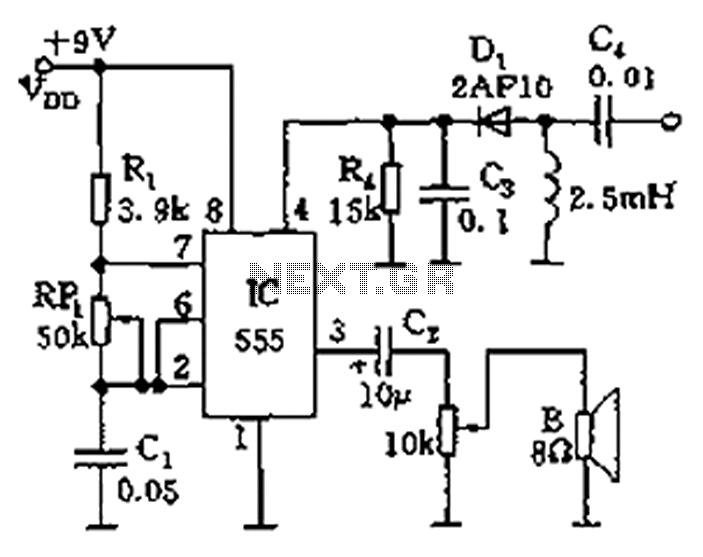
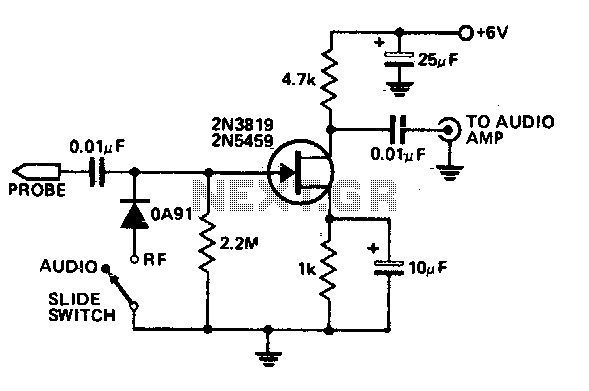
Examples of RF and audio ANL circuits. Positive and negative clipping occurs in both circuits. The circuit is self-adjusting. This noise limiter operates at the IF output. Adequate gain is needed at the IF frequency so that several volts peak-to-peak of audio is available.
The RF (Radio Frequency) and audio ANL (Automatic Noise Limiter) circuits serve critical functions in signal processing, particularly in minimizing unwanted noise while maintaining signal integrity. These circuits are designed to handle both positive and negative clipping, ensuring that signal distortions are effectively managed.
The self-adjusting feature of the circuit allows it to adapt to varying input signal levels, which is particularly beneficial in environments with fluctuating noise levels. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining audio quality, as it ensures that the limiter can respond dynamically to changes in the incoming signal.
Operating at the Intermediate Frequency (IF) output, the noise limiter plays a vital role in enhancing the performance of RF systems. It is essential for the circuit to achieve adequate gain at the IF frequency. This gain is necessary to ensure that the output audio signal can reach several volts peak-to-peak, providing sufficient amplitude for further processing or amplification stages.
In practical applications, these circuits can be integrated into various devices, including radios, audio processors, and communication systems, where they contribute to clearer sound reproduction and improved overall performance by effectively managing noise and signal clipping. Proper design considerations must be taken into account to optimize the gain and ensure the self-adjusting mechanism functions as intended, thereby achieving the desired audio quality and reliability in the output signal. Examples of RF and audio ANL circuits. Positive and negative clipping occurs in both circuits. The circuit at A i s self-adjusting. This noise limiter operates at the IF output. It is self-adjusting. Adequate gain is needed at the IF frequency so that several volts p-p of audio is available.
The RF (Radio Frequency) and audio ANL (Automatic Noise Limiter) circuits serve critical functions in signal processing, particularly in minimizing unwanted noise while maintaining signal integrity. These circuits are designed to handle both positive and negative clipping, ensuring that signal distortions are effectively managed.
The self-adjusting feature of the circuit allows it to adapt to varying input signal levels, which is particularly beneficial in environments with fluctuating noise levels. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining audio quality, as it ensures that the limiter can respond dynamically to changes in the incoming signal.
Operating at the Intermediate Frequency (IF) output, the noise limiter plays a vital role in enhancing the performance of RF systems. It is essential for the circuit to achieve adequate gain at the IF frequency. This gain is necessary to ensure that the output audio signal can reach several volts peak-to-peak, providing sufficient amplitude for further processing or amplification stages.
In practical applications, these circuits can be integrated into various devices, including radios, audio processors, and communication systems, where they contribute to clearer sound reproduction and improved overall performance by effectively managing noise and signal clipping. Proper design considerations must be taken into account to optimize the gain and ensure the self-adjusting mechanism functions as intended, thereby achieving the desired audio quality and reliability in the output signal. Examples of RF and audio ANL circuits. Positive and negative clipping occurs in both circuits. The circuit at A i s self-adjusting. This noise limiter operates at the IF output. It is self-adjusting. Adequate gain is needed at the IF frequency so that several volts p-p of audio is available.