LED 12 Volt Lead Acid Battery Meter

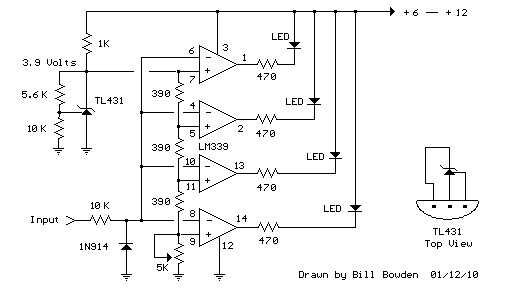
The circuit described utilizes a quad voltage comparator (LM339) to function as a simple bar graph meter that indicates the charge status of a 12-volt lead-acid battery. A 5-volt reference voltage is employed for this purpose.
The circuit leverages the LM339, which contains four independent voltage comparators, to monitor the voltage levels of the lead-acid battery. The output of each comparator is connected to a set of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) arranged in a bar graph configuration. As the battery voltage changes, the comparators compare the battery voltage against predefined reference levels, which are set by a voltage divider network.
The reference levels are typically calibrated to correspond with the state of charge of a 12-volt lead-acid battery. For instance, the voltage thresholds may be set at approximately 12.0V, 12.2V, 12.4V, and 12.6V, indicating low, moderate, high, and fully charged states, respectively. When the battery voltage exceeds a certain threshold, the corresponding comparator output switches from low to high, illuminating the associated LED. This visual representation provides an intuitive understanding of the battery's charge condition.
Powering the circuit requires a stable 5-volt supply for the LM339 and the LEDs. A zener diode can be used to ensure that the reference voltage remains constant despite fluctuations in the input voltage. Additionally, current-limiting resistors should be included in series with the LEDs to prevent excessive current flow, which could damage the components.
The design is compact and can be integrated into various applications where monitoring the charge state of a lead-acid battery is crucial, such as in automotive systems, solar energy storage systems, or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it an ideal choice for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.LED 12 Volt Lead Acid Battery Meter Circuit In the circuit below, a quad voltage comparator (LM339) is used as a simple bar graph meter to indicate the charge condition of a 12 volt, lead acid battery. A 5 volt reference voltage.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit leverages the LM339, which contains four independent voltage comparators, to monitor the voltage levels of the lead-acid battery. The output of each comparator is connected to a set of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) arranged in a bar graph configuration. As the battery voltage changes, the comparators compare the battery voltage against predefined reference levels, which are set by a voltage divider network.
The reference levels are typically calibrated to correspond with the state of charge of a 12-volt lead-acid battery. For instance, the voltage thresholds may be set at approximately 12.0V, 12.2V, 12.4V, and 12.6V, indicating low, moderate, high, and fully charged states, respectively. When the battery voltage exceeds a certain threshold, the corresponding comparator output switches from low to high, illuminating the associated LED. This visual representation provides an intuitive understanding of the battery's charge condition.
Powering the circuit requires a stable 5-volt supply for the LM339 and the LEDs. A zener diode can be used to ensure that the reference voltage remains constant despite fluctuations in the input voltage. Additionally, current-limiting resistors should be included in series with the LEDs to prevent excessive current flow, which could damage the components.
The design is compact and can be integrated into various applications where monitoring the charge state of a lead-acid battery is crucial, such as in automotive systems, solar energy storage systems, or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it an ideal choice for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.LED 12 Volt Lead Acid Battery Meter Circuit In the circuit below, a quad voltage comparator (LM339) is used as a simple bar graph meter to indicate the charge condition of a 12 volt, lead acid battery. A 5 volt reference voltage.. 🔗 External reference