led Calculate expected voltage around a resistor
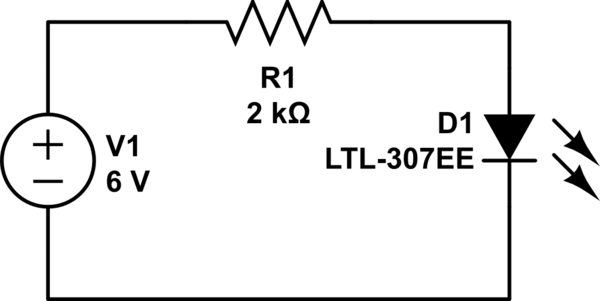
It cannot be 0 volts, as the current does not flow freely due to the presence of the resistor. This results in one side being more negatively charged and the other side more positively charged, as electrons can move more quickly to one end of the battery than through the resistor.
In electrical circuits, the behavior of current flow is significantly impacted by the components present, particularly resistors. When a resistor is introduced into a circuit, it restricts the flow of electrons, leading to a voltage drop across the resistor. This voltage drop is responsible for the difference in charge between the two sides of the circuit.
In a typical scenario, a battery provides a potential difference that drives the current through the circuit. The electrons, which are negatively charged, are attracted towards the positive terminal of the battery. However, as they encounter the resistor, their movement is impeded. This resistance causes a buildup of charge on one side of the resistor, leading to a negative charge accumulation on the side connected to the negative terminal of the battery, while the other side becomes positively charged due to the lack of electrons.
The relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) is described by Ohm's Law, which states that V = I * R. In a circuit with a resistor, the voltage across the resistor can be calculated by multiplying the current flowing through it by its resistance value. This principle helps explain why the voltage cannot be zero; there must always be a potential difference across the resistor as long as current is flowing.
In summary, the presence of a resistor in a circuit creates a scenario where the voltage cannot be zero due to the differential charge distribution caused by the restriction of electron flow. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for analyzing and designing electronic circuits effectively.It can`t be 0 volts, since the current does not freely move around, due to the resistor; resulting in one side being more negatively charged, and the other more positively charged, since the electrons can move faster to an end of the battery than through the resistor. 🔗 External reference
In electrical circuits, the behavior of current flow is significantly impacted by the components present, particularly resistors. When a resistor is introduced into a circuit, it restricts the flow of electrons, leading to a voltage drop across the resistor. This voltage drop is responsible for the difference in charge between the two sides of the circuit.
In a typical scenario, a battery provides a potential difference that drives the current through the circuit. The electrons, which are negatively charged, are attracted towards the positive terminal of the battery. However, as they encounter the resistor, their movement is impeded. This resistance causes a buildup of charge on one side of the resistor, leading to a negative charge accumulation on the side connected to the negative terminal of the battery, while the other side becomes positively charged due to the lack of electrons.
The relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) is described by Ohm's Law, which states that V = I * R. In a circuit with a resistor, the voltage across the resistor can be calculated by multiplying the current flowing through it by its resistance value. This principle helps explain why the voltage cannot be zero; there must always be a potential difference across the resistor as long as current is flowing.
In summary, the presence of a resistor in a circuit creates a scenario where the voltage cannot be zero due to the differential charge distribution caused by the restriction of electron flow. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for analyzing and designing electronic circuits effectively.It can`t be 0 volts, since the current does not freely move around, due to the resistor; resulting in one side being more negatively charged, and the other more positively charged, since the electrons can move faster to an end of the battery than through the resistor. 🔗 External reference