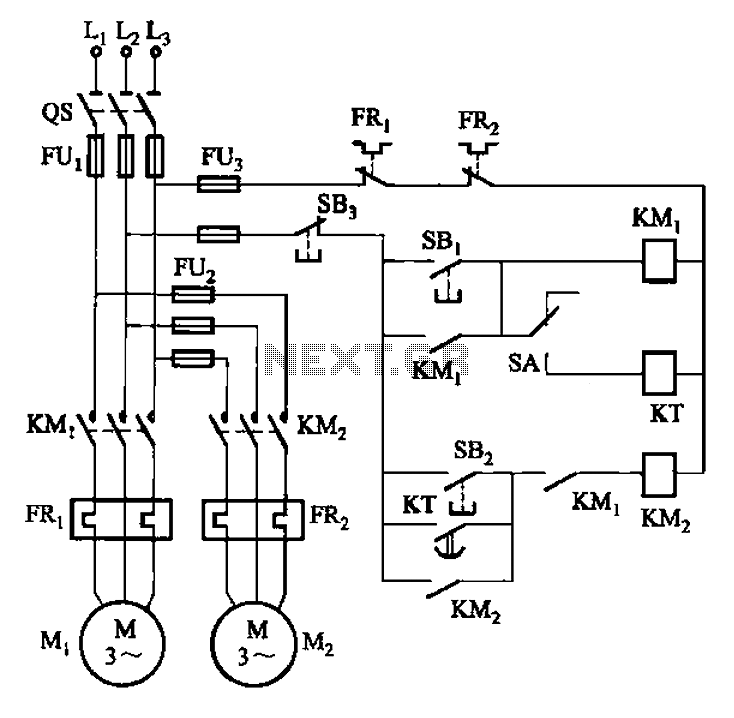
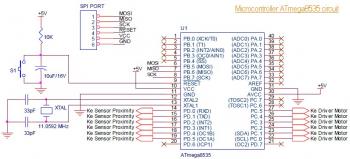
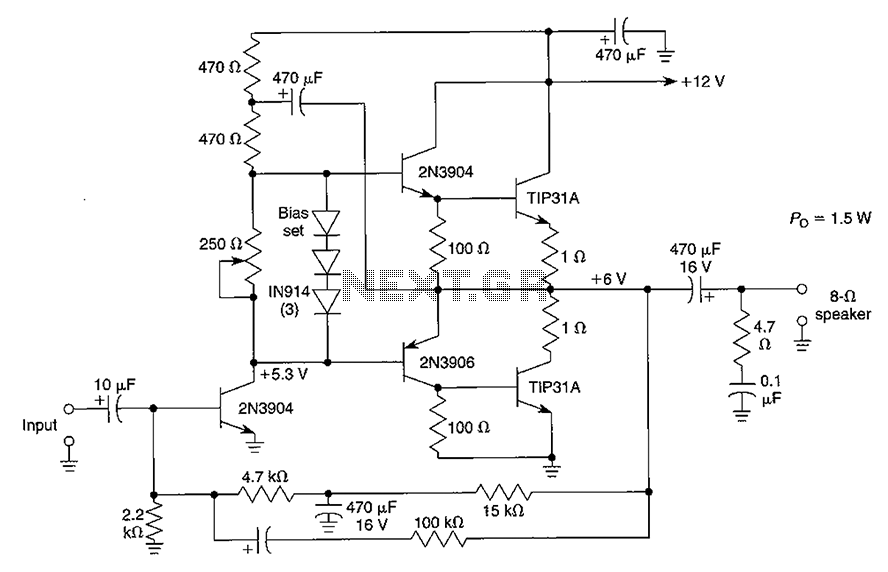
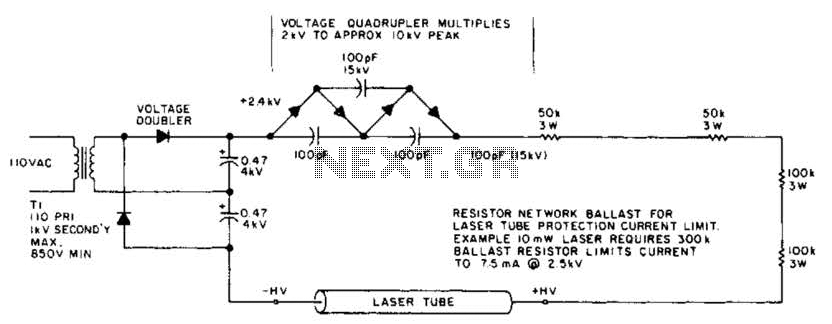
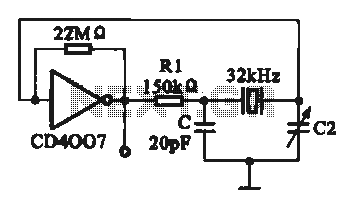
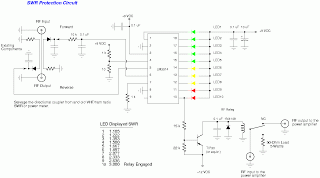
LED signal amplifying circuit diagram
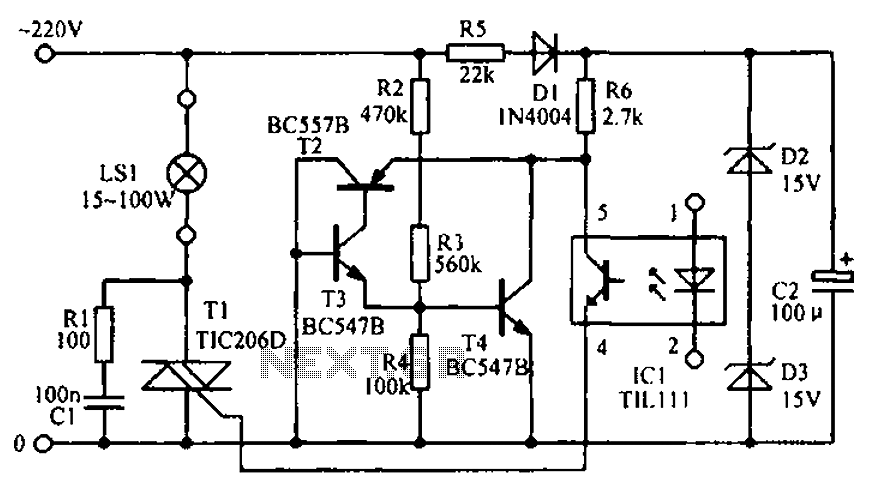
The circuit diagram illustrates the LED signal amplification.
The LED signal amplification circuit is designed to enhance the output signal from an LED, allowing it to drive larger loads or to be interfaced with other electronic components effectively. The primary components of this circuit typically include an LED, a transistor, resistors, and capacitors.
In this configuration, the LED serves as the light source, which emits light when current flows through it. The transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, controlling the larger current that can be supplied to the load based on the input signal received from the LED. Resistors are used to limit the current flowing through the LED and to set the biasing conditions for the transistor, ensuring it operates within its safe limits. Capacitors may be included to filter noise and stabilize the circuit, ensuring smooth operation.
The circuit may be powered by a DC supply, and the output can be connected to various loads, such as additional LEDs, speakers, or other electronic devices. Proper design considerations, such as selecting the right transistor type (NPN or PNP), determining resistor values for biasing, and ensuring that the power supply voltage is compatible with the components, are crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability of the LED signal amplification circuit. As shown in the circuit diagram for the LED signal amplification:
The LED signal amplification circuit is designed to enhance the output signal from an LED, allowing it to drive larger loads or to be interfaced with other electronic components effectively. The primary components of this circuit typically include an LED, a transistor, resistors, and capacitors.
In this configuration, the LED serves as the light source, which emits light when current flows through it. The transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, controlling the larger current that can be supplied to the load based on the input signal received from the LED. Resistors are used to limit the current flowing through the LED and to set the biasing conditions for the transistor, ensuring it operates within its safe limits. Capacitors may be included to filter noise and stabilize the circuit, ensuring smooth operation.
The circuit may be powered by a DC supply, and the output can be connected to various loads, such as additional LEDs, speakers, or other electronic devices. Proper design considerations, such as selecting the right transistor type (NPN or PNP), determining resistor values for biasing, and ensuring that the power supply voltage is compatible with the components, are crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability of the LED signal amplification circuit. As shown in the circuit diagram for the LED signal amplification: