LED Torch circuit
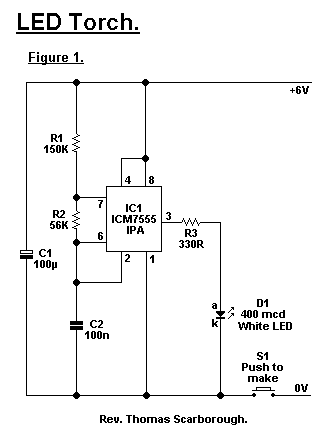
A common issue with small flashlights is the limited lifespan of both the batteries and the bulb. For example, a typical incandescent flashlight consumes approximately 2 Watts, while the LED flashlight shown in Fig. 1 consumes only 24 mW. This results in over 80 times longer operation from four AA alkaline batteries, providing up to one month of continuous use.
The LED flashlight design significantly enhances energy efficiency compared to traditional incandescent models. The low power consumption of 24 mW allows the LED flashlight to maximize the energy stored in the AA alkaline batteries. The circuit typically consists of a power source, which in this case is the four AA alkaline batteries connected in series to provide a combined voltage of approximately 6 volts.
The LED is connected to a current-limiting resistor to ensure that it operates within its specified current range, preventing damage due to excessive current. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage drop of the LED, which is typically around 2 to 3 volts, and the desired forward current, often around 20 mA for standard LEDs.
Additionally, the circuit may include a simple switch to control the on/off operation of the flashlight. To further enhance efficiency, a microcontroller could be integrated to manage power distribution, allowing for features such as dimming or flashing modes, thereby extending battery life even further.
Overall, the LED flashlight circuit not only provides longer operational life but also offers greater reliability and reduced heat generation compared to incandescent flashlights, making it an ideal choice for portable lighting solutions.A common problem with small torches is the short life-span both of the batteries and the bulb. The average incandescent torch, for instance, consumes around 2 Watts. The LED Torch in Fig. 1 consumes just 24 mW, giving it more than 80 times longer service from 4 AA alkaline batteries (that is, up to one month`s continuous service).. 🔗 External reference
The LED flashlight design significantly enhances energy efficiency compared to traditional incandescent models. The low power consumption of 24 mW allows the LED flashlight to maximize the energy stored in the AA alkaline batteries. The circuit typically consists of a power source, which in this case is the four AA alkaline batteries connected in series to provide a combined voltage of approximately 6 volts.
The LED is connected to a current-limiting resistor to ensure that it operates within its specified current range, preventing damage due to excessive current. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage drop of the LED, which is typically around 2 to 3 volts, and the desired forward current, often around 20 mA for standard LEDs.
Additionally, the circuit may include a simple switch to control the on/off operation of the flashlight. To further enhance efficiency, a microcontroller could be integrated to manage power distribution, allowing for features such as dimming or flashing modes, thereby extending battery life even further.
Overall, the LED flashlight circuit not only provides longer operational life but also offers greater reliability and reduced heat generation compared to incandescent flashlights, making it an ideal choice for portable lighting solutions.A common problem with small torches is the short life-span both of the batteries and the bulb. The average incandescent torch, for instance, consumes around 2 Watts. The LED Torch in Fig. 1 consumes just 24 mW, giving it more than 80 times longer service from 4 AA alkaline batteries (that is, up to one month`s continuous service).. 🔗 External reference