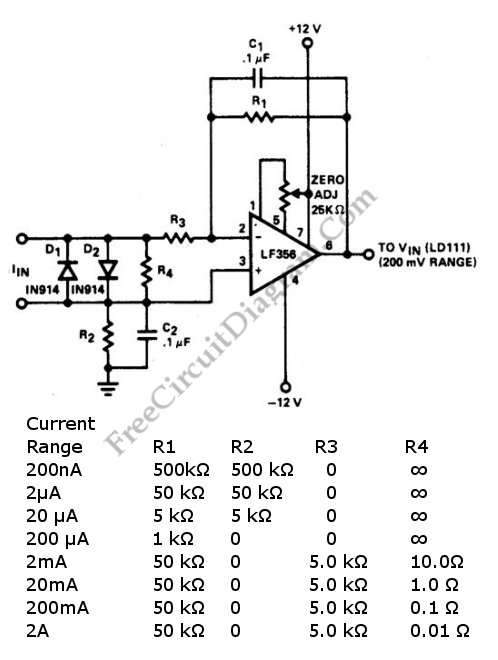
LF356 Wide Range Current-To-Voltage Converter
A current-to-voltage converter circuit can be constructed using a single resistor. This design is straightforward, as any current flowing through a resistor will naturally generate a voltage.
A current-to-voltage converter, also known as a transimpedance amplifier, is primarily utilized to convert an input current signal into a corresponding output voltage signal. This type of circuit is particularly useful in applications such as photodetectors, where the output is a current generated by light exposure, and it needs to be converted into a voltage for further processing.
In its simplest form, the circuit consists of a resistor (R) connected to the output terminal. When an input current (I_in) flows through the resistor, Ohm's Law (V = I × R) dictates that a voltage (V_out) will be developed across the resistor. The output voltage can be expressed as V_out = I_in × R, where V_out is the voltage across the resistor, I_in is the input current, and R is the resistance value.
The choice of resistor value is critical in determining the sensitivity and range of the circuit. A higher resistance will produce a larger output voltage for a given input current, but may also increase noise and reduce bandwidth. Conversely, a lower resistance will yield a smaller output voltage but may provide better performance in terms of speed and noise immunity.
For practical applications, additional components such as operational amplifiers (op-amps) may be integrated into the design to improve performance characteristics, such as input impedance, gain stability, and noise reduction. In these configurations, the op-amp can be used to buffer the output, thereby isolating the load from the current-to-voltage conversion stage and allowing for more precise voltage readings.
Overall, the current-to-voltage converter is a fundamental circuit that serves as a building block in various electronic systems, enabling the effective translation of current signals into voltage signals for further analysis or processing.Current to voltage converter circuit can be made using a single resistor, it is very simple since any current will naturally develop a voltage when flow through. 🔗 External reference
A current-to-voltage converter, also known as a transimpedance amplifier, is primarily utilized to convert an input current signal into a corresponding output voltage signal. This type of circuit is particularly useful in applications such as photodetectors, where the output is a current generated by light exposure, and it needs to be converted into a voltage for further processing.
In its simplest form, the circuit consists of a resistor (R) connected to the output terminal. When an input current (I_in) flows through the resistor, Ohm's Law (V = I × R) dictates that a voltage (V_out) will be developed across the resistor. The output voltage can be expressed as V_out = I_in × R, where V_out is the voltage across the resistor, I_in is the input current, and R is the resistance value.
The choice of resistor value is critical in determining the sensitivity and range of the circuit. A higher resistance will produce a larger output voltage for a given input current, but may also increase noise and reduce bandwidth. Conversely, a lower resistance will yield a smaller output voltage but may provide better performance in terms of speed and noise immunity.
For practical applications, additional components such as operational amplifiers (op-amps) may be integrated into the design to improve performance characteristics, such as input impedance, gain stability, and noise reduction. In these configurations, the op-amp can be used to buffer the output, thereby isolating the load from the current-to-voltage conversion stage and allowing for more precise voltage readings.
Overall, the current-to-voltage converter is a fundamental circuit that serves as a building block in various electronic systems, enabling the effective translation of current signals into voltage signals for further analysis or processing.Current to voltage converter circuit can be made using a single resistor, it is very simple since any current will naturally develop a voltage when flow through. 🔗 External reference