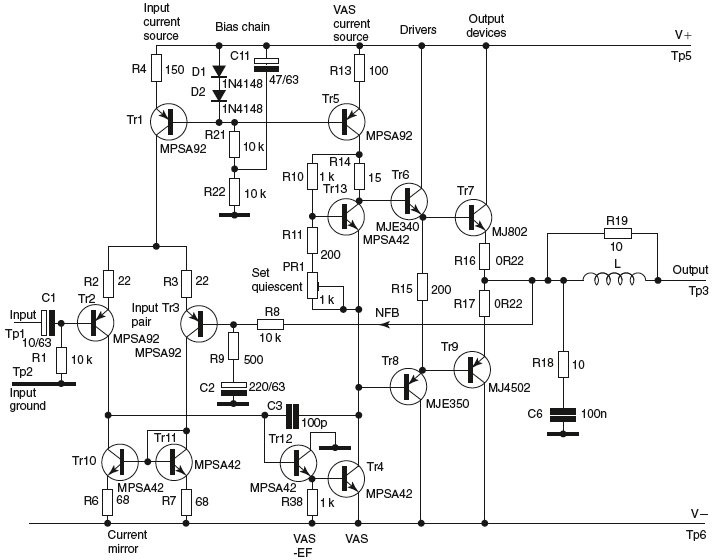
Audio Signal Strength Detector/Converter
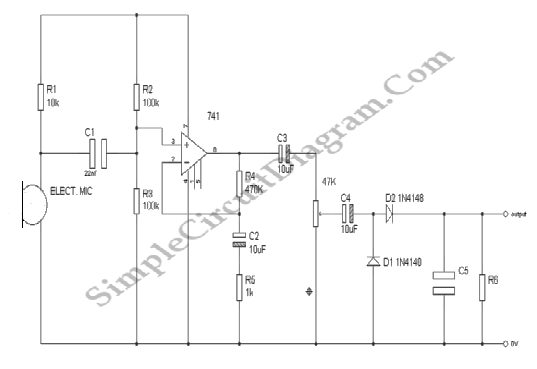
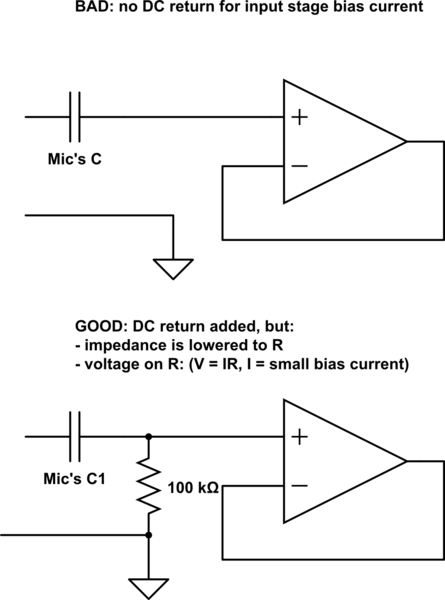
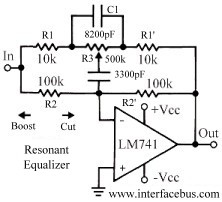
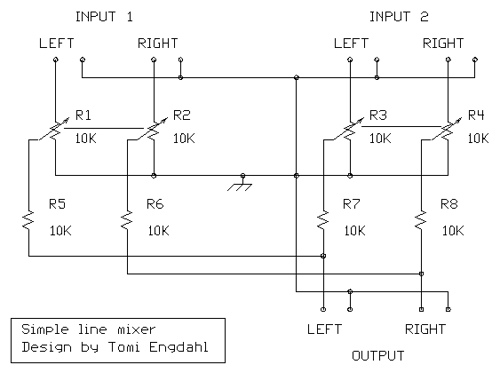
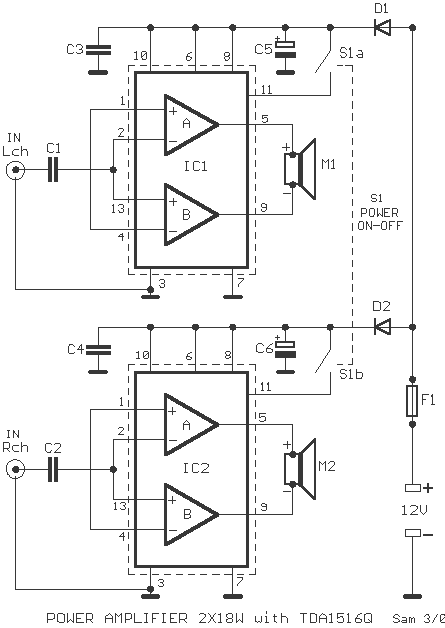
Below is the schematic diagram of an audio input module. This module is capable of producing a DC output voltage that is proportional to the amplitude of the input signal.
The audio input module typically consists of several key components that work together to convert an AC audio signal into a DC voltage level. At the core of this module is an operational amplifier (op-amp), which is configured in a non-inverting mode to amplify the incoming audio signal. The op-amp's gain can be adjusted using external resistors, allowing for customization based on the desired output level.
The input stage may include a coupling capacitor, which serves to block any DC offset from the audio signal while allowing the AC component to pass through. This ensures that only the varying part of the signal is processed by the op-amp. The output of the op-amp is then fed into a rectifier circuit, which converts the AC signal into a pulsating DC voltage. A smoothing capacitor is often employed after the rectifier to filter out the ripples in the DC output, providing a more stable voltage level that accurately reflects the amplitude of the original audio signal.
To further enhance performance, a voltage divider may be implemented at the output stage to scale the DC voltage to a desired range, making it suitable for interfacing with other electronic components or systems. Additionally, protection diodes can be included to safeguard the circuit against voltage spikes or reverse polarity, ensuring longevity and reliability in various operating conditions.
The schematic diagram visually represents these components and their interconnections, providing a clear understanding of the audio input module's functionality and operation.Below is the schematic diagram of an audio input module. We can produce a DC output voltage that is proportional to the input signal amplitude (the signal.. 🔗 External reference
The audio input module typically consists of several key components that work together to convert an AC audio signal into a DC voltage level. At the core of this module is an operational amplifier (op-amp), which is configured in a non-inverting mode to amplify the incoming audio signal. The op-amp's gain can be adjusted using external resistors, allowing for customization based on the desired output level.
The input stage may include a coupling capacitor, which serves to block any DC offset from the audio signal while allowing the AC component to pass through. This ensures that only the varying part of the signal is processed by the op-amp. The output of the op-amp is then fed into a rectifier circuit, which converts the AC signal into a pulsating DC voltage. A smoothing capacitor is often employed after the rectifier to filter out the ripples in the DC output, providing a more stable voltage level that accurately reflects the amplitude of the original audio signal.
To further enhance performance, a voltage divider may be implemented at the output stage to scale the DC voltage to a desired range, making it suitable for interfacing with other electronic components or systems. Additionally, protection diodes can be included to safeguard the circuit against voltage spikes or reverse polarity, ensuring longevity and reliability in various operating conditions.
The schematic diagram visually represents these components and their interconnections, providing a clear understanding of the audio input module's functionality and operation.Below is the schematic diagram of an audio input module. We can produce a DC output voltage that is proportional to the input signal amplitude (the signal.. 🔗 External reference