light flasher pcb
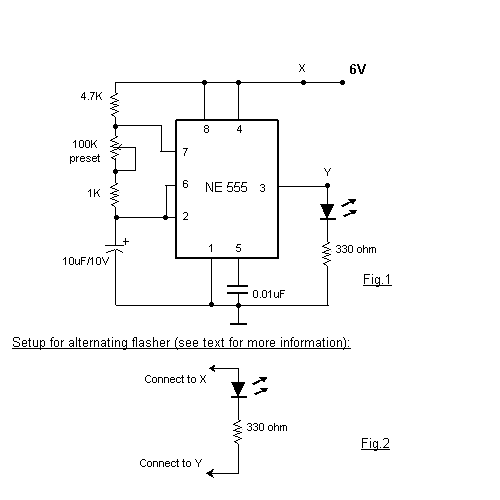
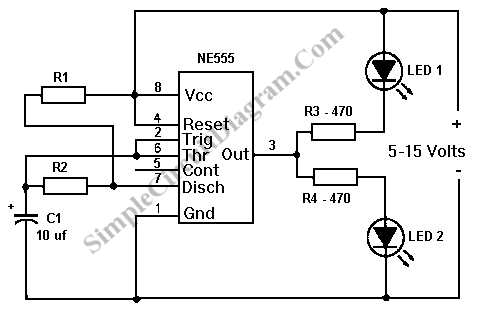
This circuit is a basic design for flashing one or more LEDs, as well as for alternately flashing multiple LEDs. It employs a 555 timer configured as an astable multivibrator, allowing for variable frequency operation. When the preset is set to its maximum, the LED flashing rate is approximately 0.5 seconds. This rate can be increased by using a larger capacitor; for instance, replacing the 10μF capacitor with a 22μF capacitor will change the flashing rate to 1 second. Additionally, the circuit can be modified to function as an alternating flasher by connecting an LED and a 330-ohm resistor to specific points in the circuit. This modification enables both LEDs to flash alternately. The 555 timer is capable of supplying or sinking up to 200mA of current, allowing for the connection of approximately 18 LEDs in parallel for both the standard and alternating flashing configurations, resulting in a total of 36 LEDs for the alternating flasher setup.
This LED flashing circuit utilizes the 555 timer IC in an astable mode, which is a common application for generating square wave signals. The frequency of the output signal, which determines the flashing rate of the LEDs, is influenced by the resistor values and the timing capacitor used in the circuit. The formula for calculating the frequency (f) of the output signal in an astable configuration is given by:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2R2) * C)
Where R1 and R2 are the resistances connected to the 555 timer, and C is the capacitance of the timing capacitor. By adjusting these components, the user can control the flashing rate of the LEDs.
To implement the circuit, the following components are required:
- 1 x NE555 timer IC
- 1 x capacitor (10μF or higher for adjustable flashing rates)
- 2 x resistors (R1 and R2, values to be determined based on the desired frequency)
- 1 x 330-ohm resistor for the alternating LED configuration
- 2 x LEDs (for alternating flashing)
- Power supply (typically 5V to 15V depending on the LEDs and timer specifications)
The circuit can be built on a breadboard or a PCB for more permanent applications. The layout should ensure that the connections are secure, and the power supply is correctly polarized to prevent damage to the components.
In the alternating flasher configuration, when the LEDs are connected at points X and Y, the circuit will alternate the flashing of the two LEDs, enhancing the visual effect. The capability of the 555 timer to handle up to 200mA allows for a significant number of LEDs to be connected in parallel, making this circuit suitable for decorative lighting applications, indicators, or visual signals in various electronic projects.
Overall, this circuit serves as an excellent introduction to timer-based applications and provides a practical demonstration of how to control LED behavior using simple electronic components.This is a very basic circuit for flashing one or more LEDS and also to alternately flash one or more LEDs. It uses a 555 timer setup as an astable multivibrator with a variable frequency. With the preset at its max. the flashing rate of the LED is about 1/2 a second. It can be increased by increasing the value of the capacitor from 10uF to a highe r value. For example if it is increased to 22uF the flashing rate becomes 1 second. There is also provision to convert it into an alternating flasher. You just have to connect a LED and a 330ohm as shown in Fig. 2 to the points X and Y of Fig. 1. Then both the LEDs flash alternately. Since the 555 can supply or sink in upto 200mA of current, you can connect upto about 18 LEDS in parallel both for the flasher and alternating flasher (that makes a total of 36 LEDs for alternating flasher). 🔗 External reference
This LED flashing circuit utilizes the 555 timer IC in an astable mode, which is a common application for generating square wave signals. The frequency of the output signal, which determines the flashing rate of the LEDs, is influenced by the resistor values and the timing capacitor used in the circuit. The formula for calculating the frequency (f) of the output signal in an astable configuration is given by:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2R2) * C)
Where R1 and R2 are the resistances connected to the 555 timer, and C is the capacitance of the timing capacitor. By adjusting these components, the user can control the flashing rate of the LEDs.
To implement the circuit, the following components are required:
- 1 x NE555 timer IC
- 1 x capacitor (10μF or higher for adjustable flashing rates)
- 2 x resistors (R1 and R2, values to be determined based on the desired frequency)
- 1 x 330-ohm resistor for the alternating LED configuration
- 2 x LEDs (for alternating flashing)
- Power supply (typically 5V to 15V depending on the LEDs and timer specifications)
The circuit can be built on a breadboard or a PCB for more permanent applications. The layout should ensure that the connections are secure, and the power supply is correctly polarized to prevent damage to the components.
In the alternating flasher configuration, when the LEDs are connected at points X and Y, the circuit will alternate the flashing of the two LEDs, enhancing the visual effect. The capability of the 555 timer to handle up to 200mA allows for a significant number of LEDs to be connected in parallel, making this circuit suitable for decorative lighting applications, indicators, or visual signals in various electronic projects.
Overall, this circuit serves as an excellent introduction to timer-based applications and provides a practical demonstration of how to control LED behavior using simple electronic components.This is a very basic circuit for flashing one or more LEDS and also to alternately flash one or more LEDs. It uses a 555 timer setup as an astable multivibrator with a variable frequency. With the preset at its max. the flashing rate of the LED is about 1/2 a second. It can be increased by increasing the value of the capacitor from 10uF to a highe r value. For example if it is increased to 22uF the flashing rate becomes 1 second. There is also provision to convert it into an alternating flasher. You just have to connect a LED and a 330ohm as shown in Fig. 2 to the points X and Y of Fig. 1. Then both the LEDs flash alternately. Since the 555 can supply or sink in upto 200mA of current, you can connect upto about 18 LEDS in parallel both for the flasher and alternating flasher (that makes a total of 36 LEDs for alternating flasher). 🔗 External reference