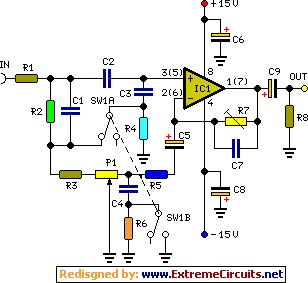
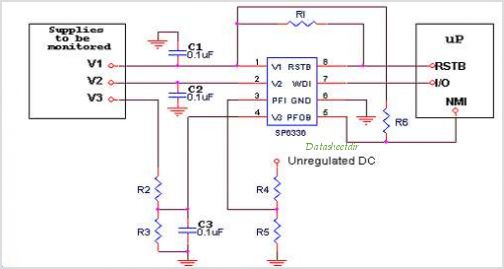
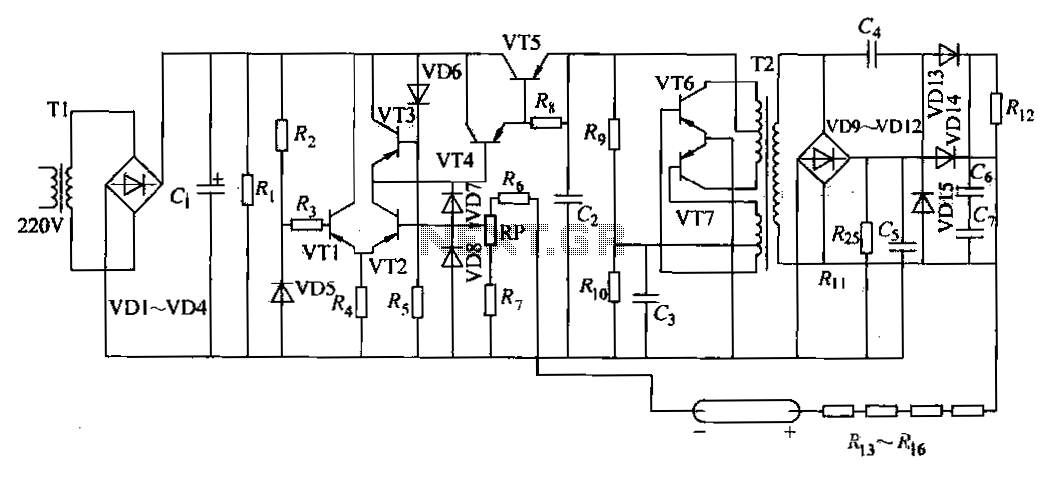
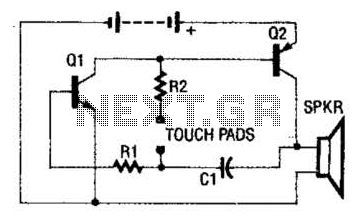
Light flashing circuit
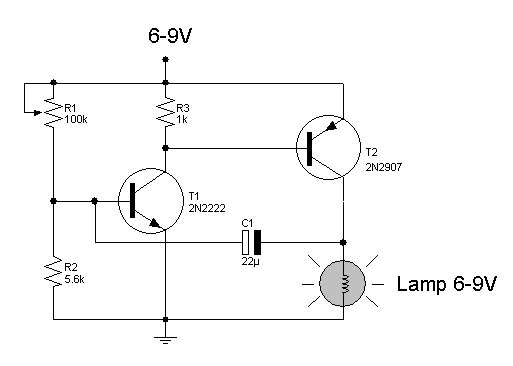
Light flashing circuit. This circuit is designed to create a small lamp that flashes with a signal at a rate of one flash per second, controlled by adjusting the lamp voltage through resistor R1. The rate is adjustable to generate different flashing frequencies.
The light flashing circuit typically consists of a few key components: a power source, a lamp (LED or incandescent), a resistor (R1), and a timing element, which can be a capacitor and a transistor or an integrated circuit (IC) designed for timing applications.
In this configuration, the resistor R1 is crucial for controlling the current flowing to the lamp. By adjusting R1, the voltage across the lamp can be varied, effectively changing the brightness and the flashing rate. The timing element, often implemented with a capacitor (C) and a transistor, establishes the timing cycle. The capacitor charges and discharges through R1, creating a time delay that results in the one-second flashing interval.
For a basic implementation, a common timing circuit can be based on a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this setup, the 555 timer generates a square wave output, which can be used to drive the lamp. The frequency of the oscillation is determined by the values of R1, R2 (another resistor), and C.
The standard formula for calculating the frequency (f) of the output signal in an astable 555 timer circuit is given by:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C)
By selecting appropriate values for R1, R2, and C, the desired flashing rate can be achieved. Adjustments to R1 allow for fine-tuning of the flash rate while maintaining the overall functionality of the circuit.
Safety considerations should be taken into account, especially when working with higher voltages or currents. Proper heat dissipation methods for the lamp and the components should be ensured to prevent overheating and potential damage.
This light flashing circuit can be applied in various applications, such as decorative lighting, signaling devices, or as an attention-grabbing indicator in electronic projects.Light flashing circuit.This circuit is the small lamp flashing signal on every 1 second flash rate control by adjusting the lamp voltage R1.The rate is to generate. 🔗 External reference
The light flashing circuit typically consists of a few key components: a power source, a lamp (LED or incandescent), a resistor (R1), and a timing element, which can be a capacitor and a transistor or an integrated circuit (IC) designed for timing applications.
In this configuration, the resistor R1 is crucial for controlling the current flowing to the lamp. By adjusting R1, the voltage across the lamp can be varied, effectively changing the brightness and the flashing rate. The timing element, often implemented with a capacitor (C) and a transistor, establishes the timing cycle. The capacitor charges and discharges through R1, creating a time delay that results in the one-second flashing interval.
For a basic implementation, a common timing circuit can be based on a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this setup, the 555 timer generates a square wave output, which can be used to drive the lamp. The frequency of the oscillation is determined by the values of R1, R2 (another resistor), and C.
The standard formula for calculating the frequency (f) of the output signal in an astable 555 timer circuit is given by:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C)
By selecting appropriate values for R1, R2, and C, the desired flashing rate can be achieved. Adjustments to R1 allow for fine-tuning of the flash rate while maintaining the overall functionality of the circuit.
Safety considerations should be taken into account, especially when working with higher voltages or currents. Proper heat dissipation methods for the lamp and the components should be ensured to prevent overheating and potential damage.
This light flashing circuit can be applied in various applications, such as decorative lighting, signaling devices, or as an attention-grabbing indicator in electronic projects.Light flashing circuit.