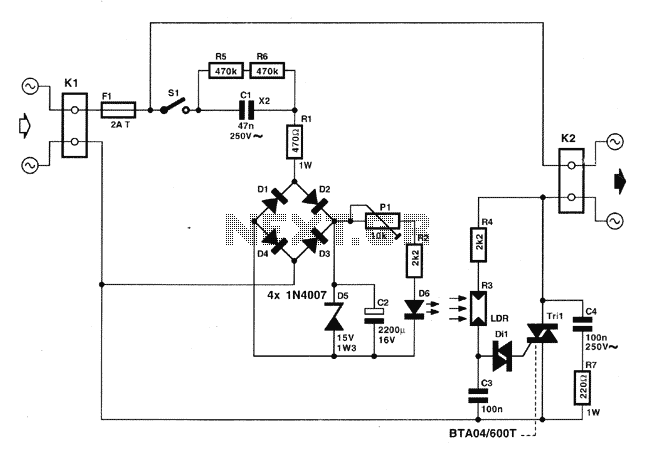
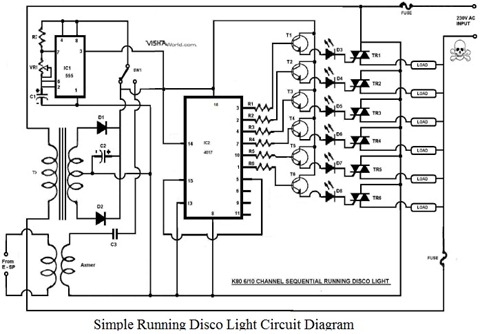
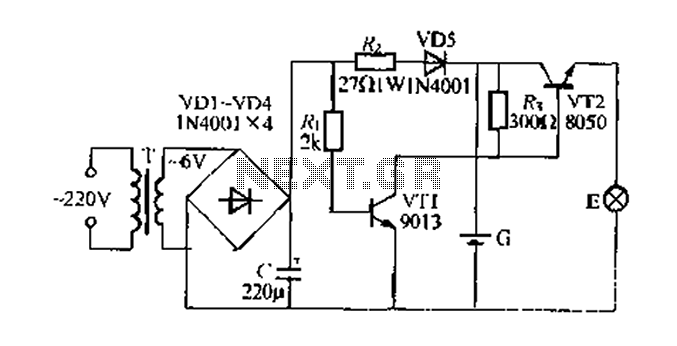
Light to Frequency converter
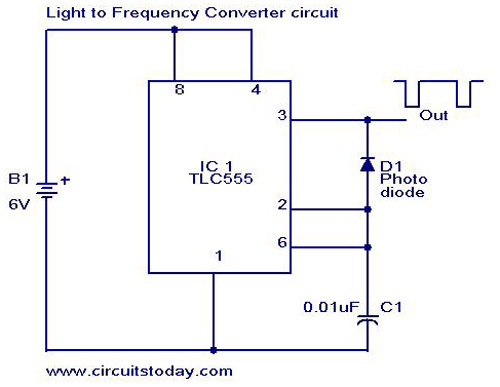
A simple light-to-frequency converter circuit with a diagram and schematic. It is used as a light intensity measurement circuit. The design utilizes the TLC555, a CMOS version of the NE555 timer IC.
The light-to-frequency converter circuit is designed to convert varying light intensities into corresponding frequency signals, facilitating the measurement of light levels. The circuit employs the TLC555 timer IC, which operates in an astable mode to generate a square wave output whose frequency is proportional to the input light intensity.
The primary components of the circuit include the TLC555 timer IC, a photodetector (such as a photodiode or phototransistor), resistors, and capacitors. The photodetector captures the incoming light and produces a current proportional to the light intensity. This current is fed into the TLC555, which is configured to convert the current signal into a frequency output.
In the astable mode of operation, the TLC555 continuously switches between its high and low states, producing a square wave. The frequency of this output is determined by the values of the timing resistors and capacitor connected to the IC. The relationship between the light intensity and the output frequency can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values, allowing for calibration based on specific measurement requirements.
The schematic diagram typically shows the TLC555 connected with the photodetector and timing components. It is essential to ensure proper connections and component values for accurate light intensity measurement. This circuit can be applied in various applications, including ambient light sensing, automatic lighting systems, and scientific experiments that require precise light intensity monitoring.A simple light to frequency converter circuit with diagram and schematic.Used as Light intensity measurement circuit.Design using TLC555, a cmos version of NE 555 timer IC.. 🔗 External reference
The light-to-frequency converter circuit is designed to convert varying light intensities into corresponding frequency signals, facilitating the measurement of light levels. The circuit employs the TLC555 timer IC, which operates in an astable mode to generate a square wave output whose frequency is proportional to the input light intensity.
The primary components of the circuit include the TLC555 timer IC, a photodetector (such as a photodiode or phototransistor), resistors, and capacitors. The photodetector captures the incoming light and produces a current proportional to the light intensity. This current is fed into the TLC555, which is configured to convert the current signal into a frequency output.
In the astable mode of operation, the TLC555 continuously switches between its high and low states, producing a square wave. The frequency of this output is determined by the values of the timing resistors and capacitor connected to the IC. The relationship between the light intensity and the output frequency can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values, allowing for calibration based on specific measurement requirements.
The schematic diagram typically shows the TLC555 connected with the photodetector and timing components. It is essential to ensure proper connections and component values for accurate light intensity measurement. This circuit can be applied in various applications, including ambient light sensing, automatic lighting systems, and scientific experiments that require precise light intensity monitoring.A simple light to frequency converter circuit with diagram and schematic.Used as Light intensity measurement circuit.Design using TLC555, a cmos version of NE 555 timer IC.. 🔗 External reference