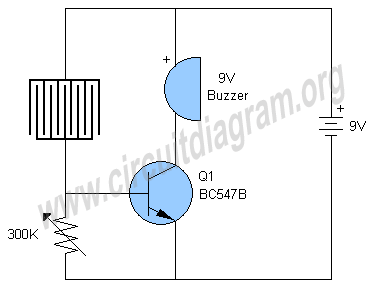
Line Following Robot Sensor
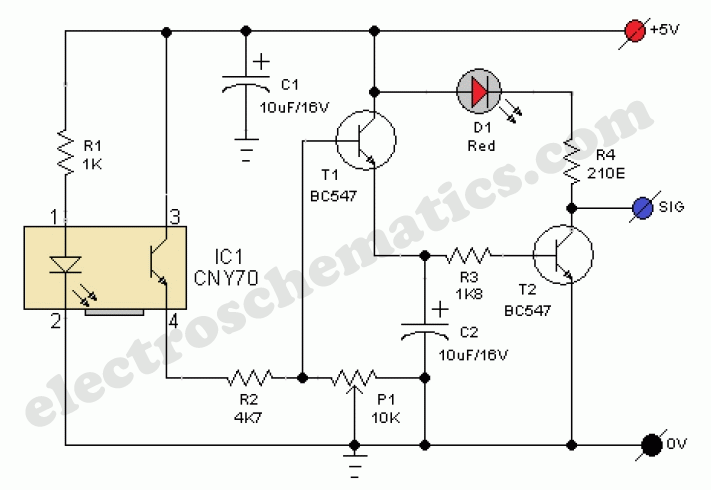
This line-following robot sensor, or surface scanner for robots, is a compact, stamp-sized infrared proximity detector designed for short-range detection, operating within a range of 5 to 10 mm.
The line-following robot sensor operates using infrared light to detect the presence of surfaces or lines beneath the robot. The sensor typically consists of an infrared LED and a photodiode or phototransistor. The LED emits infrared light, which is reflected by the surface below. The photodiode or phototransistor receives the reflected light, and the intensity of this light is used to determine the proximity of the surface.
In a typical application, the sensor is mounted on the underside of the robot. When the robot approaches a line or edge, the amount of reflected infrared light changes, allowing the robot's control system to make real-time adjustments to its movement. This feedback loop enables the robot to follow lines or navigate around obstacles effectively.
The circuit design for this sensor can include additional components such as resistors to limit current through the LED, capacitors for noise filtering, and operational amplifiers to enhance the signal from the photodiode. The output can be connected to a microcontroller or a simple comparator circuit to determine the appropriate response based on the detected signal.
Overall, the line-following robot sensor is an essential component for autonomous robotics, providing reliable surface detection in a compact form factor, enabling efficient navigation and obstacle avoidance.This Line Following Robot sensor or surface scanner for robots is a very simple, stamp-sized, short range (5-10mm) Infrared proximity detector wired around.. 🔗 External reference
The line-following robot sensor operates using infrared light to detect the presence of surfaces or lines beneath the robot. The sensor typically consists of an infrared LED and a photodiode or phototransistor. The LED emits infrared light, which is reflected by the surface below. The photodiode or phototransistor receives the reflected light, and the intensity of this light is used to determine the proximity of the surface.
In a typical application, the sensor is mounted on the underside of the robot. When the robot approaches a line or edge, the amount of reflected infrared light changes, allowing the robot's control system to make real-time adjustments to its movement. This feedback loop enables the robot to follow lines or navigate around obstacles effectively.
The circuit design for this sensor can include additional components such as resistors to limit current through the LED, capacitors for noise filtering, and operational amplifiers to enhance the signal from the photodiode. The output can be connected to a microcontroller or a simple comparator circuit to determine the appropriate response based on the detected signal.
Overall, the line-following robot sensor is an essential component for autonomous robotics, providing reliable surface detection in a compact form factor, enabling efficient navigation and obstacle avoidance.This Line Following Robot sensor or surface scanner for robots is a very simple, stamp-sized, short range (5-10mm) Infrared proximity detector wired around.. 🔗 External reference