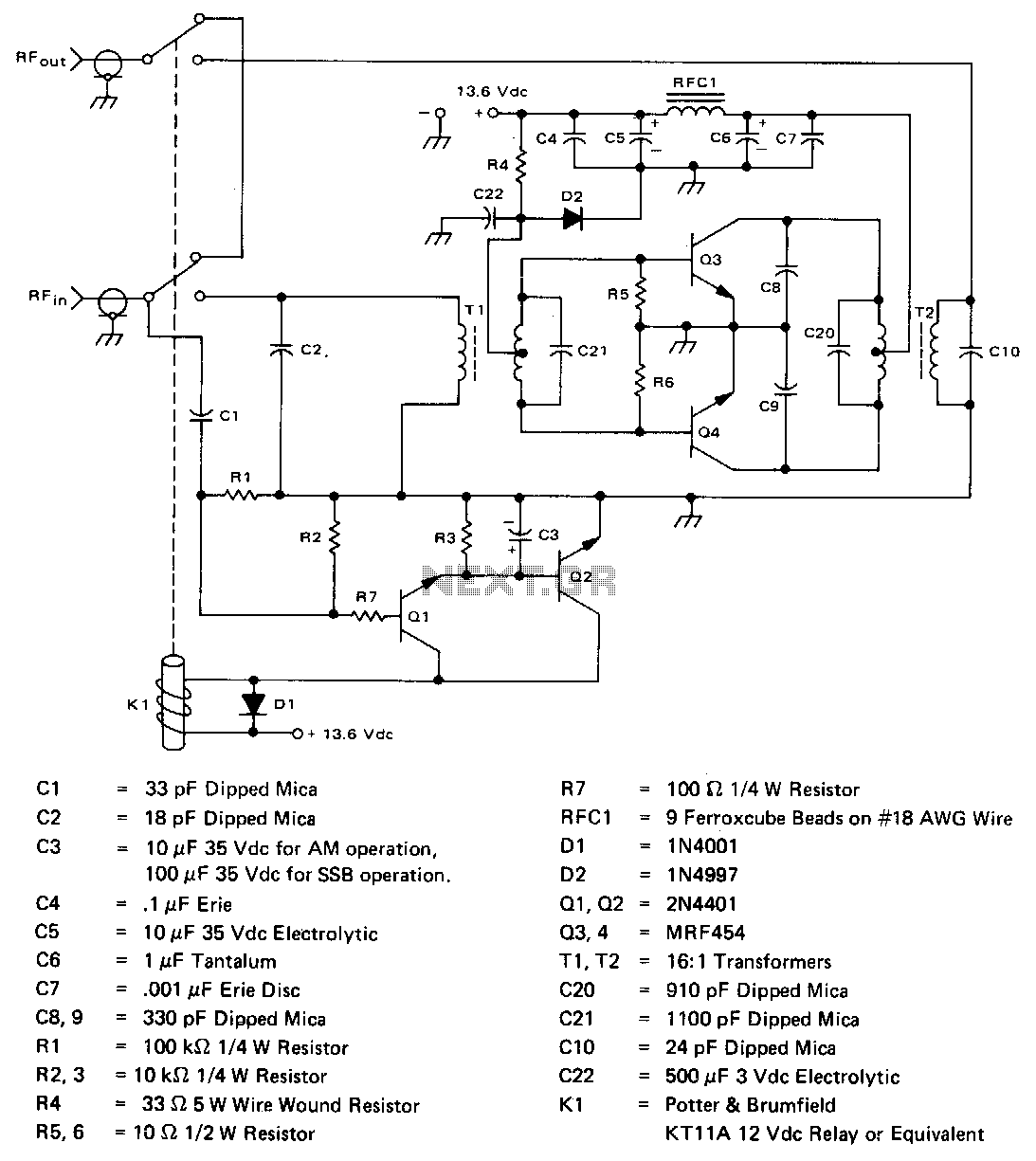
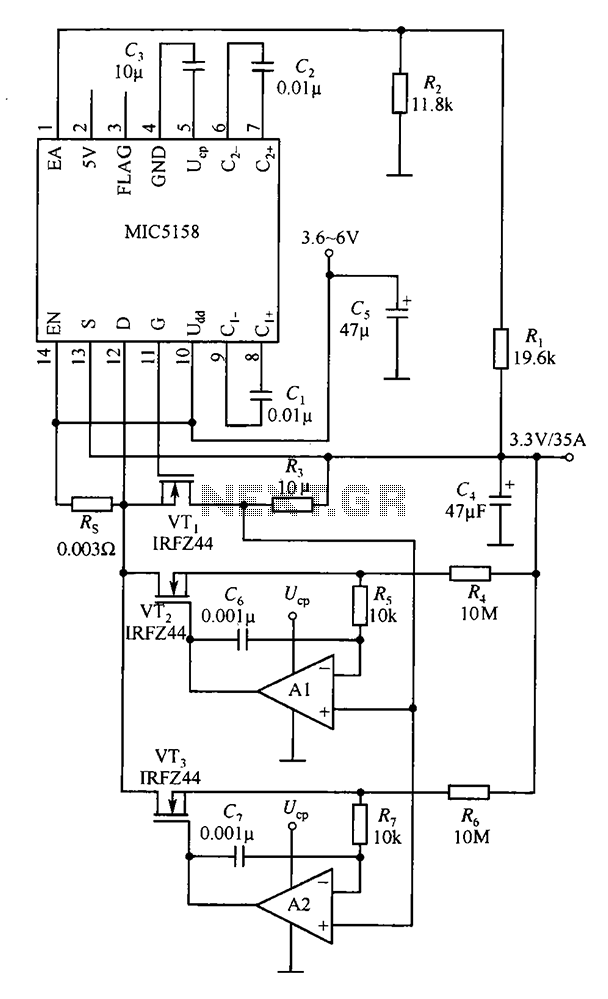
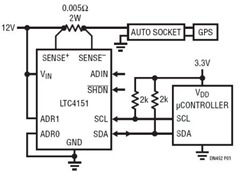
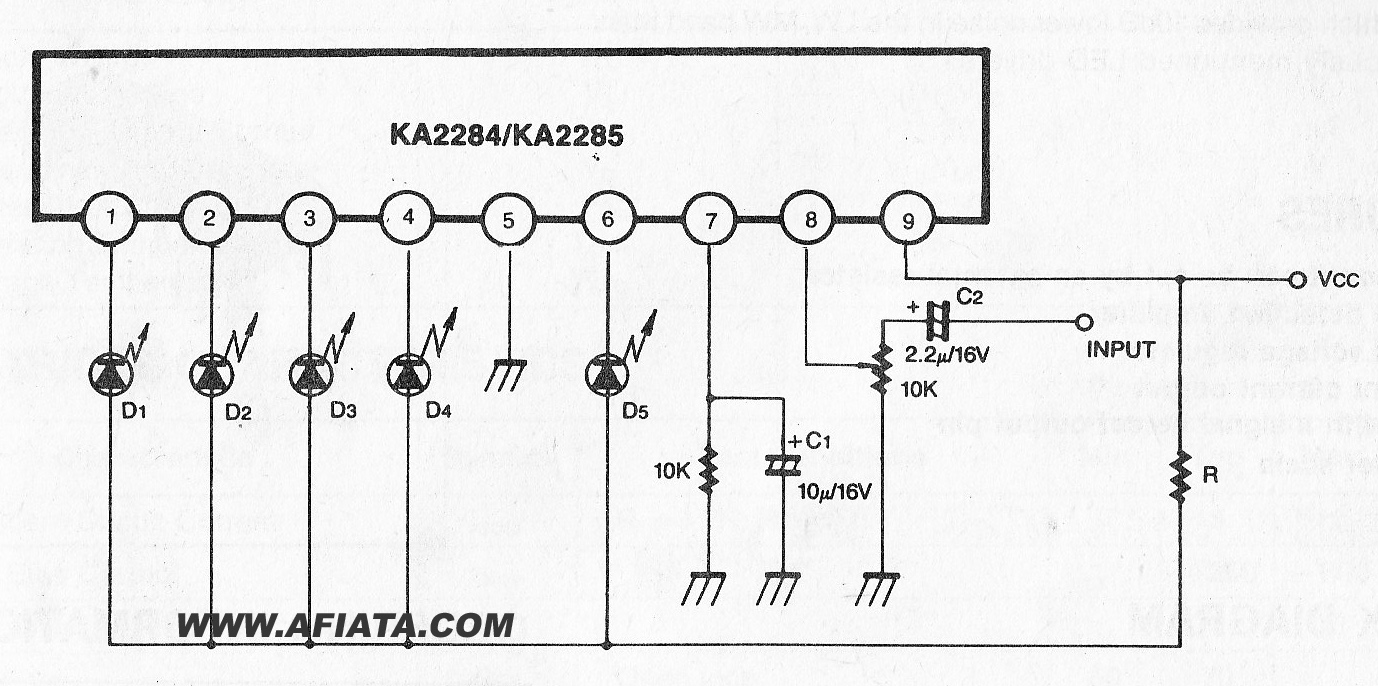
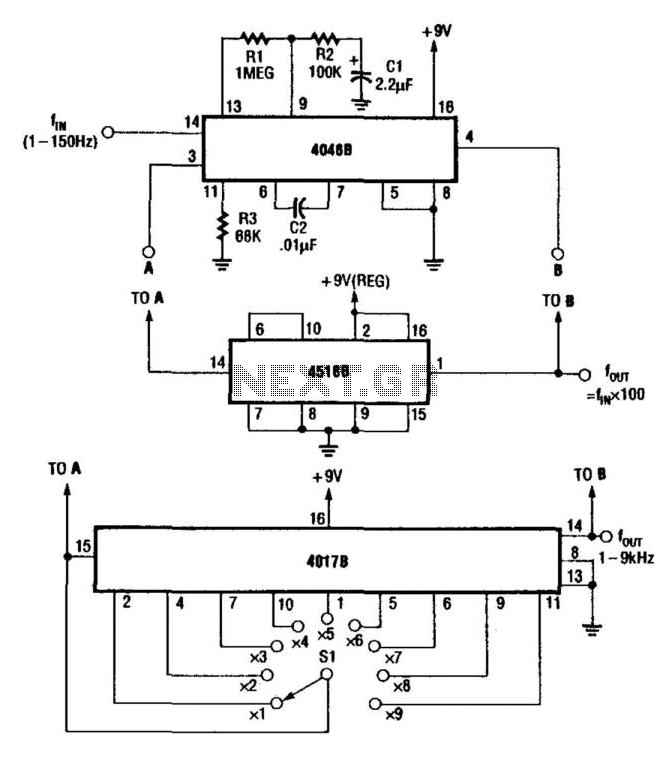
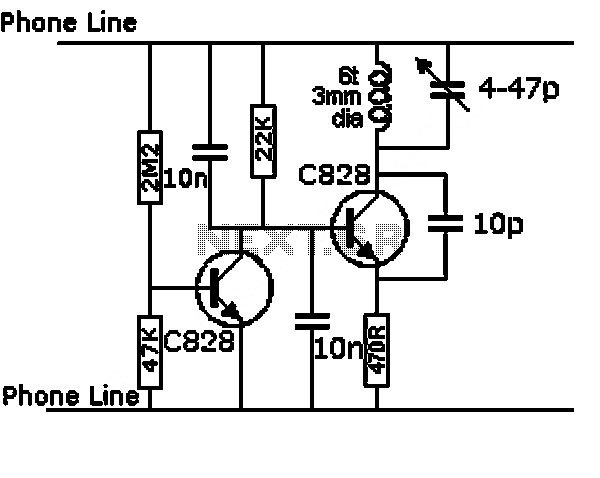
Linear scale ohmmeter
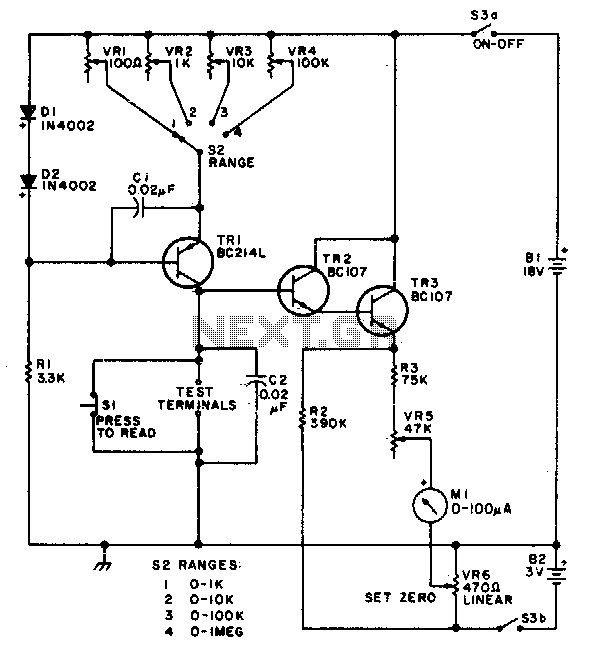
This circuit is designed to provide accurate measurement and a linear resistance scale at the high end. The circuit has four ranges. Additionally, another meter with a current range of 10 µA to 10 mA and a sensitivity of 10,000 ohms per volt is required for setup.
The circuit is structured to deliver precise measurements across multiple resistance ranges, enhancing its utility in various applications. The four ranges facilitate the measurement of different resistance values, allowing users to select the appropriate scale based on the specific requirements of the task at hand. This feature is particularly beneficial in laboratory settings, where accurate resistance measurements are critical.
The inclusion of a second meter capable of measuring current from 10 µA to 10 mA adds versatility to the setup. This meter's high sensitivity of 10,000 ohms per volt indicates its ability to measure low currents with great accuracy, making it suitable for applications involving sensitive electronic components.
In addition to the basic functionality, the circuit may incorporate operational amplifiers to enhance measurement precision and linearity. These amplifiers can be configured to provide a stable reference voltage, improving the overall accuracy of the resistance measurements.
Furthermore, the circuit design may include a switch mechanism that allows users to easily change between the different resistance ranges. This switch can be implemented using rotary or slide switches, ensuring a user-friendly interface.
Overall, the combination of a multi-range resistance measurement circuit and a high-sensitivity current meter provides a comprehensive solution for precise electronic measurements, making it an essential tool for engineers and technicians in the field.This circuit is designed to provide accurate measurement and a linear resistance scale at the high end. The circuit has four ranges Another meter with a current range of 10 µ A to 10 mA and sensitivity of 10,000 ohms per volt is needed for setting up.
The circuit is structured to deliver precise measurements across multiple resistance ranges, enhancing its utility in various applications. The four ranges facilitate the measurement of different resistance values, allowing users to select the appropriate scale based on the specific requirements of the task at hand. This feature is particularly beneficial in laboratory settings, where accurate resistance measurements are critical.
The inclusion of a second meter capable of measuring current from 10 µA to 10 mA adds versatility to the setup. This meter's high sensitivity of 10,000 ohms per volt indicates its ability to measure low currents with great accuracy, making it suitable for applications involving sensitive electronic components.
In addition to the basic functionality, the circuit may incorporate operational amplifiers to enhance measurement precision and linearity. These amplifiers can be configured to provide a stable reference voltage, improving the overall accuracy of the resistance measurements.
Furthermore, the circuit design may include a switch mechanism that allows users to easily change between the different resistance ranges. This switch can be implemented using rotary or slide switches, ensuring a user-friendly interface.
Overall, the combination of a multi-range resistance measurement circuit and a high-sensitivity current meter provides a comprehensive solution for precise electronic measurements, making it an essential tool for engineers and technicians in the field.This circuit is designed to provide accurate measurement and a linear resistance scale at the high end. The circuit has four ranges Another meter with a current range of 10 µ A to 10 mA and sensitivity of 10,000 ohms per volt is needed for setting up.