Liquid level and temperature monitoring circuit diagrams
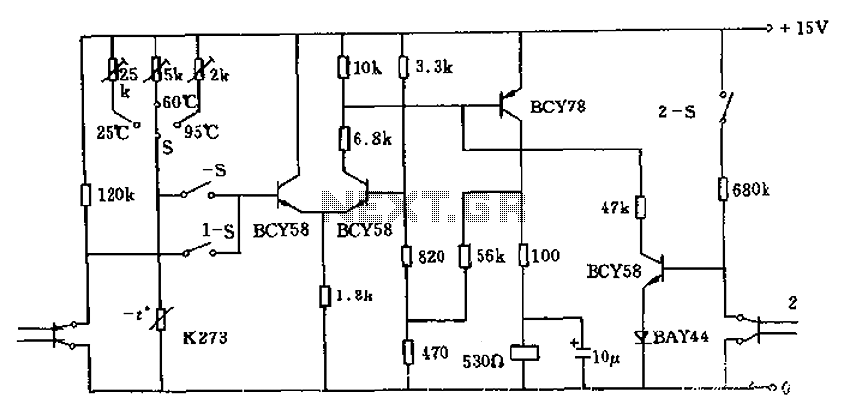
The circuit utilizes a thermistor (K273) to monitor temperature levels and control a relay based on the immersion of two sensor electrodes in a liquid. When the temperature reaches a predetermined threshold, the relay activates to heat the liquid. This mechanism ensures that a minimum volume of liquid is maintained in the container during heating. Additionally, the circuit can be adapted for monitoring other liquid levels. The level sensor connects to a differential amplifier, which can be configured with an additional relay contact to halt the liquid supply once the desired level is achieved, thereby stabilizing the liquid level. Technical specifications include an operating voltage of 15V, an adjustable temperature set point of 95 degrees Celsius, tolerances for voltage fluctuations of -15% to +10%, and a temperature range of 0 to 70 degrees Celsius with a deviation of 1 degree Celsius.
The described circuit operates effectively to maintain and monitor liquid temperatures and levels through a combination of thermal sensing and relay control. The thermistor (K273) serves as the primary temperature sensor, detecting when the liquid reaches the set temperature of 95 degrees Celsius. Upon reaching this threshold, the thermistor's resistance changes, triggering the differential amplifier to send a signal to the relay. The relay, when activated, allows current to flow to the heating element, ensuring that the liquid is heated efficiently.
In terms of liquid level monitoring, the circuit employs two electrodes that are placed within the liquid. These electrodes act as a level sensor, detecting the presence or absence of liquid. The differential amplifier processes the signals from the electrodes to determine the liquid level accurately. When the liquid level falls below a pre-defined minimum, the circuit can be designed to activate the relay, allowing more liquid to flow into the container. Conversely, when the liquid level reaches the desired maximum, the additional relay contact can be engaged to stop the supply of liquid, thus maintaining a constant level.
The circuit's technical specifications highlight its versatility and reliability. Operating at a voltage of 15V ensures compatibility with standard power supplies, while the adjustable temperature setting allows for customization based on specific application requirements. The tolerance for voltage fluctuations and the specified temperature range further enhance the circuit's robustness in various environmental conditions. The temperature deviation of 1 degree Celsius provides a precise control mechanism, ensuring that the system reacts promptly to any changes in temperature or liquid level.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for applications requiring precise temperature and liquid level management, making it ideal for use in industrial processes, laboratory settings, or any scenario where liquid heating and monitoring are critical. Circuit, if the thermistor K273 temperature reaches the setting level or not two sensor electrodes immersed in liquid, so that it is heated by turning on the relay. This ensure s that, when the heating is turned on there is always a minimum amount of liquid in the container. The circuit can also be used to monitor other liquid level. As shown in the level sensor is connected to the differential amplifier 1, the use of additional relay contact can be made to stop the supply of the liquid when the liquid level reaches the required so as to maintain the liquid level constant. Technical data: Operating voltage: 15V adjustable temperature: 95 degrees Celsius at 25.60 or voltage fluctuations (-15 ~ + 10%) and temperature (0 to 70 degrees Celsius) temperature deviation: 1 degree Celsius.
The described circuit operates effectively to maintain and monitor liquid temperatures and levels through a combination of thermal sensing and relay control. The thermistor (K273) serves as the primary temperature sensor, detecting when the liquid reaches the set temperature of 95 degrees Celsius. Upon reaching this threshold, the thermistor's resistance changes, triggering the differential amplifier to send a signal to the relay. The relay, when activated, allows current to flow to the heating element, ensuring that the liquid is heated efficiently.
In terms of liquid level monitoring, the circuit employs two electrodes that are placed within the liquid. These electrodes act as a level sensor, detecting the presence or absence of liquid. The differential amplifier processes the signals from the electrodes to determine the liquid level accurately. When the liquid level falls below a pre-defined minimum, the circuit can be designed to activate the relay, allowing more liquid to flow into the container. Conversely, when the liquid level reaches the desired maximum, the additional relay contact can be engaged to stop the supply of liquid, thus maintaining a constant level.
The circuit's technical specifications highlight its versatility and reliability. Operating at a voltage of 15V ensures compatibility with standard power supplies, while the adjustable temperature setting allows for customization based on specific application requirements. The tolerance for voltage fluctuations and the specified temperature range further enhance the circuit's robustness in various environmental conditions. The temperature deviation of 1 degree Celsius provides a precise control mechanism, ensuring that the system reacts promptly to any changes in temperature or liquid level.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for applications requiring precise temperature and liquid level management, making it ideal for use in industrial processes, laboratory settings, or any scenario where liquid heating and monitoring are critical. Circuit, if the thermistor K273 temperature reaches the setting level or not two sensor electrodes immersed in liquid, so that it is heated by turning on the relay. This ensure s that, when the heating is turned on there is always a minimum amount of liquid in the container. The circuit can also be used to monitor other liquid level. As shown in the level sensor is connected to the differential amplifier 1, the use of additional relay contact can be made to stop the supply of the liquid when the liquid level reaches the required so as to maintain the liquid level constant. Technical data: Operating voltage: 15V adjustable temperature: 95 degrees Celsius at 25.60 or voltage fluctuations (-15 ~ + 10%) and temperature (0 to 70 degrees Celsius) temperature deviation: 1 degree Celsius.