liquid level sensor using 741 op amp

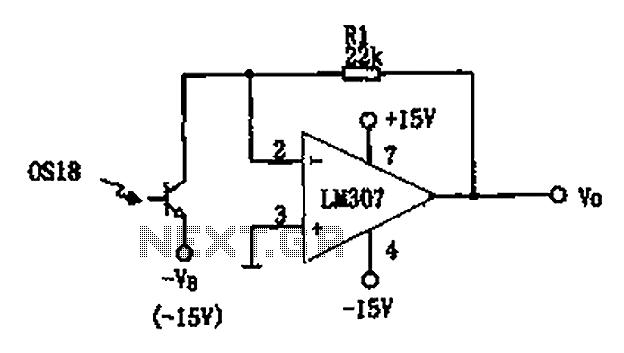
This liquid level sensor circuit employs a common operational amplifier IC 741 configured as a comparator. When the sensor detects that the two fluid levels (which can be represented by two small pieces of PCB or similar conductors) are not present in the liquid, the output voltage of the operational amplifier 741 becomes negative, causing transistor T1 to turn off, resulting in an output voltage of 0 volts. Conversely, when the liquid level sensor is submerged in the fluid, the output voltage of the operational amplifier 741 rises to a few hundred millivolts, allowing transistor T1 to conduct and producing an output voltage of approximately 4 volts across resistor R5.
The circuit operates by utilizing the characteristics of the operational amplifier 741 as a comparator. In this configuration, two input terminals are monitored: one connected to a reference voltage and the other connected to the liquid level sensor. The reference voltage can be set using a voltage divider network to establish a threshold level that corresponds to the desired liquid level.
When the liquid level drops below the threshold, the voltage at the inverting input of the operational amplifier becomes greater than the voltage at the non-inverting input. As a result, the output of the operational amplifier swings to a negative voltage, which turns off transistor T1. Consequently, the voltage across resistor R5 drops to 0 volts, indicating a low liquid level.
On the other hand, when the liquid level rises and the sensor is submerged, the voltage at the non-inverting input increases, surpassing the reference voltage at the inverting input. This condition causes the output of the operational amplifier to rise, producing a positive voltage that turns on transistor T1. As T1 conducts, the output voltage across resistor R5 increases to approximately 4 volts, signaling that the liquid level is above the desired threshold.
This circuit can be easily implemented and modified for various applications by adjusting the reference voltage or using different types of sensors to suit specific liquid detection needs. The use of the operational amplifier 741 ensures reliable performance in detecting liquid levels, making it a suitable choice for various industrial and household applications.This circuit liquid level sensor is using a simple and common operational amplifier IC 741 used as a comparator. When the sensor two-fluid levels (you can use two small pieces of PCB or drivers of some of them) are not found in the fluid of the output voltage of operational amplifier 741 is negative and the T1 is blocked as a result 0 volt voltage
resistor R5. If the liquid level sensor is placed in the fluid of the output voltage of operational amplifier 741 is about a few hundred milli-volts and the transistor T1 conducts, which is an output voltage in the resistance around R5 4 volts. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing the characteristics of the operational amplifier 741 as a comparator. In this configuration, two input terminals are monitored: one connected to a reference voltage and the other connected to the liquid level sensor. The reference voltage can be set using a voltage divider network to establish a threshold level that corresponds to the desired liquid level.
When the liquid level drops below the threshold, the voltage at the inverting input of the operational amplifier becomes greater than the voltage at the non-inverting input. As a result, the output of the operational amplifier swings to a negative voltage, which turns off transistor T1. Consequently, the voltage across resistor R5 drops to 0 volts, indicating a low liquid level.
On the other hand, when the liquid level rises and the sensor is submerged, the voltage at the non-inverting input increases, surpassing the reference voltage at the inverting input. This condition causes the output of the operational amplifier to rise, producing a positive voltage that turns on transistor T1. As T1 conducts, the output voltage across resistor R5 increases to approximately 4 volts, signaling that the liquid level is above the desired threshold.
This circuit can be easily implemented and modified for various applications by adjusting the reference voltage or using different types of sensors to suit specific liquid detection needs. The use of the operational amplifier 741 ensures reliable performance in detecting liquid levels, making it a suitable choice for various industrial and household applications.This circuit liquid level sensor is using a simple and common operational amplifier IC 741 used as a comparator. When the sensor two-fluid levels (you can use two small pieces of PCB or drivers of some of them) are not found in the fluid of the output voltage of operational amplifier 741 is negative and the T1 is blocked as a result 0 volt voltage
resistor R5. If the liquid level sensor is placed in the fluid of the output voltage of operational amplifier 741 is about a few hundred milli-volts and the transistor T1 conducts, which is an output voltage in the resistance around R5 4 volts. 🔗 External reference