LMD18245 bipolar stepper motor driver circuit design
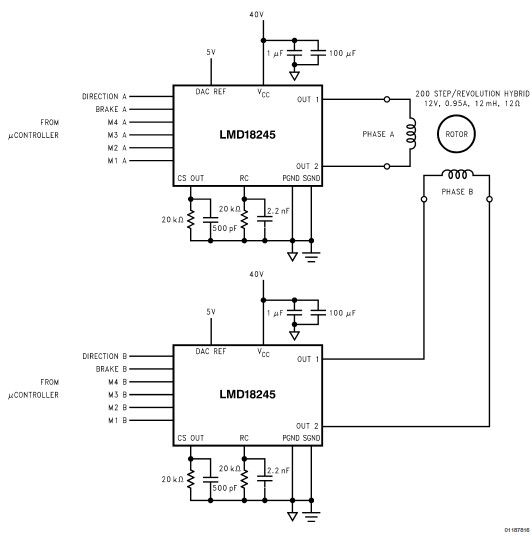
LMD18245 bipolar stepper motor driver circuit design using few electronic parts
The LMD18245 is a versatile bipolar stepper motor driver designed to control stepper motors with precision and efficiency. This circuit utilizes a minimal number of electronic components, making it suitable for applications where space and cost are critical factors. The LMD18245 integrates power and control functionalities, enabling seamless operation of stepper motors in various configurations.
The circuit typically includes the LMD18245 driver IC, which can handle a wide range of input voltages and provides high current output, accommodating different stepper motor specifications. Additional components often involved in the design are resistors, capacitors, and diodes, which help in managing the input signals, filtering noise, and protecting the circuit from voltage spikes.
The design can be configured for both full-step and half-step driving modes, allowing for flexibility in motor control. Full-step mode provides maximum torque, while half-step mode offers smoother motion and increased resolution. The circuit can be controlled via a microcontroller or a dedicated stepper motor controller, which sends pulses to the LMD18245 to dictate the stepping sequence.
To ensure reliable operation, the circuit may incorporate thermal management features, such as heat sinks or temperature sensors, to monitor the temperature of the driver IC. Proper heat dissipation is critical to maintain performance and prevent thermal shutdown.
Overall, the LMD18245 bipolar stepper motor driver circuit design is an efficient solution for driving stepper motors in various applications, including robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice among engineers and hobbyists alike.LMD18245 bipolar stepper motor driver circuit design using few electronic parts 🔗 External reference
The LMD18245 is a versatile bipolar stepper motor driver designed to control stepper motors with precision and efficiency. This circuit utilizes a minimal number of electronic components, making it suitable for applications where space and cost are critical factors. The LMD18245 integrates power and control functionalities, enabling seamless operation of stepper motors in various configurations.
The circuit typically includes the LMD18245 driver IC, which can handle a wide range of input voltages and provides high current output, accommodating different stepper motor specifications. Additional components often involved in the design are resistors, capacitors, and diodes, which help in managing the input signals, filtering noise, and protecting the circuit from voltage spikes.
The design can be configured for both full-step and half-step driving modes, allowing for flexibility in motor control. Full-step mode provides maximum torque, while half-step mode offers smoother motion and increased resolution. The circuit can be controlled via a microcontroller or a dedicated stepper motor controller, which sends pulses to the LMD18245 to dictate the stepping sequence.
To ensure reliable operation, the circuit may incorporate thermal management features, such as heat sinks or temperature sensors, to monitor the temperature of the driver IC. Proper heat dissipation is critical to maintain performance and prevent thermal shutdown.
Overall, the LMD18245 bipolar stepper motor driver circuit design is an efficient solution for driving stepper motors in various applications, including robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice among engineers and hobbyists alike.LMD18245 bipolar stepper motor driver circuit design using few electronic parts 🔗 External reference