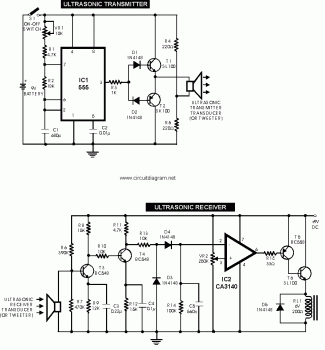
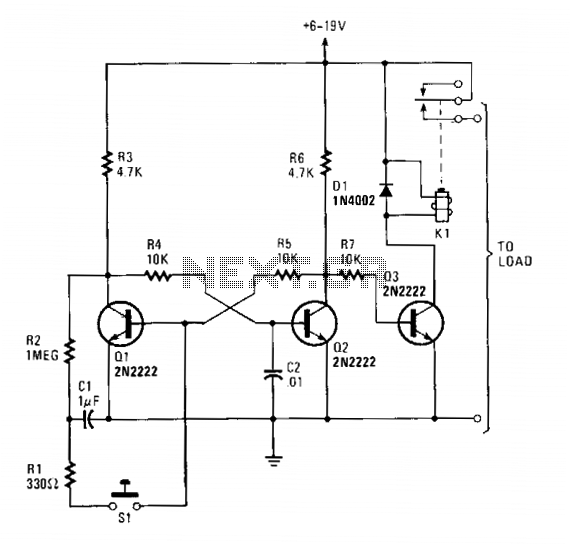
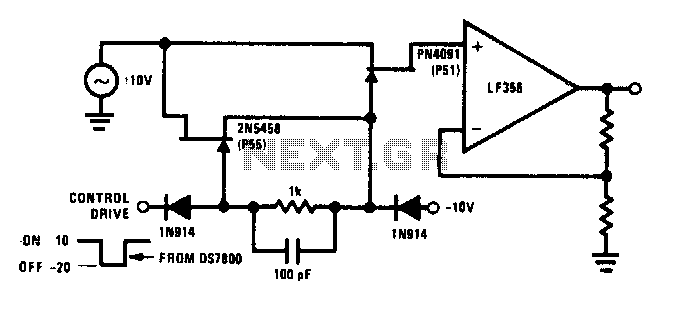
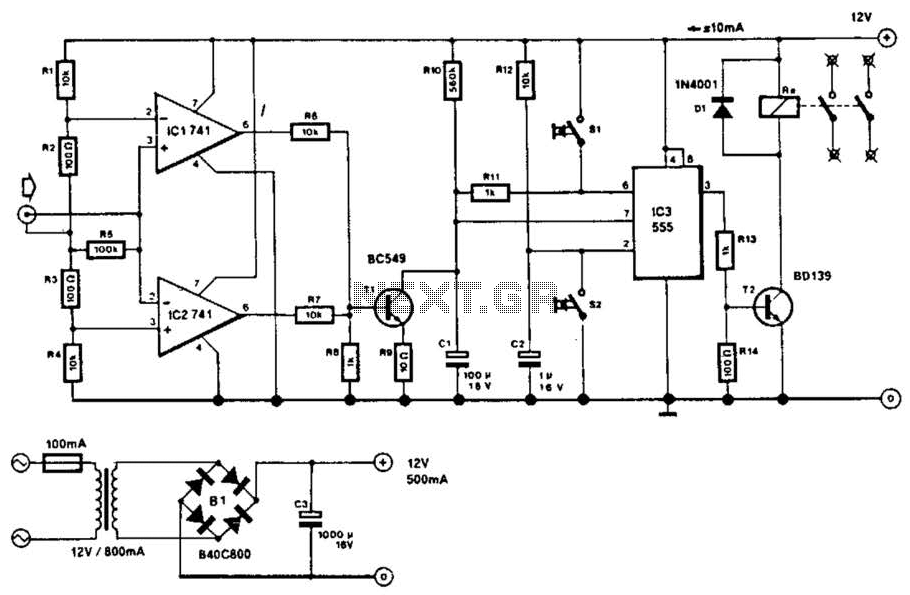
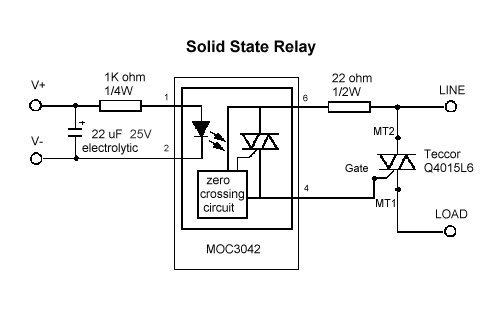
Load Sensing Automatic Switch
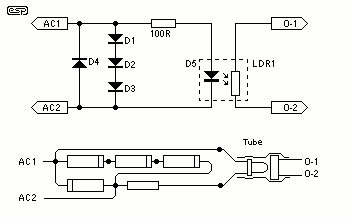
The circuit of the mains current detector is shown in Figure 1. By using a few cheap diodes, a resistor, LED and LDR, a simple opto-isolated detector can be created. This entire circuit dissipates very low power, and can safely be housed in a heatshrink wrapper to ensure that contact with live wiring is not possible. This will also keep light away from the LDR. These are cheap and easy to use. I found that I could detect as little as 10mA of mains current with this circuit, and no distress was created at 0.5A. The diodes will get very warm at higher currents. Note that because of the 1A diodes used, this is the absolute maximum current of the switched load. If a higher current is expected, you must use high current diodes to prevent failure.
The mains current detector circuit utilizes a minimalistic design to achieve effective opto-isolation while detecting AC current. The primary components include low-cost diodes, a resistor, an LED, and a light-dependent resistor (LDR). The diodes are arranged to rectify the AC mains current, allowing the circuit to operate with minimal power dissipation.
The LED serves as an indicator, illuminating when current is detected, while the LDR is utilized to enhance the opto-isolation aspect of the circuit. The heatshrink wrapper serves a dual purpose: it protects the circuit from accidental contact with live wiring and shields the LDR from ambient light, ensuring accurate detection of current.
The circuit has been tested to detect currents as low as 10mA, demonstrating its sensitivity and effectiveness. At a load of 0.5A, the circuit operates without distress, although it is noted that the diodes may become warm under higher current conditions. It is crucial to adhere to the specifications of the components used; the current rating of the diodes is a critical factor, as the circuit is designed for a maximum switched load of 1A. For applications requiring higher current detection, the use of diodes rated for higher currents is strongly recommended to prevent component failure.
This circuit design exemplifies a practical solution for current detection in various applications, leveraging simple components for reliable operation while maintaining safety standards.The circuit of the mains current detector is shown in Figure 1. By using a few cheap diodes, a resistor, LED and LDR, a simple opto-isolated detector can be created. This entire circuit dissipates very low power, and can safely be housed in a heatshrink wrapper to ensure that contact with live wiring is not possible.
This will also keep light away from the LDR. These are cheap and easy to use. I found that I could detect as little as 10mA of mains current with this circuit, and no distress was created at 0.5A. The diodes will get very warm at higher currents. Note that because of the 1A diodes used, this is the absolute maximum current of the switched load. If a higher current is expected, you must use high current diodes to prevent failure. I shall leave it to the reader and the local electronics supplier t 🔗 External reference
The mains current detector circuit utilizes a minimalistic design to achieve effective opto-isolation while detecting AC current. The primary components include low-cost diodes, a resistor, an LED, and a light-dependent resistor (LDR). The diodes are arranged to rectify the AC mains current, allowing the circuit to operate with minimal power dissipation.
The LED serves as an indicator, illuminating when current is detected, while the LDR is utilized to enhance the opto-isolation aspect of the circuit. The heatshrink wrapper serves a dual purpose: it protects the circuit from accidental contact with live wiring and shields the LDR from ambient light, ensuring accurate detection of current.
The circuit has been tested to detect currents as low as 10mA, demonstrating its sensitivity and effectiveness. At a load of 0.5A, the circuit operates without distress, although it is noted that the diodes may become warm under higher current conditions. It is crucial to adhere to the specifications of the components used; the current rating of the diodes is a critical factor, as the circuit is designed for a maximum switched load of 1A. For applications requiring higher current detection, the use of diodes rated for higher currents is strongly recommended to prevent component failure.
This circuit design exemplifies a practical solution for current detection in various applications, leveraging simple components for reliable operation while maintaining safety standards.The circuit of the mains current detector is shown in Figure 1. By using a few cheap diodes, a resistor, LED and LDR, a simple opto-isolated detector can be created. This entire circuit dissipates very low power, and can safely be housed in a heatshrink wrapper to ensure that contact with live wiring is not possible.
This will also keep light away from the LDR. These are cheap and easy to use. I found that I could detect as little as 10mA of mains current with this circuit, and no distress was created at 0.5A. The diodes will get very warm at higher currents. Note that because of the 1A diodes used, this is the absolute maximum current of the switched load. If a higher current is expected, you must use high current diodes to prevent failure. I shall leave it to the reader and the local electronics supplier t 🔗 External reference