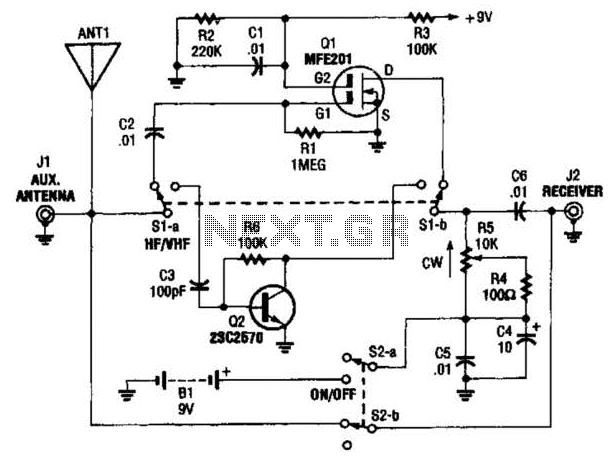
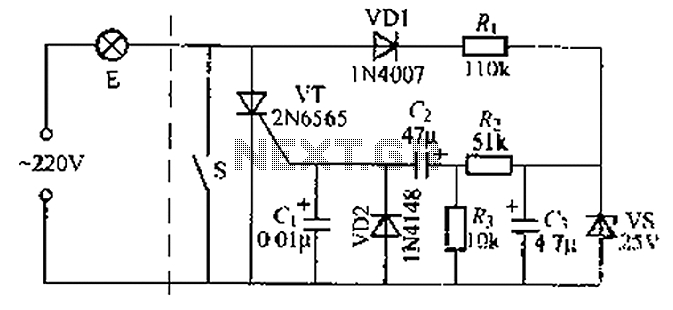
High frequency analog switch
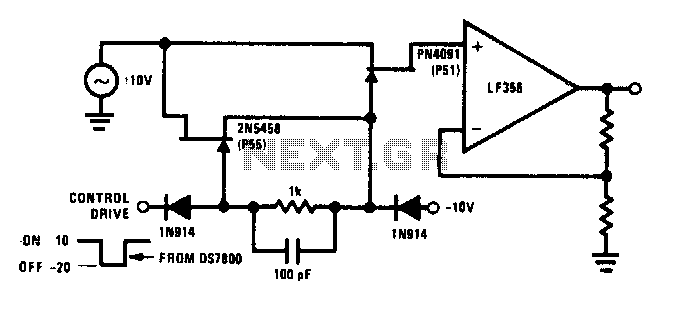
The commutator circuit delivers low impedance gate drive to the PN4091 analog switch for both on and off drive conditions. This circuit also achieves near-ideal gate drive conditions for high-frequency signal handling by offering low AC impedance during off drive and high AC impedance during on drive to the PN4091.
The commutator circuit is designed to optimize the performance of the PN4091 analog switch, which is critical in applications requiring efficient signal routing and switching. The low impedance gate drive ensures that the switch can be turned on and off rapidly, which is essential for high-frequency operations.
In the on state, the circuit provides high AC impedance, which minimizes power loss and allows for better signal integrity. This high impedance state is crucial for maintaining the quality of the signal being switched, particularly in high-speed applications where signal degradation can lead to performance issues.
Conversely, during the off state, the circuit presents a low AC impedance to the PN4091. This characteristic is vital for quickly discharging any residual charge from the gate of the switch, ensuring that it turns off efficiently and without delay. The low impedance allows for faster recovery times, enhancing the overall switching speed and responsiveness of the circuit.
The careful design of the commutator circuit, including the selection of components and their arrangement, plays a significant role in achieving these impedance characteristics. Capacitors, resistors, and possibly inductive elements are strategically utilized to create the desired impedance profiles. The circuit may also incorporate feedback mechanisms to further refine the gate drive characteristics, ensuring that the PN4091 operates effectively across a range of frequencies and signal conditions.
Overall, the commutator circuit is a critical component in systems utilizing the PN4091 analog switch, enabling high-performance operation with minimal signal degradation and rapid switching capabilities.Commutator circuit provides low impedance gate drive to the PN4091 analog switch for both on and off drive conditions This circuit also approaches the ideal gate drive conditions for high frequency signal handling by providing a low ac impedance for off drive and high ac impedance for on drive to the PN4091.
The commutator circuit is designed to optimize the performance of the PN4091 analog switch, which is critical in applications requiring efficient signal routing and switching. The low impedance gate drive ensures that the switch can be turned on and off rapidly, which is essential for high-frequency operations.
In the on state, the circuit provides high AC impedance, which minimizes power loss and allows for better signal integrity. This high impedance state is crucial for maintaining the quality of the signal being switched, particularly in high-speed applications where signal degradation can lead to performance issues.
Conversely, during the off state, the circuit presents a low AC impedance to the PN4091. This characteristic is vital for quickly discharging any residual charge from the gate of the switch, ensuring that it turns off efficiently and without delay. The low impedance allows for faster recovery times, enhancing the overall switching speed and responsiveness of the circuit.
The careful design of the commutator circuit, including the selection of components and their arrangement, plays a significant role in achieving these impedance characteristics. Capacitors, resistors, and possibly inductive elements are strategically utilized to create the desired impedance profiles. The circuit may also incorporate feedback mechanisms to further refine the gate drive characteristics, ensuring that the PN4091 operates effectively across a range of frequencies and signal conditions.
Overall, the commutator circuit is a critical component in systems utilizing the PN4091 analog switch, enabling high-performance operation with minimal signal degradation and rapid switching capabilities.Commutator circuit provides low impedance gate drive to the PN4091 analog switch for both on and off drive conditions This circuit also approaches the ideal gate drive conditions for high frequency signal handling by providing a low ac impedance for off drive and high ac impedance for on drive to the PN4091.