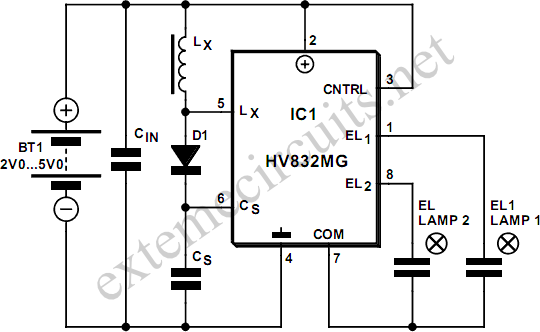
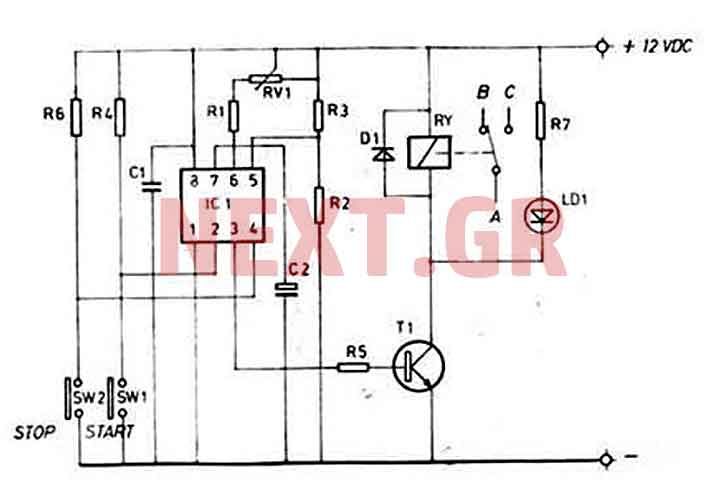
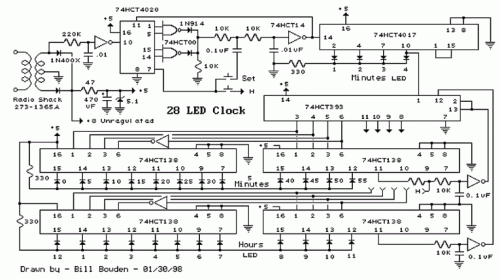
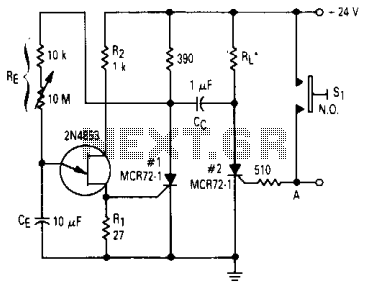
Long Interval RC Timer Using Op-Amp
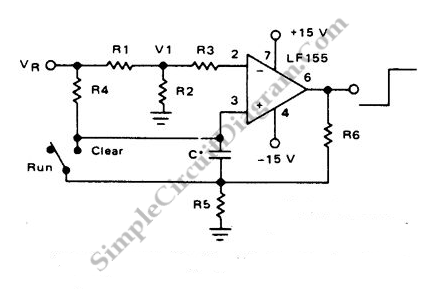
By utilizing a high-gain, high-impedance operational amplifier, it is possible to construct a long time delay circuit using a resistor-capacitor (RC) configuration, as it allows for high...
An operational amplifier (op-amp) is a versatile component widely used in electronic circuits, particularly in signal processing and conditioning applications. When designing a long time delay circuit with an op-amp, the resistor-capacitor (RC) network plays a crucial role in determining the delay time. The time constant (τ) of an RC circuit is given by the product of the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values, expressed as τ = R × C. This time constant dictates how quickly the capacitor charges and discharges, thereby influencing the delay duration.
In a typical configuration, the op-amp is used in a non-inverting configuration to achieve high input impedance, allowing for minimal loading on the preceding circuit stage. This is particularly beneficial in applications where the signal source has a high output impedance. The high gain of the op-amp ensures that even small voltage changes across the capacitor can significantly affect the output voltage, thus providing a controlled and precise delay.
To implement the RC time delay, the resistor is connected in series with the capacitor, which is then connected to the inverting input of the op-amp. The non-inverting input is typically connected to a reference voltage or ground. When a voltage is applied to the circuit, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor, and the op-amp amplifies the voltage across the capacitor. The output voltage of the op-amp will rise gradually, following the exponential charging curve of the capacitor, until it reaches a predefined threshold.
The feedback configuration can also be adjusted to set a specific output level or to create a trigger point for subsequent stages in the circuit. For instance, a Schmitt trigger can be incorporated to provide hysteresis, preventing false triggering due to noise or small fluctuations in the input signal.
In summary, the use of a high-gain, high-impedance operational amplifier in conjunction with an RC circuit enables the design of effective time delay circuits. The selection of appropriate resistor and capacitor values is essential for achieving the desired delay duration, while the op-amp's characteristics ensure high performance in terms of signal integrity and responsiveness.With the help of high gain high impedance operational amplifier, we can build a long time delay with resistor-capacitor (RC) circuit since it allow high.. 🔗 External reference
An operational amplifier (op-amp) is a versatile component widely used in electronic circuits, particularly in signal processing and conditioning applications. When designing a long time delay circuit with an op-amp, the resistor-capacitor (RC) network plays a crucial role in determining the delay time. The time constant (τ) of an RC circuit is given by the product of the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values, expressed as τ = R × C. This time constant dictates how quickly the capacitor charges and discharges, thereby influencing the delay duration.
In a typical configuration, the op-amp is used in a non-inverting configuration to achieve high input impedance, allowing for minimal loading on the preceding circuit stage. This is particularly beneficial in applications where the signal source has a high output impedance. The high gain of the op-amp ensures that even small voltage changes across the capacitor can significantly affect the output voltage, thus providing a controlled and precise delay.
To implement the RC time delay, the resistor is connected in series with the capacitor, which is then connected to the inverting input of the op-amp. The non-inverting input is typically connected to a reference voltage or ground. When a voltage is applied to the circuit, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor, and the op-amp amplifies the voltage across the capacitor. The output voltage of the op-amp will rise gradually, following the exponential charging curve of the capacitor, until it reaches a predefined threshold.
The feedback configuration can also be adjusted to set a specific output level or to create a trigger point for subsequent stages in the circuit. For instance, a Schmitt trigger can be incorporated to provide hysteresis, preventing false triggering due to noise or small fluctuations in the input signal.
In summary, the use of a high-gain, high-impedance operational amplifier in conjunction with an RC circuit enables the design of effective time delay circuits. The selection of appropriate resistor and capacitor values is essential for achieving the desired delay duration, while the op-amp's characteristics ensure high performance in terms of signal integrity and responsiveness.With the help of high gain high impedance operational amplifier, we can build a long time delay with resistor-capacitor (RC) circuit since it allow high.. 🔗 External reference