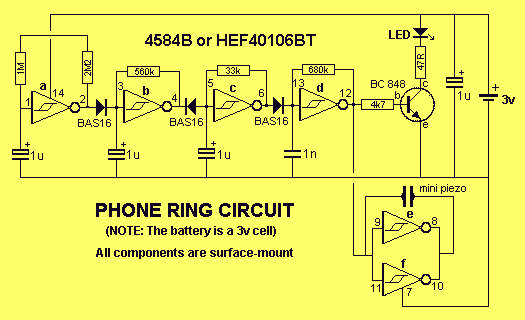
Loud ringer for phone using KA2411
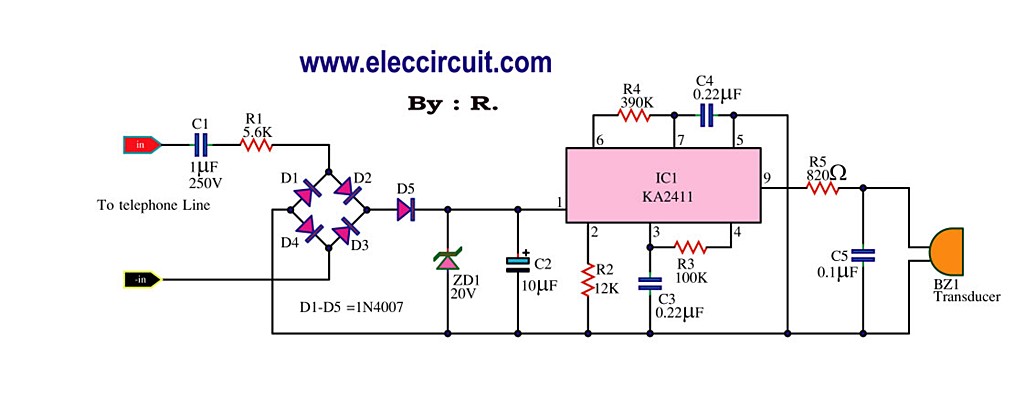
This circuit is designed to generate a loud ringing tone for an electricity bell in older telephones. It serves as a replacement for the original ringer, which may be lost, eliminating the need for a new phone. The circuit detects the ringing signal tone, providing both visual and audible alerts. It is user-friendly and of good quality. The power supply detects the ringing signal on the telephone line, indicating incoming calls. When a call is received, capacitors C1 and C2 couple the AC voltage to diodes D1 and D2, reducing the signal voltage to approximately 10V. Diode D2 detects only the negative signal, while D1 detects the positive signal. Four LEDs flash in sync with the ringing tone frequency of about 20 Hz, and a piezo speaker emits audio beeps corresponding to the ringing tone. The incoming call signal from the telephone lines passes through C1 and R1 to the bridge diode circuit D1-D4, generating a positive voltage of 20V supplied to pin 1 of IC1 (either KA2411 or CS8205), which functions as the telephone bell replacement IC. When supplied with voltage, IC1 generates ringing signals through R5, driving the piezoelectric transducer BZ1 to produce a bell tone. The sound is generated by an oscillator circuit consisting of R3 and C3, which creates a low-frequency output.
This circuit operates by utilizing a combination of passive and active components to effectively detect and respond to incoming telephone calls. The coupling capacitors, C1 and C2, are essential for isolating the AC ringing signal from the DC bias of the telephone line, ensuring that only the AC component is processed. The bridge rectifier formed by diodes D1 to D4 converts the AC signal to a DC voltage suitable for powering the IC.
The IC (KA2411 or CS8205) is specifically designed for generating ringing signals, making it an ideal choice for this application. Upon receiving the 20V supply, the IC activates its internal oscillator, which produces a square wave output at the desired frequency. This output is then fed through a resistor (R5) to the piezoelectric transducer (BZ1), which converts the electrical signal back into audible sound.
The flashing LEDs serve a dual purpose: they provide a visual indication of the incoming call and synchronize their flashing with the ringing frequency, enhancing the circuit's functionality. The frequency of the oscillation can be adjusted by changing the values of R3 and C3, allowing for customization of the ringing tone.
Overall, this circuit is a practical solution for anyone needing to replace a missing telephone ringer, combining simplicity, effectiveness, and ease of use in a compact design.This phone is loud ringing tone circuit for generating the electricity bell in the old telephone. This circuit is relatively loud. so can use to replacement the same ringer or the original telephone may be lost. We do not need a new phone. The detect ringing signal tone circuit with light and sound. It is easy to use and good quality, Do not enter the power supply. Which as Detect ringing signal tone circuit Or ring tones on the telephone line, a signal incoming calls. When an incoming call, When an incoming call, The C1, C2, will act as a coupling signal AC Volt to diodes D1, D2.
Signal voltage is reduced down to approximately 10V. By D2 to detect, only a negative signal, One extreme to the other end of the wire loop. The D1 detect a positive signal, and the 4 LED. Flashing light attached to it, with frequency of the ringging tone. Which is about 20 Hz. and piezo speaker, show the audio beep. beep, followed by a tone frequency of the ringing. The called signal from the telephone lines is entered through C1, R1 Come to the bridge diode circuit D1-D4, D5 is the positive voltage at 20V supply to pin 1 of IC1 that KA2411 or CS8205 as the Telephone Bell Replacement IC. When IC1 is given the supply volt as I said, it will generator a ringing signals through the R5, to drive the Piezoelectric transducer BZ1 be a bell tone out to hear.
We hear the sound of the Oscillator 2 series, which differ by the output frequency chops to be a frequency generator circuits. Which consists with R3, C3 is low. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates by utilizing a combination of passive and active components to effectively detect and respond to incoming telephone calls. The coupling capacitors, C1 and C2, are essential for isolating the AC ringing signal from the DC bias of the telephone line, ensuring that only the AC component is processed. The bridge rectifier formed by diodes D1 to D4 converts the AC signal to a DC voltage suitable for powering the IC.
The IC (KA2411 or CS8205) is specifically designed for generating ringing signals, making it an ideal choice for this application. Upon receiving the 20V supply, the IC activates its internal oscillator, which produces a square wave output at the desired frequency. This output is then fed through a resistor (R5) to the piezoelectric transducer (BZ1), which converts the electrical signal back into audible sound.
The flashing LEDs serve a dual purpose: they provide a visual indication of the incoming call and synchronize their flashing with the ringing frequency, enhancing the circuit's functionality. The frequency of the oscillation can be adjusted by changing the values of R3 and C3, allowing for customization of the ringing tone.
Overall, this circuit is a practical solution for anyone needing to replace a missing telephone ringer, combining simplicity, effectiveness, and ease of use in a compact design.This phone is loud ringing tone circuit for generating the electricity bell in the old telephone. This circuit is relatively loud. so can use to replacement the same ringer or the original telephone may be lost. We do not need a new phone. The detect ringing signal tone circuit with light and sound. It is easy to use and good quality, Do not enter the power supply. Which as Detect ringing signal tone circuit Or ring tones on the telephone line, a signal incoming calls. When an incoming call, When an incoming call, The C1, C2, will act as a coupling signal AC Volt to diodes D1, D2.
Signal voltage is reduced down to approximately 10V. By D2 to detect, only a negative signal, One extreme to the other end of the wire loop. The D1 detect a positive signal, and the 4 LED. Flashing light attached to it, with frequency of the ringging tone. Which is about 20 Hz. and piezo speaker, show the audio beep. beep, followed by a tone frequency of the ringing. The called signal from the telephone lines is entered through C1, R1 Come to the bridge diode circuit D1-D4, D5 is the positive voltage at 20V supply to pin 1 of IC1 that KA2411 or CS8205 as the Telephone Bell Replacement IC. When IC1 is given the supply volt as I said, it will generator a ringing signals through the R5, to drive the Piezoelectric transducer BZ1 be a bell tone out to hear.
We hear the sound of the Oscillator 2 series, which differ by the output frequency chops to be a frequency generator circuits. Which consists with R3, C3 is low. 🔗 External reference