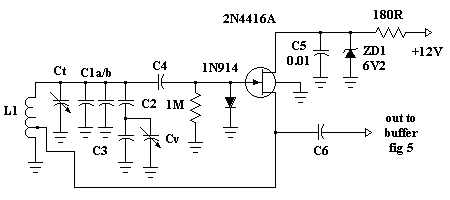
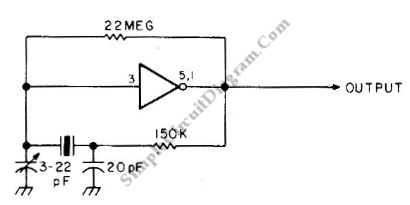
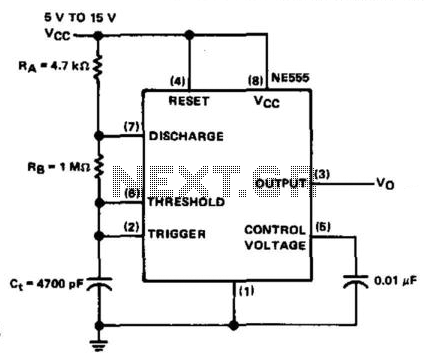
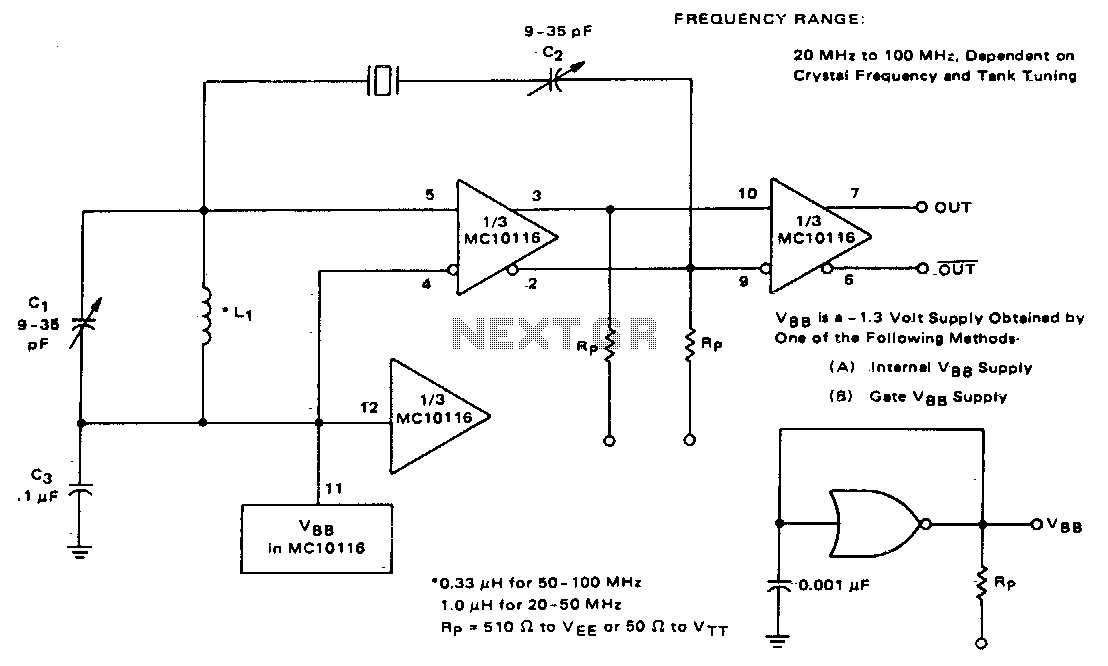
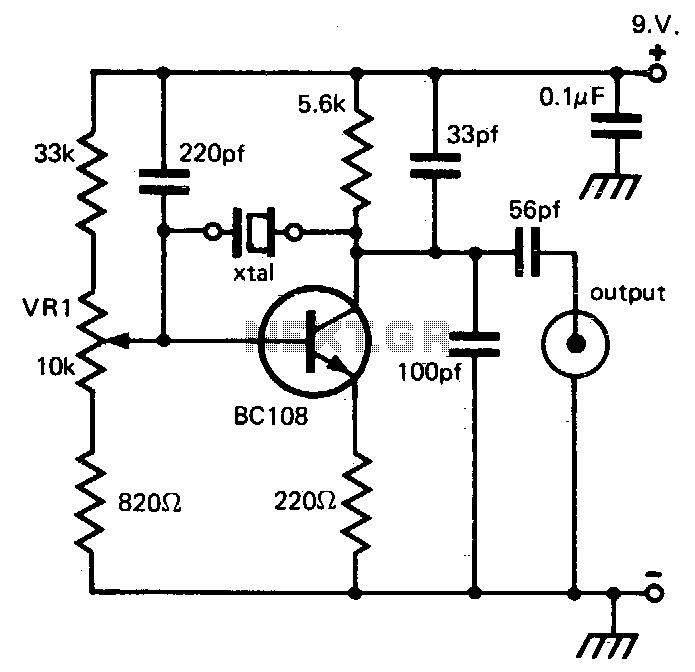
Low-frequency oscillator 10-150khz
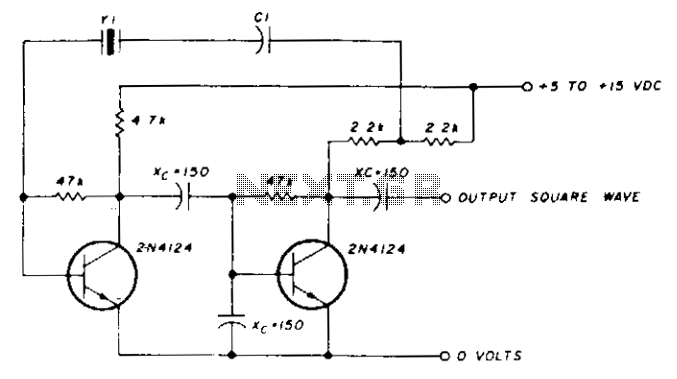
A capacitor in series with the crystal may be utilized to adjust the oscillator output frequency. The value may range between 20 pF and 0.01 µF, or it may be a trimmer capacitor, and it will approximately equal the crystal load capacitance. The values are approximate and can vary for most circuits and frequencies; this is also true for resistance values. Adequate power supply decoupling is required, and local decoupling capacitors near the oscillator are recommended. All leads should be extremely short in high-frequency circuits.
In oscillator circuits, the inclusion of a capacitor in series with the crystal plays a crucial role in fine-tuning the output frequency. The capacitor's value, which can vary from 20 picofarads (pF) to 0.01 microfarads (µF), or potentially be a variable trimmer capacitor, is selected to match the load capacitance specified for the crystal being used. This matching is essential to ensure that the oscillator operates at the desired frequency, as deviations can lead to frequency instability or inaccuracies.
The approximate nature of the capacitor and resistance values highlights the need for careful consideration during circuit design, as these values can differ based on the specific application and the frequencies involved. This variability necessitates a thorough understanding of the circuit's operational environment to ensure optimal performance.
Power supply decoupling is another critical aspect of oscillator design. It is recommended to use local decoupling capacitors placed close to the oscillator to filter out high-frequency noise and provide a stable power supply. This practice minimizes the risk of oscillation frequency drift caused by power supply fluctuations.
Additionally, in high-frequency circuits, it is imperative to maintain short lead lengths. Longer leads can introduce unwanted inductance and capacitance, which can adversely affect the circuit's performance, leading to signal integrity issues and potential oscillation problems. Therefore, careful layout and routing of traces are essential to preserve the high-frequency characteristics of the oscillator circuit.CI in series with the crystal may be used to adjust the oscillator output frequency· Value may range between 20 pF and 0.01 µ¥, or may be a trimmer capacitor and will approximately equal the crystal load capacitance. X values are approximate and can vary for most circuits and frequencies; this is also true for resistance values.
Adequate power supply decoupling is required; local decoupling capacitors near the oscillator are recommended. All leads should be extremely short in high frequency circuits.
In oscillator circuits, the inclusion of a capacitor in series with the crystal plays a crucial role in fine-tuning the output frequency. The capacitor's value, which can vary from 20 picofarads (pF) to 0.01 microfarads (µF), or potentially be a variable trimmer capacitor, is selected to match the load capacitance specified for the crystal being used. This matching is essential to ensure that the oscillator operates at the desired frequency, as deviations can lead to frequency instability or inaccuracies.
The approximate nature of the capacitor and resistance values highlights the need for careful consideration during circuit design, as these values can differ based on the specific application and the frequencies involved. This variability necessitates a thorough understanding of the circuit's operational environment to ensure optimal performance.
Power supply decoupling is another critical aspect of oscillator design. It is recommended to use local decoupling capacitors placed close to the oscillator to filter out high-frequency noise and provide a stable power supply. This practice minimizes the risk of oscillation frequency drift caused by power supply fluctuations.
Additionally, in high-frequency circuits, it is imperative to maintain short lead lengths. Longer leads can introduce unwanted inductance and capacitance, which can adversely affect the circuit's performance, leading to signal integrity issues and potential oscillation problems. Therefore, careful layout and routing of traces are essential to preserve the high-frequency characteristics of the oscillator circuit.CI in series with the crystal may be used to adjust the oscillator output frequency· Value may range between 20 pF and 0.01 µ¥, or may be a trimmer capacitor and will approximately equal the crystal load capacitance. X values are approximate and can vary for most circuits and frequencies; this is also true for resistance values.
Adequate power supply decoupling is required; local decoupling capacitors near the oscillator are recommended. All leads should be extremely short in high frequency circuits.