Design and Construction of Radio Frequency Oscillators
The RF design and construction of radio frequency oscillators.
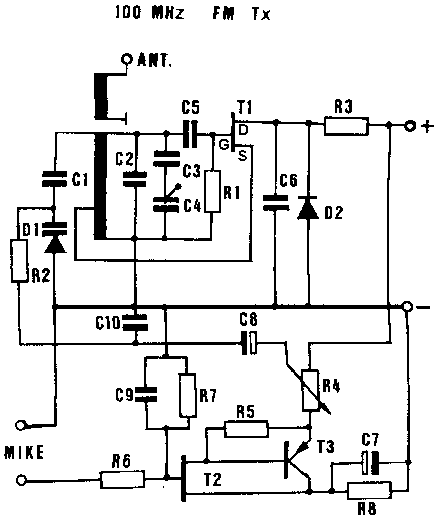
Radio frequency (RF) oscillators are essential components in various electronic systems, generating signals at specific frequencies used for communication, signal processing, and other applications. The design of RF oscillators involves several critical considerations, including frequency stability, phase noise, output power, and modulation capabilities.
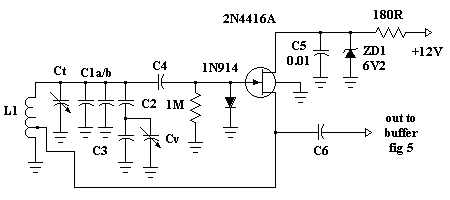
The construction of RF oscillators typically involves selecting an appropriate oscillator topology, such as Colpitts, Hartley, or phase-locked loops (PLLs). Each topology has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific application requirements. Components such as inductors, capacitors, and active devices (transistors or operational amplifiers) are carefully selected to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation and to ensure stability against variations in temperature and supply voltage.
In addition to the basic circuit design, RF oscillators often require careful layout techniques to minimize parasitic effects and electromagnetic interference (EMI). This includes the use of ground planes, shielding, and proper routing of RF traces to maintain signal integrity. The use of simulation tools can aid in predicting the performance of the oscillator before physical construction, allowing for optimization of component values and layout.
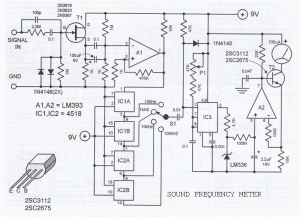
Testing and validation of RF oscillators involve measuring key parameters such as output frequency, power levels, and phase noise using specialized RF test equipment. This ensures that the oscillator meets the required specifications for its intended application, whether it be in telecommunications, broadcasting, or other RF applications.the RF design and construction of radio frequency oscillators. 🔗 External reference
Radio frequency (RF) oscillators are essential components in various electronic systems, generating signals at specific frequencies used for communication, signal processing, and other applications. The design of RF oscillators involves several critical considerations, including frequency stability, phase noise, output power, and modulation capabilities.
The construction of RF oscillators typically involves selecting an appropriate oscillator topology, such as Colpitts, Hartley, or phase-locked loops (PLLs). Each topology has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific application requirements. Components such as inductors, capacitors, and active devices (transistors or operational amplifiers) are carefully selected to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation and to ensure stability against variations in temperature and supply voltage.
In addition to the basic circuit design, RF oscillators often require careful layout techniques to minimize parasitic effects and electromagnetic interference (EMI). This includes the use of ground planes, shielding, and proper routing of RF traces to maintain signal integrity. The use of simulation tools can aid in predicting the performance of the oscillator before physical construction, allowing for optimization of component values and layout.
Testing and validation of RF oscillators involve measuring key parameters such as output frequency, power levels, and phase noise using specialized RF test equipment. This ensures that the oscillator meets the required specifications for its intended application, whether it be in telecommunications, broadcasting, or other RF applications.the RF design and construction of radio frequency oscillators. 🔗 External reference