Low frequency TTL oscillator
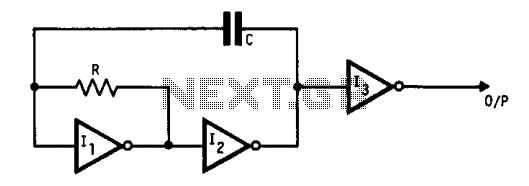
This oscillator utilizes standard inverters, one resistor, and one capacitor, and it does not have a minimum operating frequency. The resistor (R) and capacitor (C) must be selected to ensure that the currents flowing into the gates remain below the recommended operating limits and that the leakage current into the gates and capacitor is minimal compared to the current in the resistor. Additionally, the output should be buffered to prevent load variations from affecting the frequency. This circuit can also be employed to square up slowly changing logic levels by using multi-input gates such as NANDs and NORs.
The oscillator circuit described operates based on the principles of feedback and RC timing. The core components include standard inverters, which serve as the primary active elements, along with a resistor and capacitor that establish the timing characteristics. The absence of a minimum operating frequency allows for flexibility in application, making this oscillator suitable for various low-frequency applications.
In terms of component selection, the resistor and capacitor values must be carefully calculated. The resistor value should be chosen to limit the gate current to within safe operating limits specified by the inverter manufacturer. Similarly, the capacitor must be selected to ensure that its leakage current is insignificant compared to the current flowing through the resistor. This is crucial for maintaining stable operation and ensuring that the oscillator functions correctly.
Buffering the output is an essential design consideration. By using a buffer, any variations in the load connected to the oscillator output will not influence the frequency of oscillation. This buffering stage isolates the oscillator from load effects, thereby enhancing the stability and reliability of the circuit.
Furthermore, the circuit's versatility extends to its ability to square up slowly changing logic levels. By incorporating multi-input gates such as NANDs and NORs, the circuit can effectively transform gradual voltage transitions into sharp square wave outputs. This feature is particularly useful in digital applications where clean logic levels are required for reliable operation.
Overall, this oscillator circuit is a simple yet effective design that leverages standard components to achieve reliable oscillation and signal conditioning, making it suitable for various electronic applications.This oscillator uses standard inverters, one resistor and one capacitor, and has no minimum operating frequency. R and C must be chosen such that currents into the gates are below recommended operating limits and that leakage current into the gates and into C are small in comparison with the current in R also the output should be buffered (13) to prevent variations in load affecting frequency.
This circuit may also be used to square up slowly changing logic levels by use.of multi input gates (NANDS, NORS Etc).
The oscillator circuit described operates based on the principles of feedback and RC timing. The core components include standard inverters, which serve as the primary active elements, along with a resistor and capacitor that establish the timing characteristics. The absence of a minimum operating frequency allows for flexibility in application, making this oscillator suitable for various low-frequency applications.
In terms of component selection, the resistor and capacitor values must be carefully calculated. The resistor value should be chosen to limit the gate current to within safe operating limits specified by the inverter manufacturer. Similarly, the capacitor must be selected to ensure that its leakage current is insignificant compared to the current flowing through the resistor. This is crucial for maintaining stable operation and ensuring that the oscillator functions correctly.
Buffering the output is an essential design consideration. By using a buffer, any variations in the load connected to the oscillator output will not influence the frequency of oscillation. This buffering stage isolates the oscillator from load effects, thereby enhancing the stability and reliability of the circuit.
Furthermore, the circuit's versatility extends to its ability to square up slowly changing logic levels. By incorporating multi-input gates such as NANDs and NORs, the circuit can effectively transform gradual voltage transitions into sharp square wave outputs. This feature is particularly useful in digital applications where clean logic levels are required for reliable operation.
Overall, this oscillator circuit is a simple yet effective design that leverages standard components to achieve reliable oscillation and signal conditioning, making it suitable for various electronic applications.This oscillator uses standard inverters, one resistor and one capacitor, and has no minimum operating frequency. R and C must be chosen such that currents into the gates are below recommended operating limits and that leakage current into the gates and into C are small in comparison with the current in R also the output should be buffered (13) to prevent variations in load affecting frequency.
This circuit may also be used to square up slowly changing logic levels by use.of multi input gates (NANDS, NORS Etc).