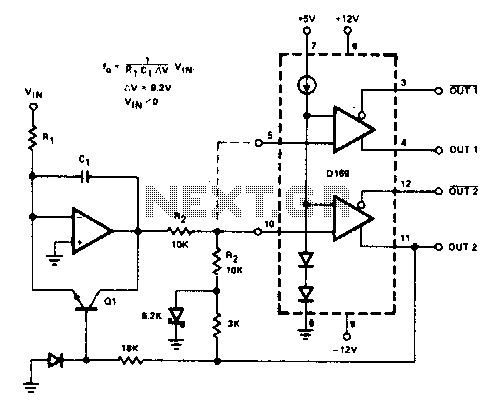
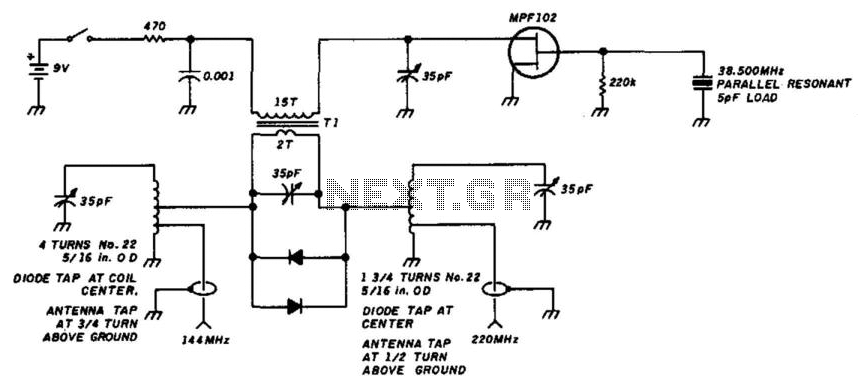
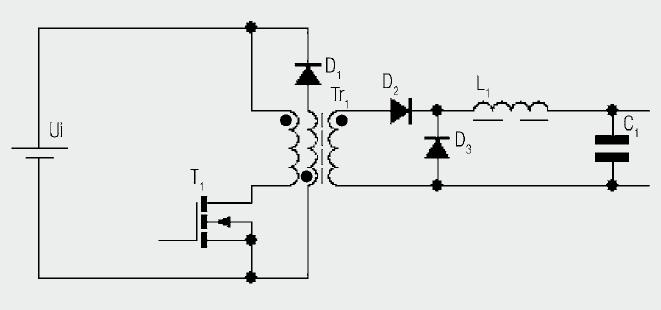
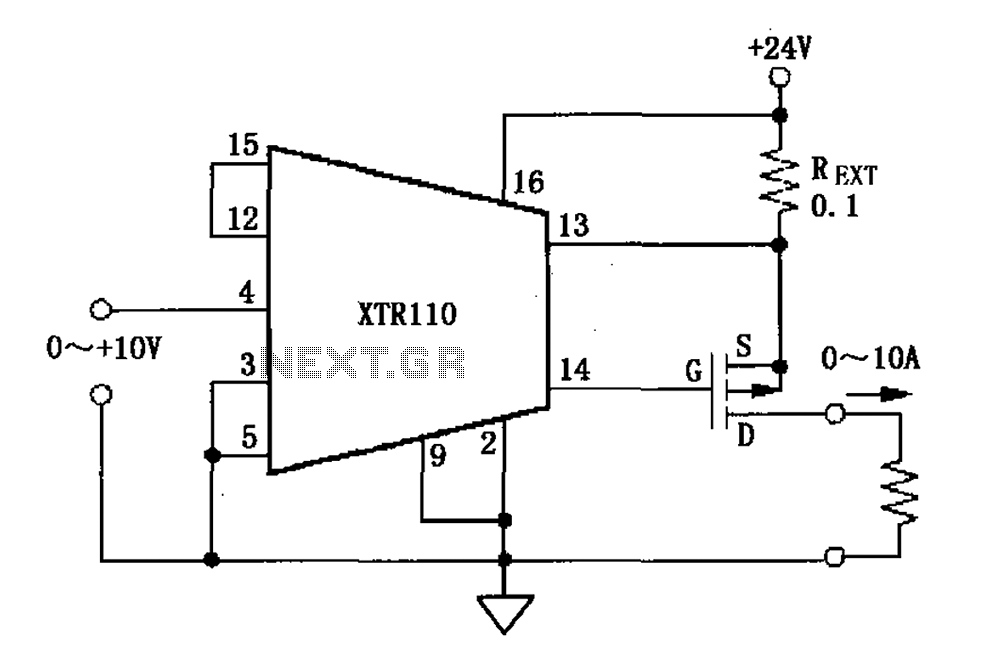
Low-Loss Step Down Converter
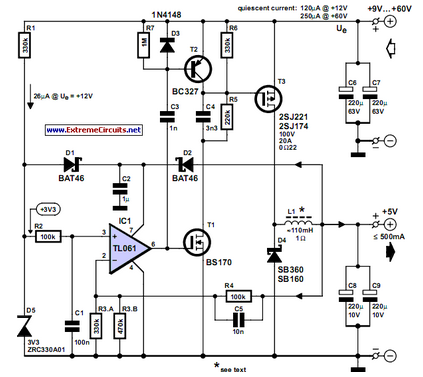
This circuit was developed to provide a 5 V output from the 24 V battery of a solar-powered generator.
The circuit is designed to efficiently step down the voltage from a 24 V source to a stable 5 V output, which is essential for powering various low-voltage devices and components in solar applications. The primary component utilized in this design is a buck converter, which is known for its ability to convert a higher voltage to a lower voltage with high efficiency.
The buck converter operates by switching the input voltage on and off rapidly using a transistor. This switching action is controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which adjusts the duty cycle to regulate the output voltage. An inductor is used to store energy during the on phase of the switch and release it during the off phase, smoothing out the voltage output.
In addition to the main switching elements, the circuit includes necessary components such as diodes for preventing reverse current flow, capacitors for filtering and stabilizing the output voltage, and resistors for setting the feedback loop that ensures the output remains constant despite variations in load or input voltage.
The design also incorporates protection features, such as overcurrent protection and thermal shutdown, to safeguard the circuit and connected devices. This ensures reliable operation in various environmental conditions typical of solar-powered systems.
Overall, this circuit effectively meets the requirement of converting a 24 V input to a 5 V output, making it suitable for a range of applications in solar energy systems.This circuit arose from the need of the author to provide a 5 V output from the 24 V battery of a solar powered generator. Although solar power is essenti.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to efficiently step down the voltage from a 24 V source to a stable 5 V output, which is essential for powering various low-voltage devices and components in solar applications. The primary component utilized in this design is a buck converter, which is known for its ability to convert a higher voltage to a lower voltage with high efficiency.
The buck converter operates by switching the input voltage on and off rapidly using a transistor. This switching action is controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which adjusts the duty cycle to regulate the output voltage. An inductor is used to store energy during the on phase of the switch and release it during the off phase, smoothing out the voltage output.
In addition to the main switching elements, the circuit includes necessary components such as diodes for preventing reverse current flow, capacitors for filtering and stabilizing the output voltage, and resistors for setting the feedback loop that ensures the output remains constant despite variations in load or input voltage.
The design also incorporates protection features, such as overcurrent protection and thermal shutdown, to safeguard the circuit and connected devices. This ensures reliable operation in various environmental conditions typical of solar-powered systems.
Overall, this circuit effectively meets the requirement of converting a 24 V input to a 5 V output, making it suitable for a range of applications in solar energy systems.This circuit arose from the need of the author to provide a 5 V output from the 24 V battery of a solar powered generator. Although solar power is essenti.. 🔗 External reference